Question
Consider the routing scenario in the Figure (figure 6) shown below. An autonomous system (AS I) is connected to the Internet via two connections. The
Consider the routing scenario in the Figure (figure 6) shown below. An autonomous system (AS I) is connected to the Internet via two connections. The router RI in Sydney is running EBGP with one provider over a TI circuit, and the router R2 in Melbourne is running EBGP with another provider over a T3 circuit.
Inside AS1, the two border routers RI and R2 are running IBGP and EBGP, but are not physically connected. All communication between RI and R2 go via internal routers R3, R4 and R5. The internal routers R3, R4, and R5 are non-BGP routers and exchange routes via an IGP with all other routers in the AS. In the current scenario, RI and R2 are both receiving full routes from their parent providers. These routers are also injecting a 0/0 default route inside AS1. Assume also that AS1 runs the primary/backup technique to enable the MEL T3 link to be the primary. The SYD link will be used as a backup, and therefore all outbound traffic that reaches RI will now need to be directed back toward R2. Interior routers R3, R4 and R5 do not see any of the exterior routes and follow defaults towards RI and R2 according to the !GP metric. Identify and describe one specific routing problem that is likely to occur in this scenario. What would you recommend as some alternate ways to avoid this problem?
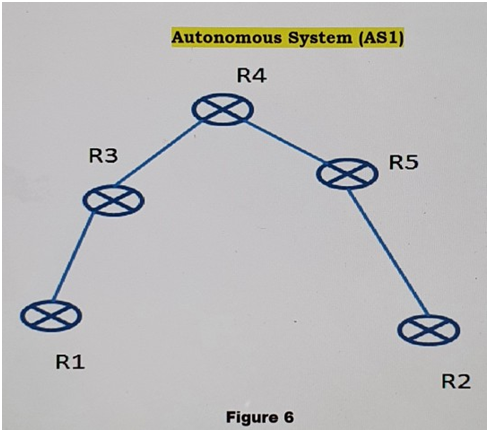
R1 R3 Autonomous System (AS1) R4 Figure 6 R5 R2
Step by Step Solution
3.58 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
P table and routing table this system is likely to fail To ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


