Question
Correcting for negative externalities - Taxes versus tradable permits Power stations emit sulfur dioxide as a waste product. This generates a cost to society that




Correcting for negative externalities - Taxes versus tradable permits
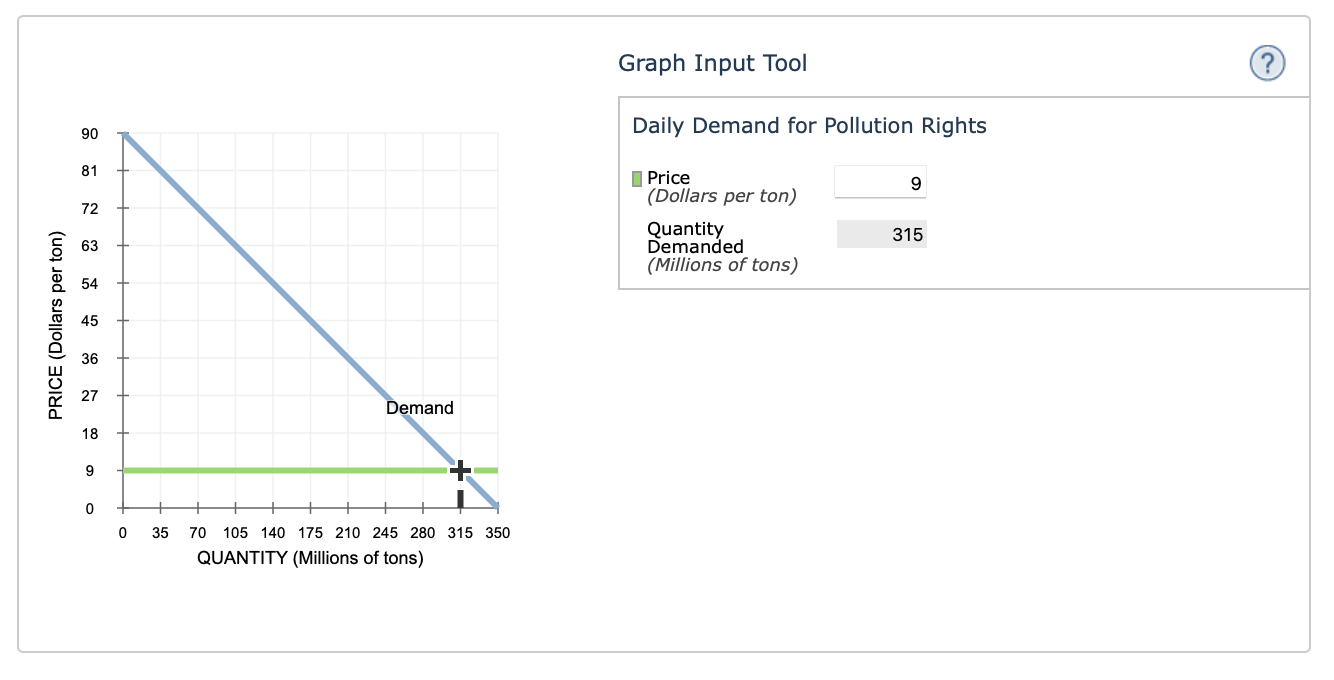
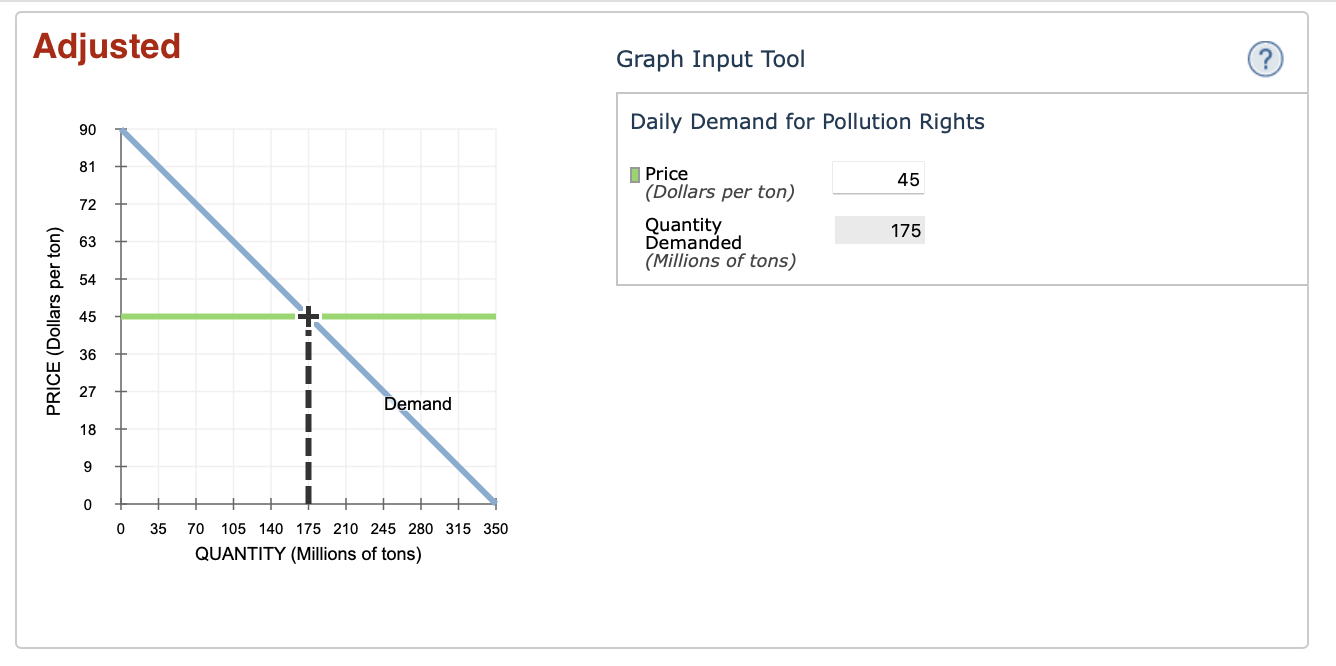
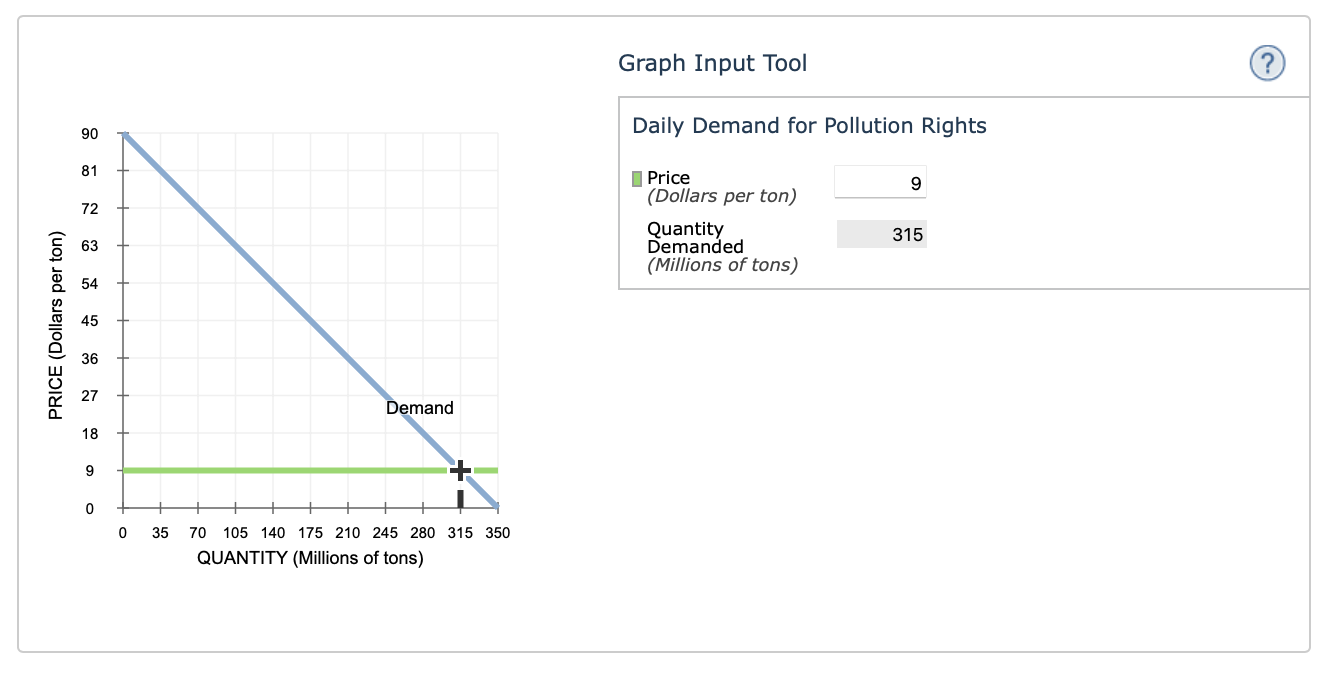
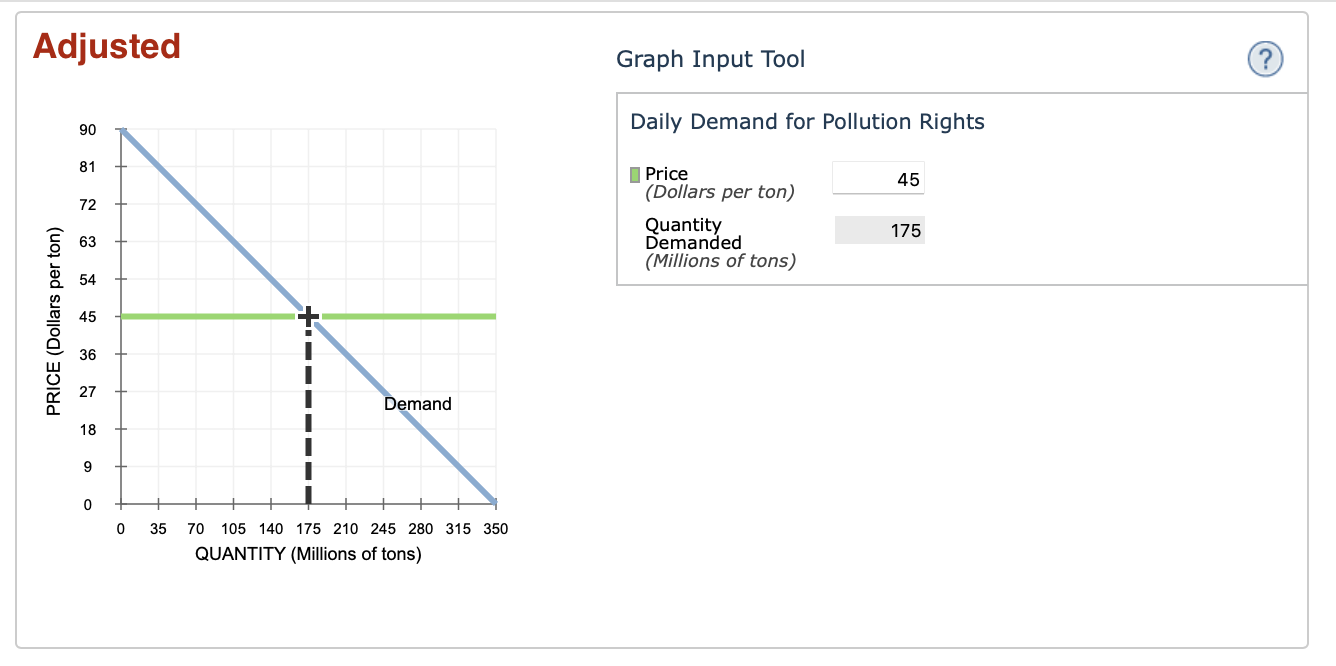
Power stations emit sulfur dioxide as a waste product. This generates a cost to society that is not paid for by the firm; therefore, pollution is a negative externality of power production. Suppose the U.S. government wants to correct this market failure by getting firms to internalize the cost of pollution. In order for this to be done, the government can charge firms for pollution rights(the right to emit a given quantity of sulfur dioxide). The following graph shows the daily demand for pollution rights.
Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph.
Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly.




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


