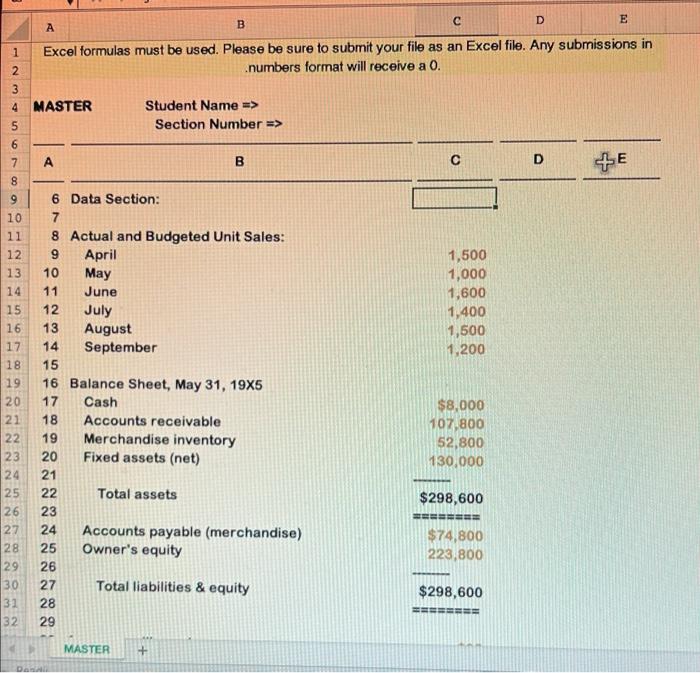
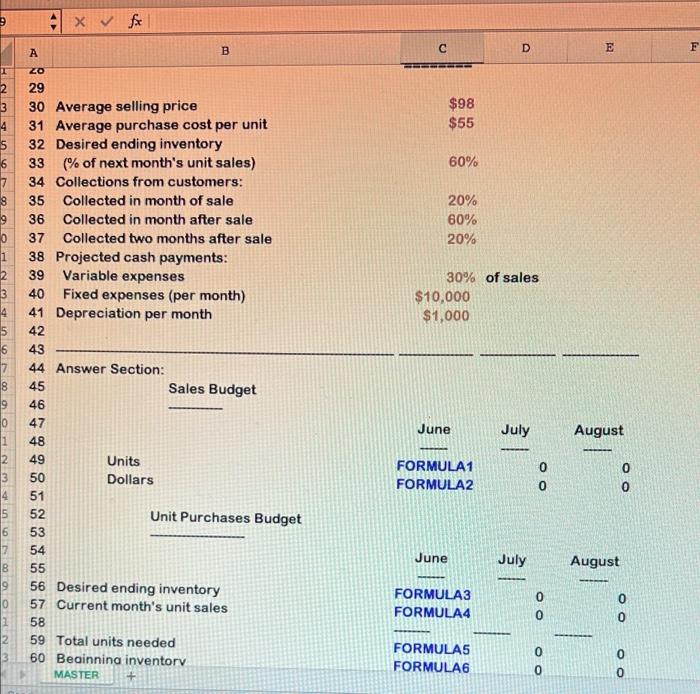
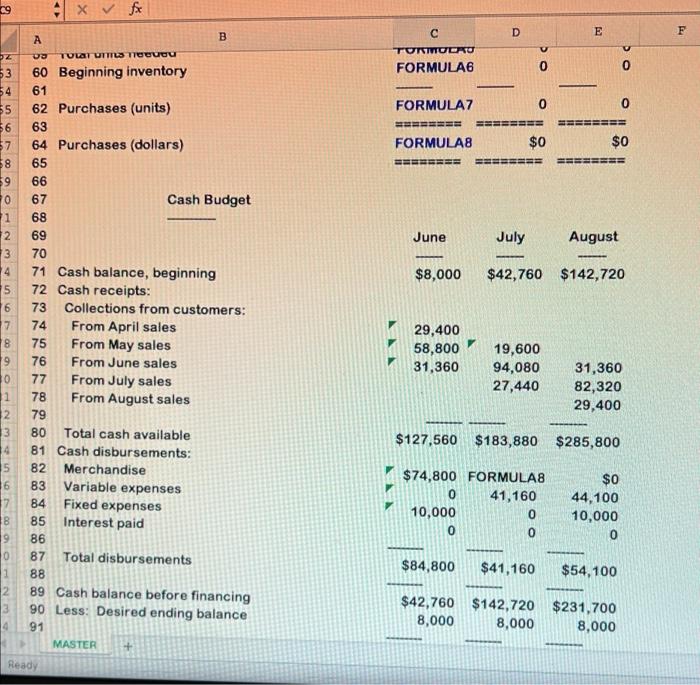
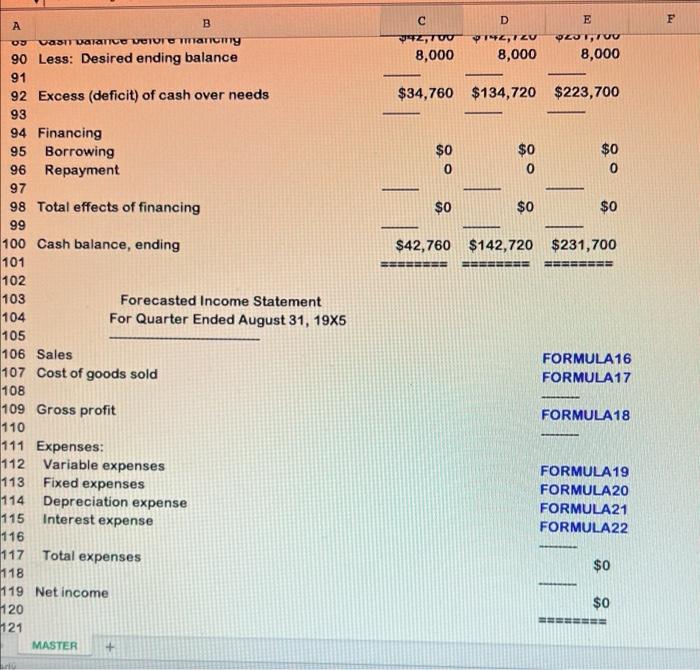
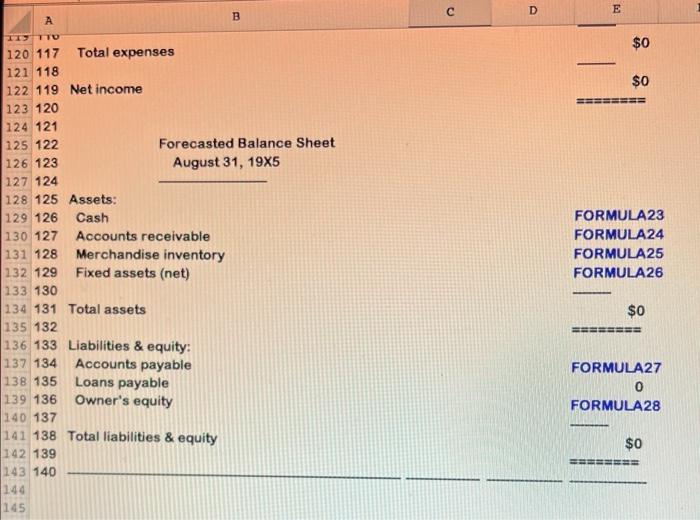
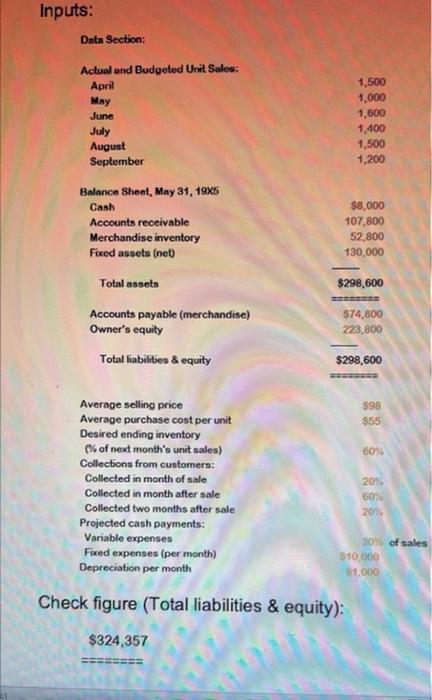
D E E B A Excel formulas must be used. Please be sure to submit your file as an Excel file. Any submissions in numbers format will receive a 0. 4 MASTER 5 Student Name => Section Number => o WN 6 7 A B D +E E 8 1,500 1,000 1,600 1,400 1,500 1,200 1000 un 10 11 12. 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 6 Data Section: 7 8 Actual and Budgeted Unit Sales: 9 April 10 May 11 June 12 July 13 August 14 September 15 16 Balance Sheet, May 31, 19X5 17 Cash 18 Accounts receivable 19 Merchandise inventory 20 Fixed assets (net) 21 22 Total assets 23 24 Accounts payable (merchandise) 25 Owner's equity 26 27 Total liabilities & equity 28 29 NN $8,000 107,800 52,800 130,000 $298,600 BEBE $74,800 223,800 $298,600 MASTER + 9 x fx D B E E F A 1 ZO 2 3 $98 $55 5 60% 9 9 20% 60% 20% 1 3 30% of sales $10,000 $1,000 6 18 29 30 Average selling price 31 Average purchase cost per unit 32 Desired ending inventory 33 % of next month's unit sales) 34 Collections from customers: 35 Collected in month of sale 36 Collected in month after sale 37 Collected two months after sale 38 Projected cash payments: 39 Variable expenses 40 Fixed expenses (per month) 41 Depreciation per month 42 43 44 Answer Section: 45 Sales Budget 46 47 48 49 Units 50 Dollars 51 52 Unit Purchases Budget 53 54 55 56 Desired ending inventory 57 Current month's unit sales 58 59 Total units needed 60 Beainnina inventory MASTER 19 0 June July August - - 2 3 14 FORMULA1 FORMULA2 OO 0 5 6 7 B 9 June July August NO VODOU 0 FORMULA3 FORMULA 0 3 FORMULAS FORMULA6 19 x fx D E F. B A TUITIVUDO FORMULAG U 2 $3 0 0 0 EEEEEE FORMULAZ 0 BRE EEEEEEEE FORMULA8 $0 BERSEE ====== lo con un 55 56 $7 58 59 10 1 2 $0 June July August 3 4 5 $8,000 $42,760 $142,720 16 17 18 19 10 60 Beginning inventory 61 62 Purchases (units) 63 64 Purchases (dollars) 65 66 67 Cash Budget 68 69 70 71 Cash balance, beginning 72 Cash receipts: 73 Collections from customers: 74 From April sales 75 From May sales 76 From June sales 77 From July sales 78 From August sales 79 80 Total cash available 81 Cash disbursements: 82 Merchandise 83 Variable expenses 84 Fixed expenses 85 Interest paid 86 87 Total disbursements 88 89 Cash balance before financing 90 Less: Desired ending balance 91 MASTER 29,400 58,800 31,360 19,600 94,080 27,440 31,360 82,320 29,400 1 $127,560 $183,880 $285,800 2 3 14 5 16 17 18 19 0 $0 $74,800 FORMULAS 0 41,160 10,000 0 0 0 44,100 10,000 0 $84,800 $41,160 $54,100 1 2 3 4 $42,760 $142,720 $231,700 8,000 8,000 8,000 Ready B E F A OD D 92,700 192,12U 8,000 8,000 OZOTTUU 8,000 $34,760 $134,720 $223,700 $0 $0 $0 0 $0 $0 $0 $42,760 $142,720 $231,700 EEEEEE EEEEEEE SEBEE 104 90 Less: Desired ending balance 91 92 Excess (deficit) of cash over needs 93 94 Financing 95 Borrowing 96 Repayment 97 98 Total effects of financing 99 100 Cash balance, ending 101 102 103 Forecasted Income Statement For Quarter Ended August 31, 19X5 105 106 Sales 107 Cost of goods sold 108 109 Gross profit 110 111 Expenses: 112 Variable expenses 113 Fixed expenses 114 Depreciation expense 115 Interest expense 116 117 Total expenses 118 119 Net income FORMULA16 FORMULA17 FORMULA18 FORMULA19 FORMULA20 FORMULA21 FORMULA22 $0 120 $0 BEBE 121 MASTER C D E A B $0 $0 EEEEEEEE 120 117 Total expenses 121 118 122 119 Net income 123 120 124 121 125 122 Forecasted Balance Sheet 126 123 August 31, 1935 127 124 128 125 Assets: 129 126 Cash 130 127 Accounts receivable 131 128 Merchandise inventory 132 129 Fixed assets (net) 133 130 134 131 Total assets 135 132 136 133 Liabilities & equity: 137 134 Accounts payable 138 135 Loans payable 139 136 Owner's equity 140 137 141 138 Total liabilities & equity 142 139 143 140 144 145 FORMULA23 FORMULA24 FORMULA25 FORMULA26 $0 ESSERE FORMULA27 0 FORMULA28 $0 EEEEEE Pa Below you will see three sets of inputs. After inputting all of your formulas, you should be able to use any of these sets of data and have the answers automatically update. For this assignment, please choose one of the data sets above and input all of the necessary formulas to find the answers. Once you are done, choose a different data set, enter it into your spreadsheet, and check the updated answers to ensure that everything is flowing through the formulas appropriately. A check answer for each one has been provided. Data set #1 Inputs: Data Section: Actual and Budgeted Unit Sales: April May June July August September 1,500 1,000 1,500 1.400 1,500 1,200 Balance Sheet, May 31, 1935 Cash Accounts receivable Merchandise inventory Fixed assets (net) $8.000 107,800 52,800 130,000 Total assets $298,600 Accounts payable (merchandise) Owner's equity $74,800 223 800 Total liabilities & equity $298,600 S98 $55 Average selling price Average purchase cost per unit Desired ending inventory (% of next month's unit sales) Collections from customers 50 Inputs: Data Section: Actual and Budgeted Unit Salou: April May June July August September 1,500 1,000 1,600 1,400 1,500 1,200 Balance Sheet, May 31, 1985 Cash Accounts receivable Merchandise inventory Fixed assets (net) $8.000 107,800 52,800 130,000 $298,600 Total assets Accounts payable (merchandise) Owner's equity Total liabilities & equity $74,800 223,800 $298,600 S98 855 60% Average selling price Average purchase cost per unit Desired ending inventory (% of next month's unit sales) Collections from customers: Collected in month of sale Collected in month after sale Collected two months after sale Projected cash payments: Variable expenses Fixed expenses (per month) Depreciation per month 20% 60% 20% 30 of sales $10.000 $1,000 Check figure (Total liabilities & equity): $324,357