Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Constants I Periodic Table When a photon passes through matter, there are three types of light-matter interactions that can occur: Part A 1. Transmission,
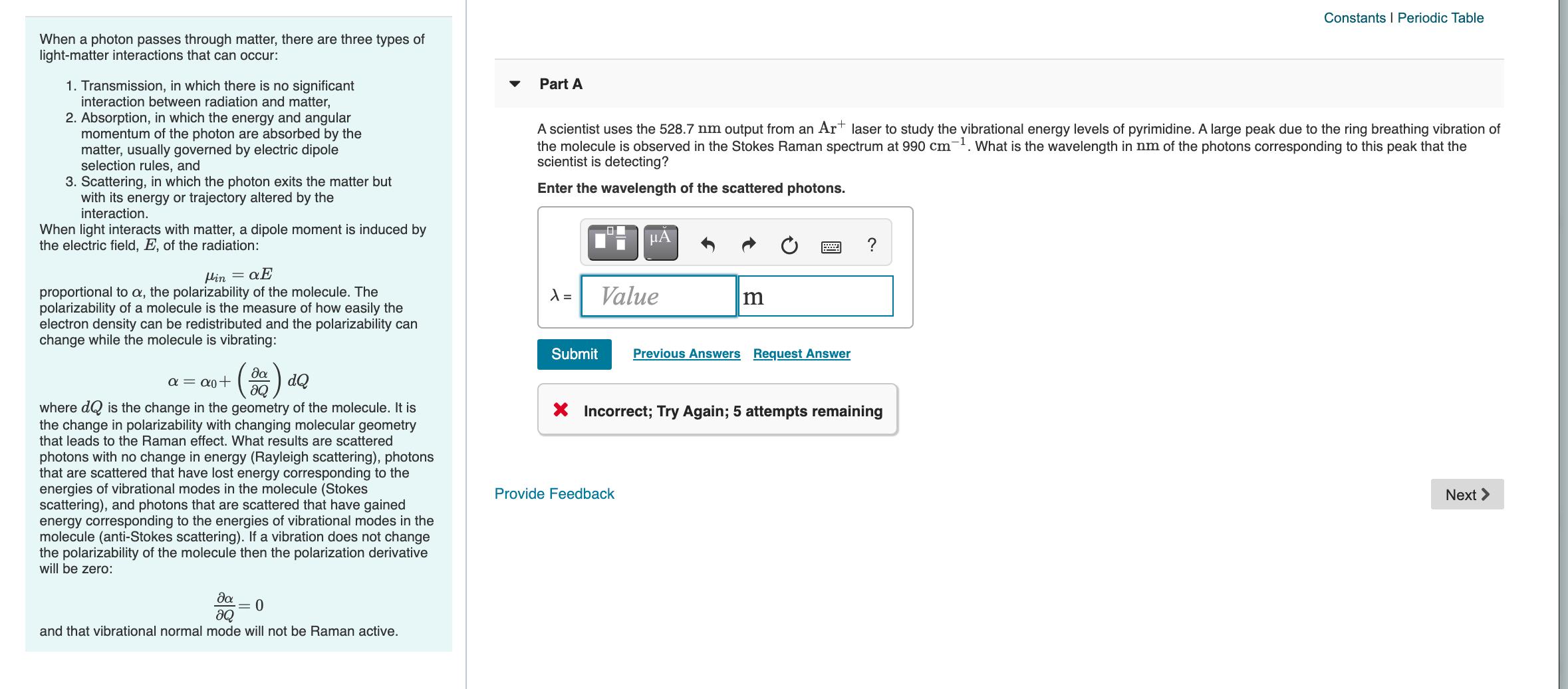
Constants I Periodic Table When a photon passes through matter, there are three types of light-matter interactions that can occur: Part A 1. Transmission, in which there is no significant interaction between radiation and matter, 2. Absorption, in which the energy and angular momentum of the photon are absorbed by the matter, usually governed by electric dipole selection rules, and 3. Scattering, in which the photon exits the matter but with its energy or trajectory altered by the interaction. A scientist uses the 528.7 nm output from an Art laser to study the vibrational energy levels of pyrimidine. A large peak due to the ring breathing vibration of the molecule is observed in the Stokes Raman spectrum at 990 cm-. What is the wavelength in nm of the photons corresponding to this peak that the scientist is detecting? Enter the wavelength of the scattered photons. When light interacts with matter, a dipole moment is induced by the electric field, E, of the radiation: HA ? Hin = Value proportional to a, the polarizability of the molecule. The polarizability of a molecule is the measure of how easily the electron density can be redistributed and the polarizability can change while the molecule is vibrating: Submit Previous Answers Request Answer da a = a0+ aQ dQ where dQ is the change in the geometry of the molecule. It is the change in polarizability with changing molecular geometry that leads to the Raman effect. What results are scattered X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining photons with no change in energy (Rayleigh scattering), photons that are scattered that have lost energy corresponding to the energies of vibrational modes in the molecule (Stokes scattering), and photons that are scattered that have gained energy corresponding to the energies of vibrational modes in the molecule (anti-Stokes scattering). If a vibration does not change the polarizability of the molecule then the polarization derivative will be zero: Provide Feedback Next > da = 0 and that vibrational normal mode will not be Raman active.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.38 Rating (142 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


