Question
Consider the following cash budgeting example for Buckeye Pharmaceutical Company: Gross Sales by month: May 2010: $5,000 June: $5,000 July: $10,000 August: $15,000 September: $20,000
Consider the following cash budgeting example for Buckeye Pharmaceutical Company:
Gross Sales by month:
- May 2010: $5,000
- June: $5,000
- July: $10,000
- August: $15,000
- September: $20,000
- October: $10,000
- November: $10,000
- December: $5,000
- January 2011: $10,000
After referring to the information provided, prepare a cash budget for the company for the period July to December 2010. All dollar amounts are in thousands.
All sales transactions are on credit, with historical data showing that 30% of current revenues are collected in the current month, 50% in the next month and 20% in the second month after sale. Assume that bad debt is negligible.
Except for supplies, assume that operating expenses are paid during the month they are incurred. Operating expenses (monthly unless indicated otherwise) for the period are as follows:
- Wages and salaries: $750
- Insurance: $250
- Depreciation: $300
- Other expenses: $3,000
- Taxes (paid in Sep. and Dec.): $500
- Payment for capital equipment in Oct.: $1,000
Supplies purchases in a month must equal 70% of the projected gross sales for the following month. Supplies are paid for in the month after purchase.
The corporation must maintain an ending cash balance of $3,500 each month and meets a cash shortfall through a short-term loan. (Ignore interest for purposes of this example.) For simplicity in this example, assume that excess cash remains as cash (i.e., is not reinvested). Assume that at the beginning of July, the company had a cash balance of $3,500 with no short-term loan outstanding.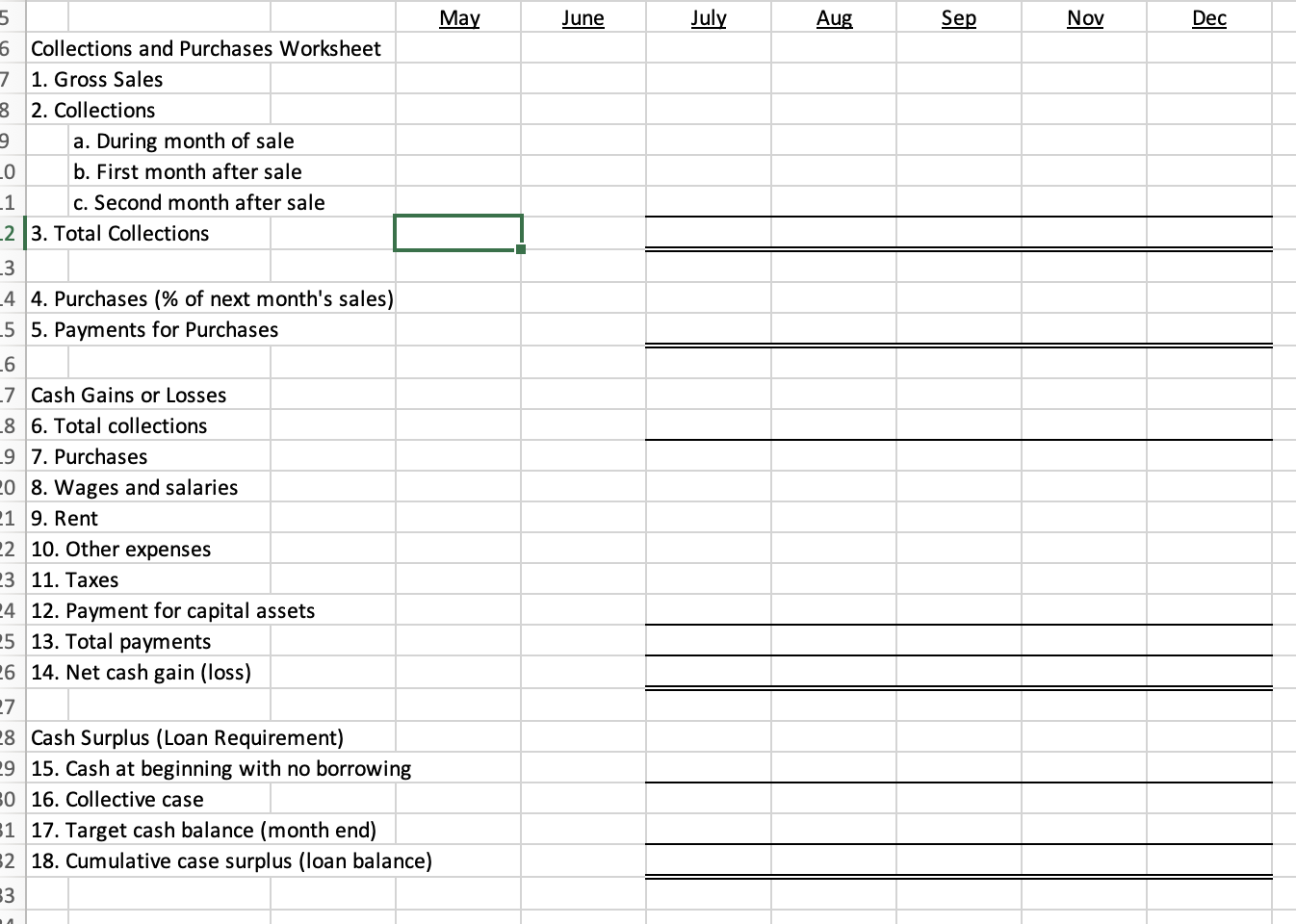
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


