Question: Consider the following three class declarations public class Animal {protected String name; public Animal(String noire) {this.name = name;} public void print() {System.out.print In (Animal);}} public
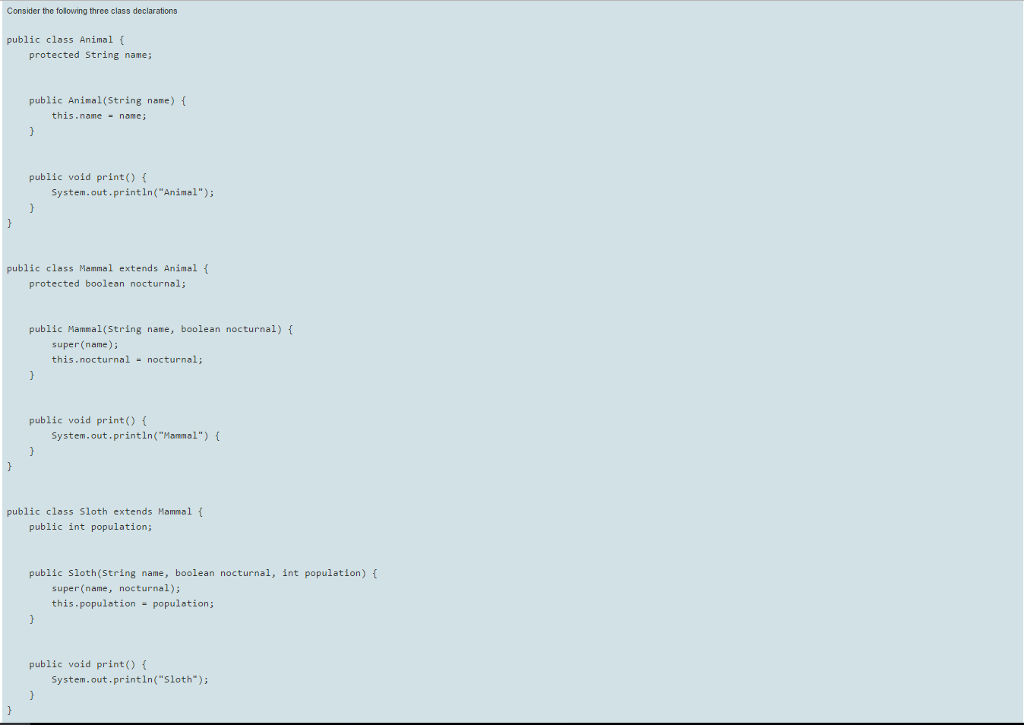
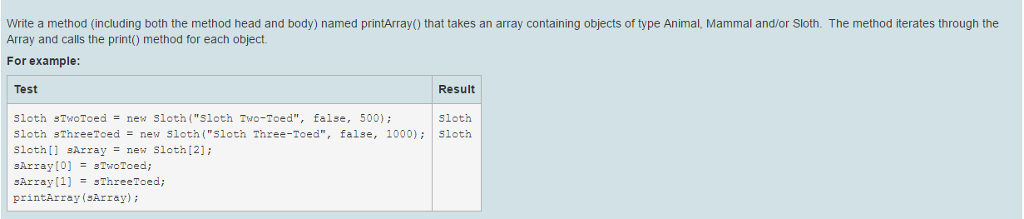
Consider the following three class declarations public class Animal {protected String name; public Animal(String noire) {this.name = name;} public void print() {System.out.print In ("Animal");}} public class Mammal extends Animal {protected boolean nocturnal; public Mammal(String name, boolean nocturnal) {super(name); this.nocturnal = nocturnal;} public void print () {System.out.println ("Mammal") {}} public class Sloth extends Mammal {public int population; public sloth(string name, boolean nocturnal, int population) {super(name, nocturnal); this.population = population;} public void print () {System.out.printIn ("Sloth");}} Write a method (including both the method head and body) named printArray() that takes an array containing objects of type Animal. Mammal and/or Sloth The method iterates through the Array and calls the print() method for each object. For example
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


