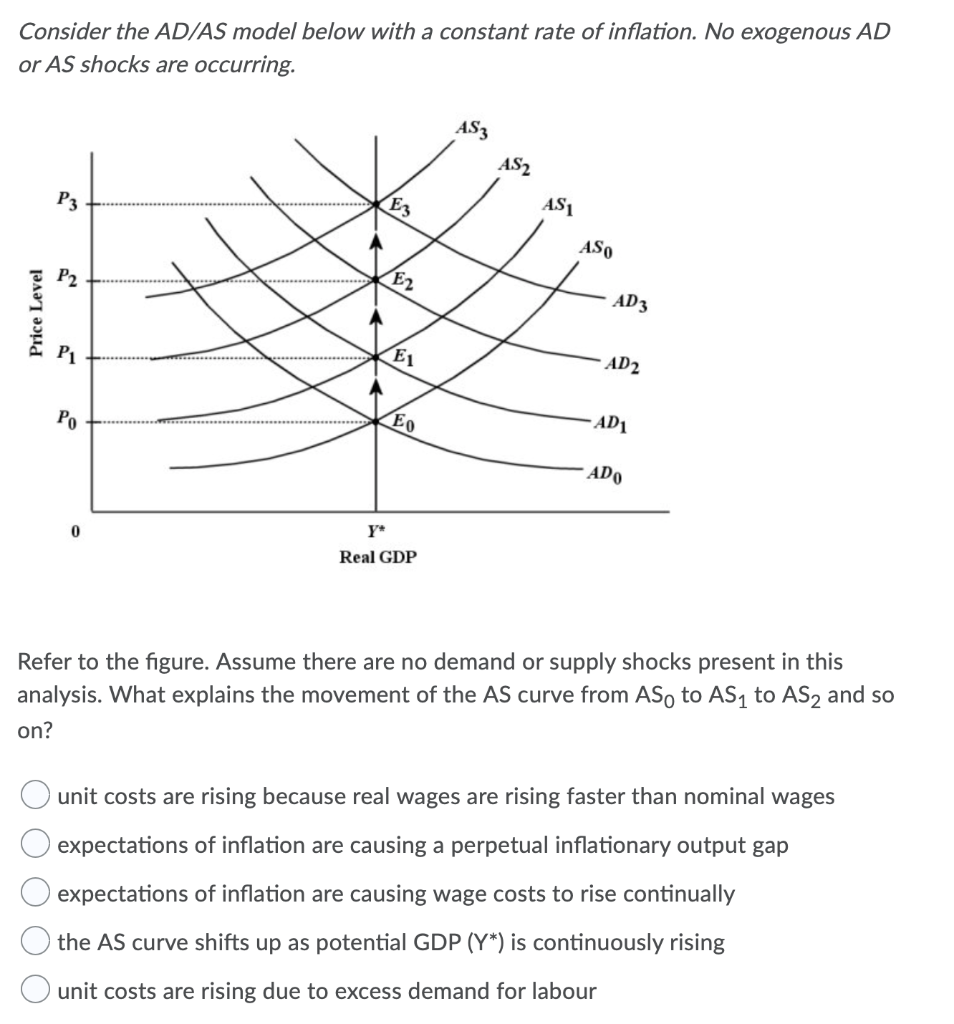
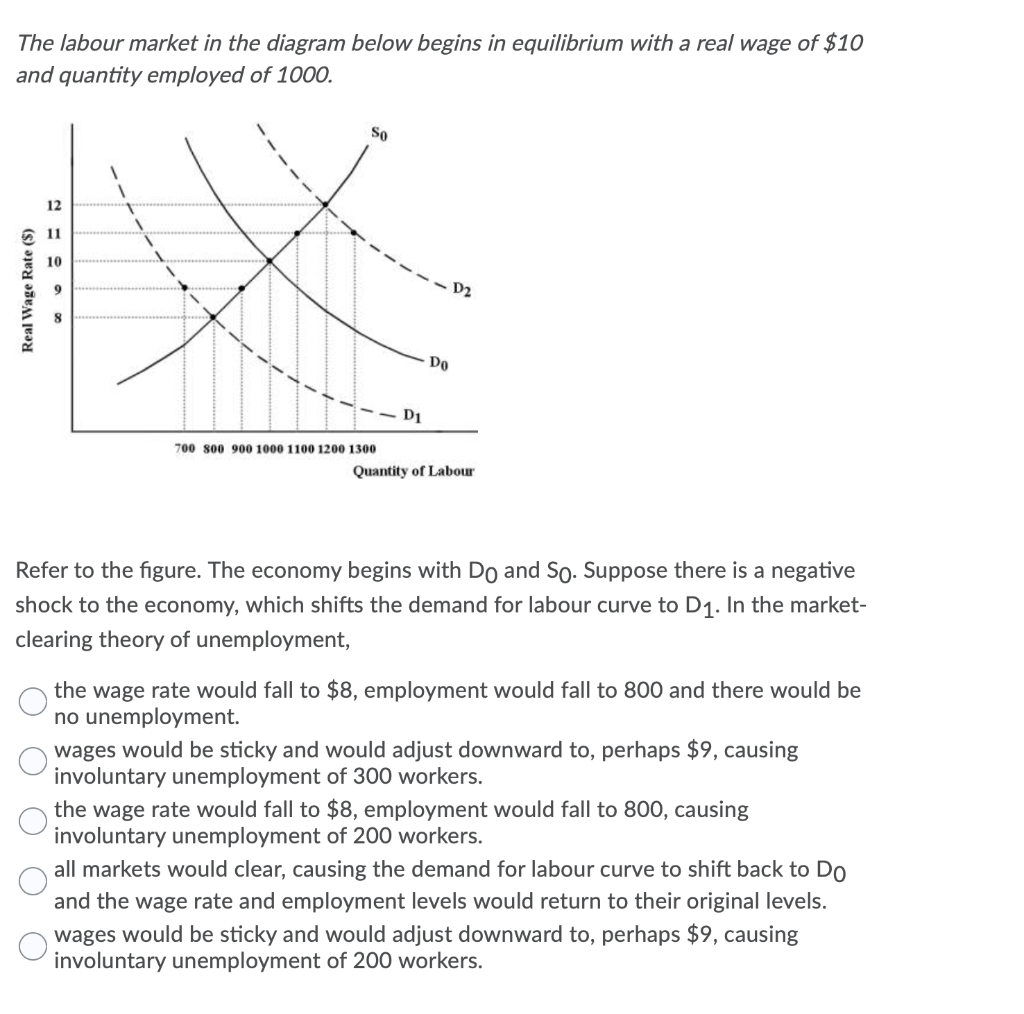

Consider the AD/AS model below with a constant rate of inflation. No exogenous AD or AS shocks are occurring. S2 ST SO Price Level *EO Real GDP Refer to the figure. Assume there are no demand or supply shocks present in this analysis. What explains the movement of the AS curve from AS, to AS, to AS, and so on? O expectations of inflation are causing a perpetual inflationary output gap O expectations of inflation are causing wage costs to rise continually O the AS curve shifts up as potential GDP (Y*) is continuously rising O unit costs are rising due to excess demand for labour Assume your salary is $2000 per month and your employer gives you a raise of 6%. Over the next twelve months the inflation rate is 12%. Your real salary will change by + 0 - 12%. O +12%. 0-6%. O+6%. O O O 0 0%. The labour market in the diagram below begins in equilibrium with a real wage of $10 and quantity employed of 1000. Real Wage Rate ($) --D1 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 1300 Quantity of Labour Refer to the figure. The economy begins with Do and So. Suppose there is a negative shock to the economy, which shifts the demand for labour curve to D1. In the market- clearing theory of unemployment, the wage rate would fall to $8, employment would fall to 800 and there would be no unemployment. wages would be sticky and would adjust downward to, perhaps $9, causing involuntary unemployment of 300 workers. the wage rate would fall to $8, employment would fall to 800, causing involuntary unemployment of 200 workers. all markets would clear, causing the demand for labour curve to shift back to Do and the wage rate and employment levels would return to their original levels. wages would be sticky and would adjust downward to, perhaps $9, causing involuntary unemployment of 200 workers. Consider the following information describing a closed economy with no government and where aggregate output is demand determined. All dollar figures are in billions. 1. the equilibrium condition is Y =C+I 2. the marginal propensity to consume is 0.90 3. the autonomous part of C is $300 4. investment is autonomous and is $100 Refer to the table. The correct expression for the aggregate expenditure function for this economy is O AE = $400 billion + 0.9Y O AE = $300 billion + 0.9Y O AE = $760 billion O AE = $200 billion + 0.1 YD. 0 AE = $400 billion + 0.1 Yo. Consider the AD/AS model below with a constant rate of inflation. No exogenous AD or AS shocks are occurring. S2 ST SO Price Level *EO Real GDP Refer to the figure. Assume there are no demand or supply shocks present in this analysis. What explains the movement of the AS curve from AS, to AS, to AS, and so on? O expectations of inflation are causing a perpetual inflationary output gap O expectations of inflation are causing wage costs to rise continually O the AS curve shifts up as potential GDP (Y*) is continuously rising O unit costs are rising due to excess demand for labour Assume your salary is $2000 per month and your employer gives you a raise of 6%. Over the next twelve months the inflation rate is 12%. Your real salary will change by + 0 - 12%. O +12%. 0-6%. O+6%. O O O 0 0%. The labour market in the diagram below begins in equilibrium with a real wage of $10 and quantity employed of 1000. Real Wage Rate ($) --D1 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 1300 Quantity of Labour Refer to the figure. The economy begins with Do and So. Suppose there is a negative shock to the economy, which shifts the demand for labour curve to D1. In the market- clearing theory of unemployment, the wage rate would fall to $8, employment would fall to 800 and there would be no unemployment. wages would be sticky and would adjust downward to, perhaps $9, causing involuntary unemployment of 300 workers. the wage rate would fall to $8, employment would fall to 800, causing involuntary unemployment of 200 workers. all markets would clear, causing the demand for labour curve to shift back to Do and the wage rate and employment levels would return to their original levels. wages would be sticky and would adjust downward to, perhaps $9, causing involuntary unemployment of 200 workers. Consider the following information describing a closed economy with no government and where aggregate output is demand determined. All dollar figures are in billions. 1. the equilibrium condition is Y =C+I 2. the marginal propensity to consume is 0.90 3. the autonomous part of C is $300 4. investment is autonomous and is $100 Refer to the table. The correct expression for the aggregate expenditure function for this economy is O AE = $400 billion + 0.9Y O AE = $300 billion + 0.9Y O AE = $760 billion O AE = $200 billion + 0.1 YD. 0 AE = $400 billion + 0.1 Yo