Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
COVID-19 (novel corona virus) took the world by surprise in late 2019. By early 2020, nearly all countries worldwide were affected. Early reports from
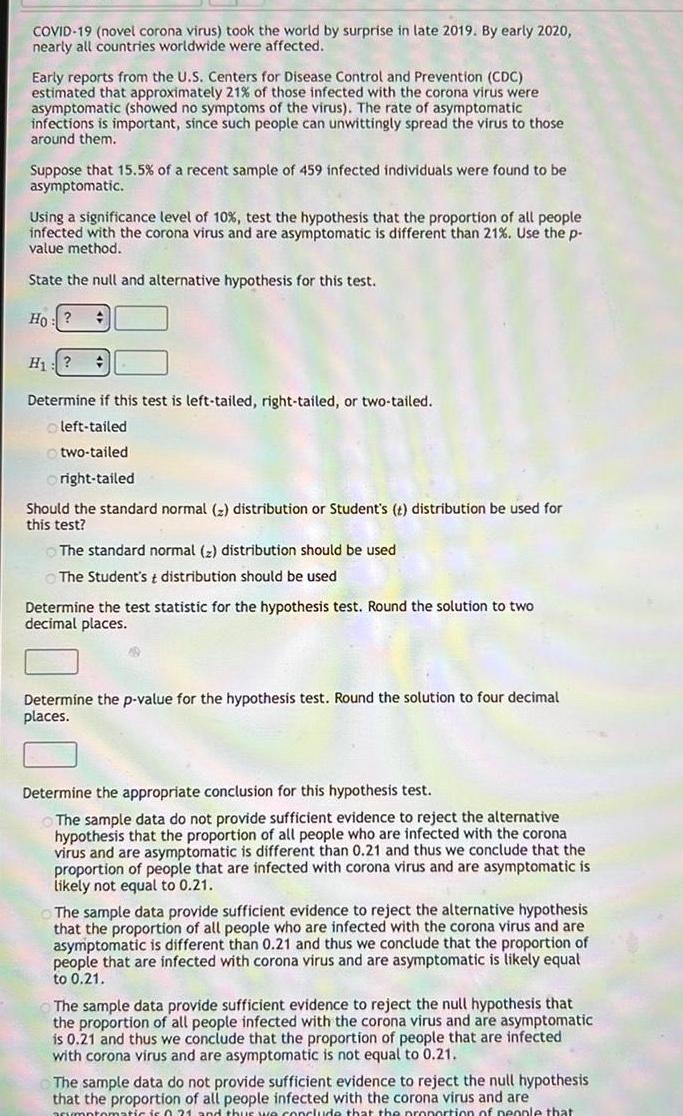
COVID-19 (novel corona virus) took the world by surprise in late 2019. By early 2020, nearly all countries worldwide were affected. Early reports from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimated that approximately 21% of those infected with the corona virus were asymptomatic (showed no symptoms of the virus). The rate of asymptomatic infections is important, since such people can unwittingly spread the virus to those around them. Suppose that 15.5% of a recent sample of 459 infected individuals were found to be asymptomatic. Using a significance level of 10%, test the hypothesis that the proportion of all people infected with the corona virus and are asymptomatic is different than 21%. Use the p- value method. State the null and alternative hypothesis for this test. Ho:? H:? Determine if this test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed. left-tailed two-tailed right-tailed Should the standard normal (2) distribution or Student's (t) distribution be used for this test? The standard normal (2) distribution should be used The Student's + distribution should be used Determine the test statistic for the hypothesis test. Round the solution to two decimal places. Determine the p-value for the hypothesis test. Round the solution to four decimal places. Determine the appropriate conclusion for this hypothesis test. The sample data do not provide sufficient evidence to reject the alternative hypothesis that the proportion of all people who are infected with the corona virus and are asymptomatic is different than 0.21 and thus we conclude that the proportion of people that are infected with corona virus and are asymptomatic is likely not equal to 0.21. The sample data provide sufficient evidence to reject the alternative hypothesis that the proportion of all people who are infected with the corona virus and are asymptomatic is different than 0.21 and thus we conclude that the proportion of people that are infected with corona virus and are asymptomatic is likely equal to 0.21. The sample data provide sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis that the proportion of all people infected with the corona virus and are asymptomatic is 0.21 and thus we conclude that the proportion of people that are infected with corona virus and are asymptomatic is not equal to 0.21. The sample data do not provide sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis that the proportion of all people infected with the corona virus and are acumptomatic is 0.21 and thus we conclude that the proportion of people that
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


