Question
Curtis's article, she lists a variety of developmental processes across three stages of adolescence. Without counting academic processes, which two processes do you see as
Curtis's article, she lists a variety of developmental processes across three stages of adolescence. Without counting "academic processes," which two processes do you see as having the most impact on your work with teenagers in school settings? Why? What theory/ies discussed in her article or in other readings this week do you think provides you with the best "lens" through which to understand this process? Generally speaking, do more biological perspectives, intrapersonal (organismic) perspectives, or contextual perspectives seem to help the most?
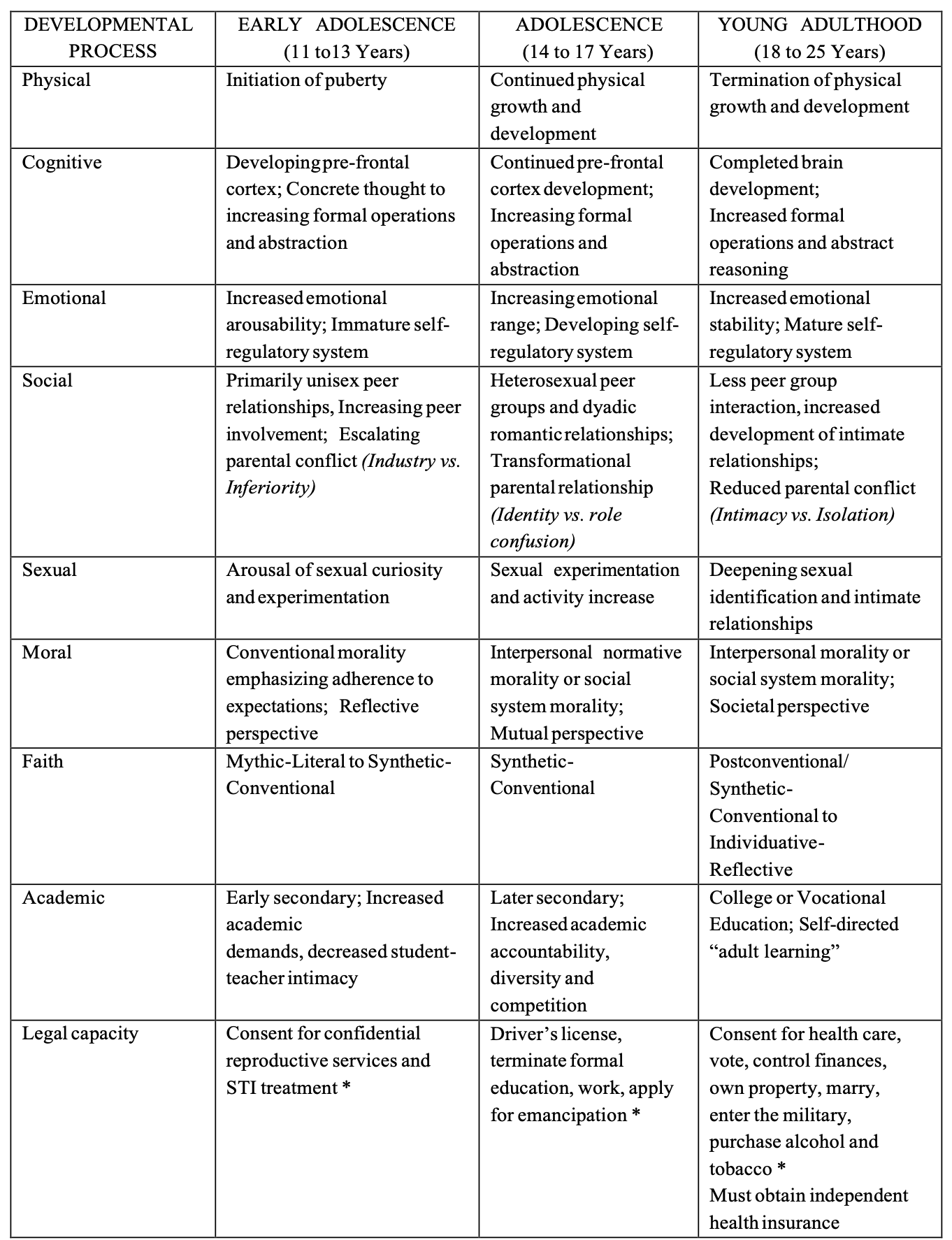
DEVELOPMENTAL PROCESS EARLY ADOLESCENCE Physical Cognitive Emotional Social Sexual Moral Faith Academic Legal capacity (11 to 13 Years) Initiation of puberty Developing pre-frontal cortex; Concrete thought to increasing formal operations and abstraction Increased emotional arousability; Immature self- regulatory system Primarily unisex peer relationships, Increasing peer involvement; Escalating parental conflict (Industry vs. Inferiority) Arousal of sexual curiosity and experimentation Conventional morality emphasizing adherence to expectations; Reflective perspective Mythic-Literal to Synthetic- Conventional Early secondary; Increased academic demands, decreased student- teacher intimacy Consent for confidential reproductive services and STI treatment * ADOLESCENCE (14 to 17 Years) Continued physical growth and development Continued pre-frontal cortex development; Increasing formal operations and abstraction Increasing emotional range; Developing self- regulatory system Heterosexual peer groups and dyadic romantic relationships; Transformational parental relationship (Identity vs. role confusion) Sexual experimentation and activity increase Interpersonal normative morality or social system morality; Mutual perspective Synthetic- Conventional Later secondary; Increased academic accountability, diversity and competition Driver's license, terminate formal education, work, apply for emancipation * YOUNG ADULTHOOD (18 to 25 Years) Termination of physical growth and development Completed brain development; Increased formal operations and abstract reasoning Increased emotional stability; Mature self- regulatory system Less peer group interaction, increased development of intimate relationships; Reduced parental conflict (Intimacy vs. Isolation) Deepening sexual identification and intimate relationships Interpersonal morality or social system morality; Societal perspective Postconventional/ Synthetic- Conventional to Individuative- Reflective College or Vocational Education; Self-directed "adult learning" Consent for health care, vote, control finances, own property, marry, enter the military, purchase alcohol and tobacco * Must obtain independent health insurance
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


