Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
cos e sin 20 -cos e E.A sin 20 sin e -sin 20 - sin 20 sin 0. [K] = he - cos -sin
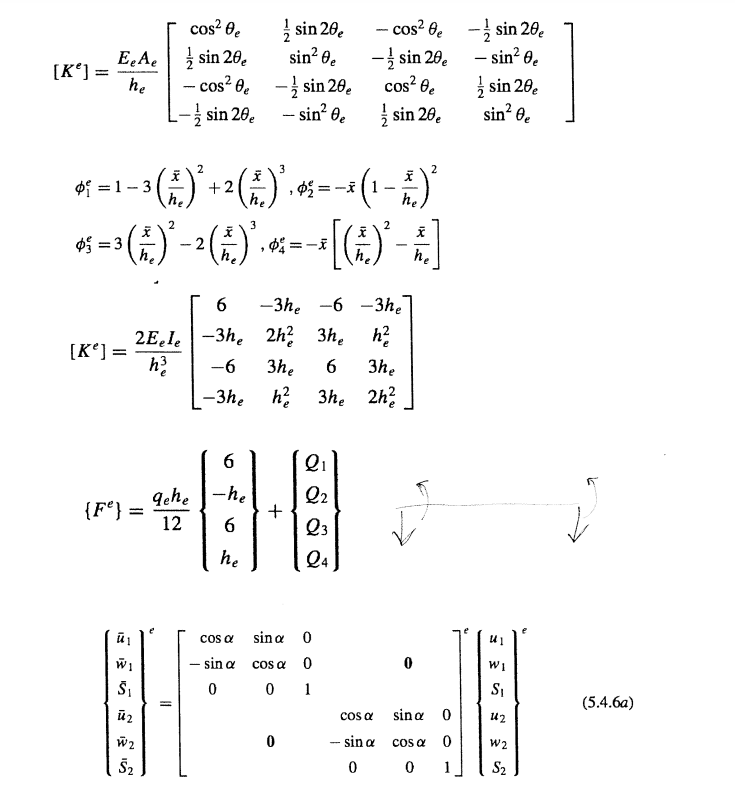
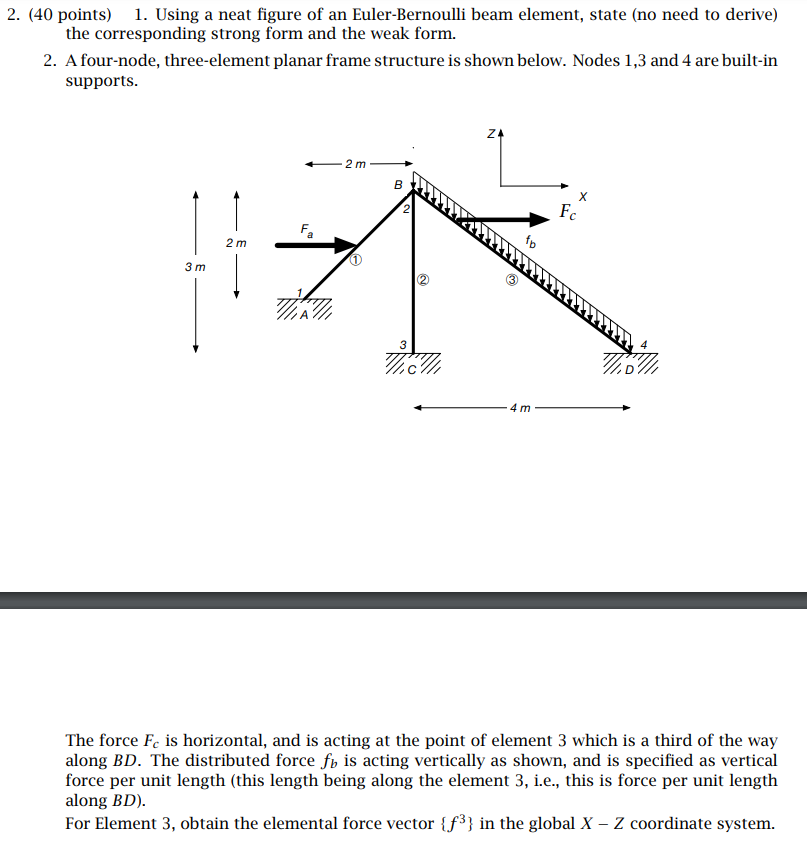
cos e sin 20 -cos e E.A sin 20 sin e -sin 20 - sin 20 sin 0. [K] = he - cos -sin 20 cos be sin 20 - - sin e sin 20 sin O sin 20 *-1-3 (A)+2(A) = 2 3 2 3 3 = (1-)* -x (1) = (#) - (#)' --[(#)**] =3 ' = -x [() 6 -3he -6 -3he ] 2Eele -3he 2h2 3he h [Ke] = h -6 3he 6 3he -3he h 3he 2h 6 Q1 gehe -he Q2 {Fe} = ==== + 12 6 Q3 he Q4 W1 S EES COS sina 0 - sin a cos 0 0 WI 001 S (5.4.6a) 2 cos sina 0 142 W2 0 - sin a cos a 0 W2 52 00 1 S 2. (40 points) 1. Using a neat figure of an Euler-Bernoulli beam element, state (no need to derive) the corresponding strong form and the weak form. 2. A four-node, three-element planar frame structure is shown below. Nodes 1,3 and 4 are built-in supports. 3 m 2 m The 2 m B ZA 4 m X Fc The The force Fc is horizontal, and is acting at the point of element 3 which is a third of the way along BD. The distributed force fb is acting vertically as shown, and is specified as vertical force per unit length (this length being along the element 3, i.e., this is force per unit length along BD). For Element 3, obtain the elemental force vector {f} in the global X - Z coordinate system.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


