

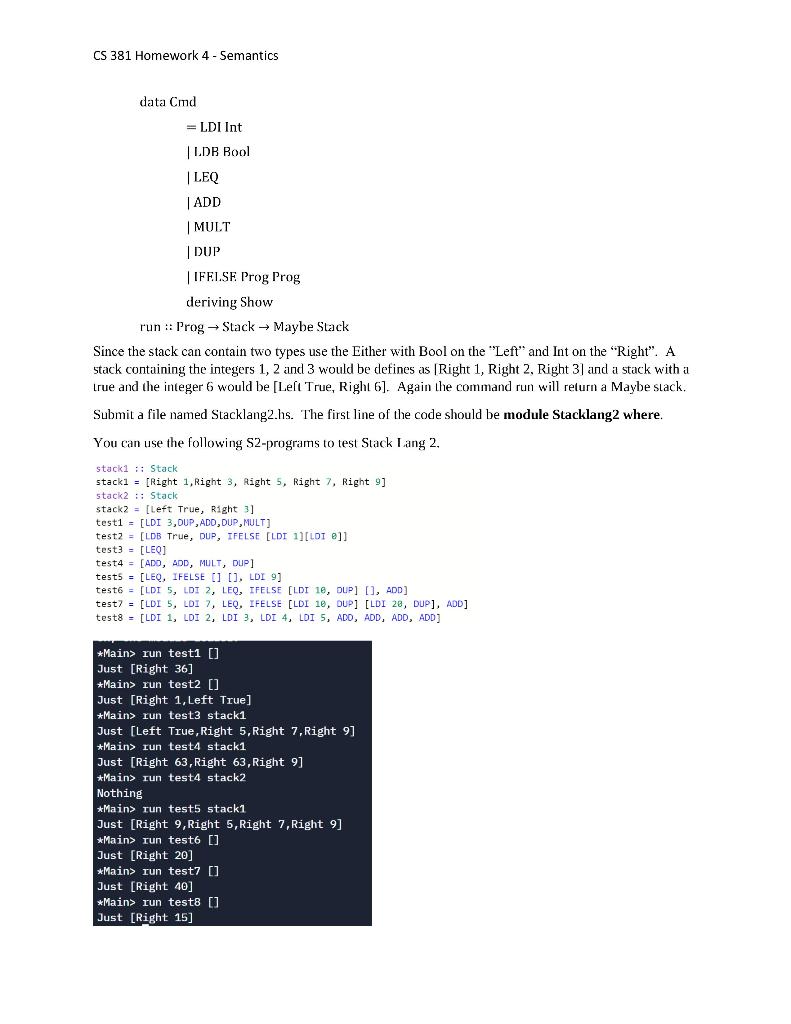
CS 381 Homework 4 - Semantics Part 1: Stack Language 1 Consider the stack language S defined by the following grammar. S:=CC,SC:=LDInt|ADD|MULT|DUP An 51-program essentially consists of a (non-empty) sequence of commands/operations C. The meaning of an S1-program is to start with an empty stack and to perform its first operation on it, which results in a new stack to which the second operation in S (if it exists) is applied, and so forth. The stack that results from the application of the last command is the result of the program. The following are the definitions of the operations. - L.D Int loads its integer parameter onto the stack. - ADD - removes the two topmost integers from the stack and puts their sum onto the stack. If the stack contains fewer than two elements, ADD produces an error. - MULT - removes the two topmost integers from the stack and puts their product onto the stack. If the stack contains fewer than two elements, MUT.T produces an error. - DUP - places a copy of the stack's topmost element on the stack. If the stack is empty then DUP produces an error. Here is a definition of the abstract syntax and type definitions that you should use. type Prog =[ Cmd] data Cmd =LDInt ADD MULT | DUP deriving Show type Stack =[ Int ] run :: Prog Stack Maybe Stack A program is ran with a stack. If there is an error in the program you can return "Nothing", otherwise return "Just" the contents of the stack. When defining the run function you will probably need auxiliary functions for the semantics of the individual operations. For example: semCind::CmdStackMaybeStacksemCmd(LDn)s=Just(n:s) Submit a file named Stacklang1.hs. The first line of the code should be module Stacklang1 where. *Main> run test1 [] Just [36] \#Main> run test1 stack1 Just [36,1,2,3,4,5] *Main> run test2 [] Nothing *Main> run test2 stack1 Just [4,2,3,4,5] *Main> run test3 [] Just [] *Main> run test3 stack1 Just [1,2,3,4,5] *Main> run test4 [] Nothing *Main> run test4 stack1 Just [15] Part 2: 5tack Language 2 A stack language with two types (integers and booleans), comparisons and if-else commands. To the Stack language in Part 1, add/modify the following commands/operations - LDI Int-loads its integer parameter onto the stack (replaces LD) - I.DB Bool loads its boolean parameter onto the stack. - ADD - same as with Stack Language 1 only adds integers - MULT - same as with Stack Language 1 only multiplies integers - DUP - places a copy of the stack's topmost element on the slack. If the stack is empty then DUP produces an error. Works with both integer and Boolean values. - LEQ - removes the top integer from the stack, removes the second integer from the stack. If top seeond the True is pushed on the stack else False is pushed onto the stack. - IFELSE Prog Prog - removes the top of the stack, if the value is tuie, then run the first program, else run the second program. If the values id not a Boolean then this is an error. Here is a definition of the abstract syntax and type definitions that you should use. type Prog =[Cmd] type Stack =[ Either Bool Int ] CS 381 Homework 4 - Semantics data Cmd =LDIInt|LDBBool|LEQ|ADD|MULT|DUP|IFFL.SEProgProgderivingShowrun::ProgStackMaybeStack Since the stack can contain two types use the Either with Bool on the "Left" and Int on the "Right". A stack containing the integers 1,2 and 3 would be defines as [Right 1, Right 2, Right 3 ] and a stack with a true and the integer 6 would be [Left True, Right 6]. Again the command run will return a Maybe stack. Submit a file named Stacklang2.hs. The first line of the code should be module Stacklang2 where. You can use the following S2-programs to test Stack Iang 2 , *Main> run test1 [] Just [Right 36] *Main> run test2 [] Just [Right 1, Left True] *Main> run test3 stack1 Just [Left True, Right 5 , Right 7 , Right 9] \#Main> run test4 stack1 Just [Right 63, Right 63, Right 9] Main> run test4 stack2 Nothing Main> run test 5 stack1 Just [Right 9,Right 5,Right 7, Right 9] *Main> run test6 [] Just [Right 20] Main> run test7 [] Just [Right 40] Main> run test8 [] Just [Right 15]









