Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
COPOLYMERIZATION ( CSTR ) Ethylene and 1 - octene are copolymerized with a coordination catalyst in a continuous - stirred tank reactor ( CSTR )
COPOLYMERIZATION CSTR
Ethylene and octene are copolymerized with a coordination catalyst in a continuousstirred tank reactor CSTR at oC The reactor system is assumed ideally mixed, and has a reactor volume of ml The ethylene and octene feeds into the reactor are gmin and gmin respectively.
The concentration of the titanium catalyst used in the reactor is moldm Due to strong catalyst deactivation, the catalysts mean residence time in the reactor is min. The reactivity ratios have been previously found to be rethylene and roctene The polymer yield from the reactor is gmin
a Calculate the concentrations of ethylene and octene when the reactor is operated at steady state.
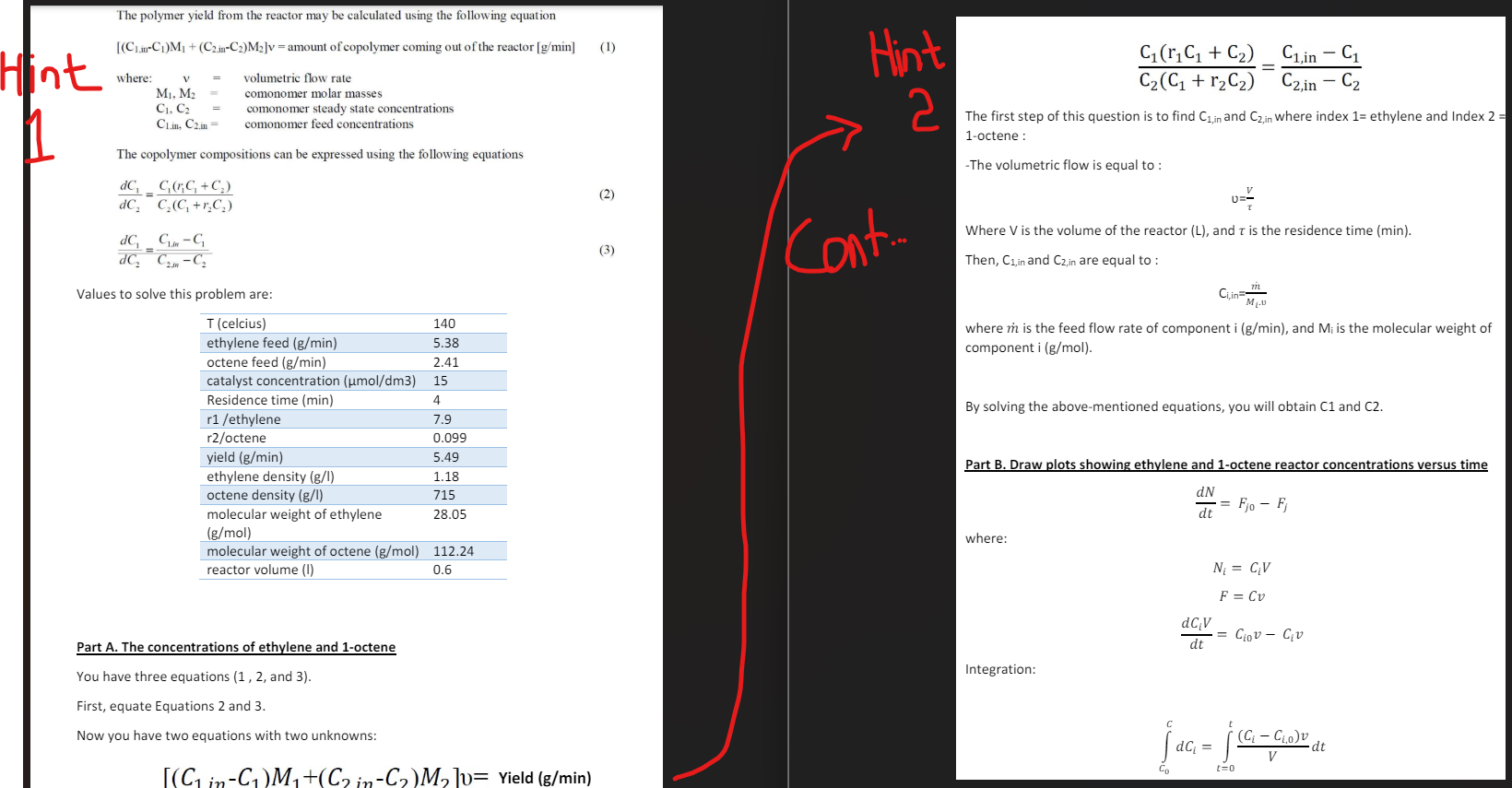
The polymer yield from the reactor may be calculated using the following equation
CinCMCinCMv amount of copolymer coming out of the reactor gmin
where:
v volumetric flow rate
M M comonomer molar masses
C C comonomer steady state concentrations
Cin Cin comonomer feed concentrations
The copolymer compositions can be expressed using the following equations
dCdC CrC CCCrC
dCdCCin CCin C
b Draw plots showing ethylene and octene reactor concentrations versus time from the initial concentrations until steady state concentrations are reached At t the reactor is full of solution. The consumption of ethylene and octene during the reaction may be neglected.
To solve equations for monomer concentrations, apply mole balances on both species:
b Draw plots showing ethylene and octene reactor concentrations versus time from the initial concentrations until steady state concentrations are reached At t the reactor is full of
solution. The consumption of ethylene and octene during the reaction may be neglected.
To solve equations for monomer concentrations, apply mole balances on both species:
dNjdt Fj Fj
where:
Nj represents the number of moles of species j in the system at time t
Fj rate of flow of j into the system mols
Fj rate of flow of j out of the system mols
Please note that the hints for solving the problem are provided along with the data in the picture attached to the problem. Use those hints and data from the picture attached to it in this question to solve it's both parts. the text elow is just some of the formulas typed from the hints
The polymer yield from the reactor may be calculated using the following equation
amount of copolymer coming out of the reactor gm
where:
volumetric flow rate
comonomer molar masses
comonomer steady state concentrations
comonomer feed concentrations
The copolymer compositions can be expressed using the following equations
Values to solve this problem are:
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


