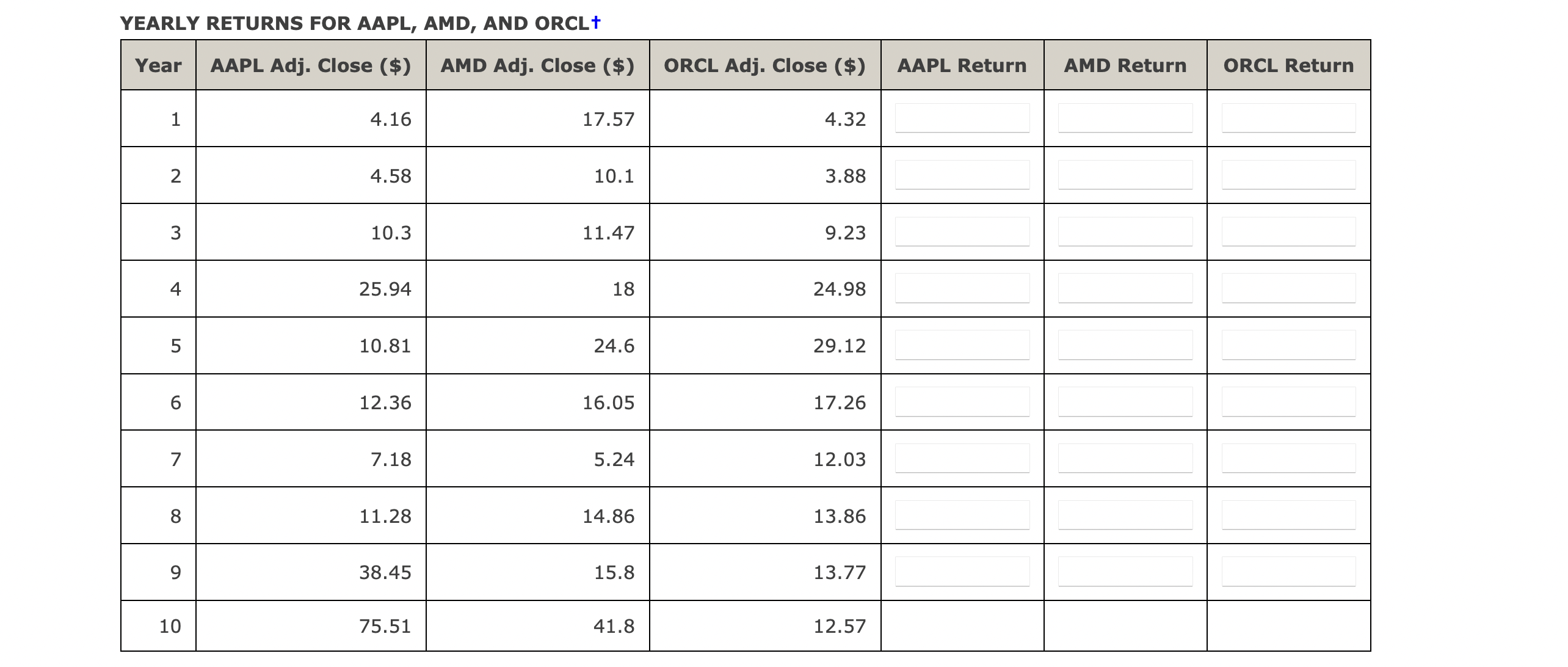
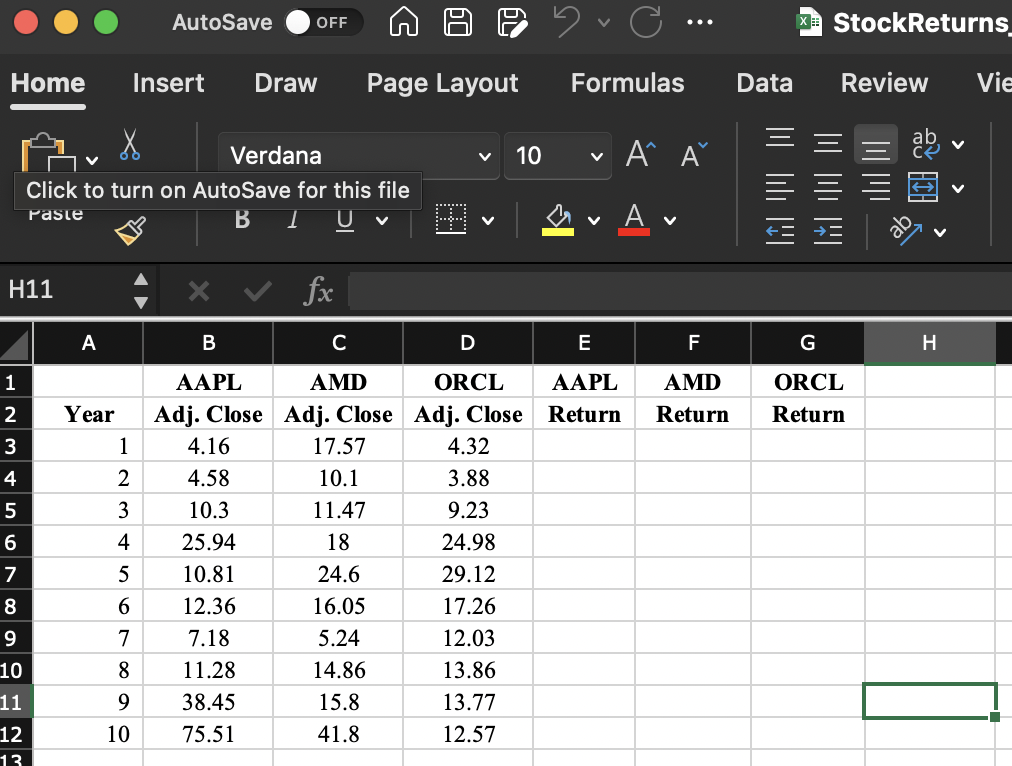
Data File Available: The purpose of this exercise is to learn how to calculate stock returns for portfolio models using actual stock price data. Ten years worth of stock price data are included the file StockReturns_8_13 for Apple Computer (AAPL), Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), and Oracle Corporation (ORCL). These data contain closing prices that are adjusted for stock dividends and splits. Using these stock price data, we now want to calculate the annual returns for each stock for the Years 1 through 9 . Returns are often calculated using continuous compounding. If the stock prices are adjusted for splits and stock dividends, then the price of stock i in period t+1,p(i,t+1), is given by p(i,t+1)=pi,teri,t where pi,t is the price of stock i in period t and ri,t is the return on stock i in period t. This calculation assumes no cash dividends were paid, which is true of Apple ri,t=ln(pi,tpi,t+1). For example, the Apple Computer adjusted closing price in Year 9 was $38.45. The closing price in Year 10 was $75.51. Thus, the continuously compounded return for Apple Computer from Year 9 to Year 10 is ln(38.4575.51)=0.6749. We use this calculation as our estimate of the annual return for Apple Computer for Year 9 . Take the closing stock prices shown in the table below and calculat returns for Years 1 through 9 for AAPL, AMD, and ORCL using ri,t=ln(pi,tpi,t+1). (Round your answers to four decimal places.) YEARLY RETURNS FOR AAPL, AMD, AND ORCL \begin{tabular}{|r|r|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline & \multicolumn{1}{|c|}{ A } & B & C & D & E & F & G & H \\ \hline 1 & & AAPL & AMD & ORCL & AAPL & AMD & ORCL & \\ \hline 2 & Year & Adj. Close & Adj. Close & Adj. Close & Return & Return & Return & \\ \hline 3 & 1 & 4.16 & 17.57 & 4.32 & & & & \\ \hline 4 & 2 & 4.58 & 10.1 & 3.88 & & & \\ \hline 5 & 3 & 10.3 & 11.47 & 9.23 & & & \\ \hline 6 & 4 & 25.94 & 18 & 24.98 & & & & \\ \hline 7 & 5 & 10.81 & 24.6 & 29.12 & & & & \\ \hline 8 & 6 & 12.36 & 16.05 & 17.26 & & & & \\ \hline 9 & 7 & 7.18 & 5.24 & 12.03 & & & & \\ \hline 10 & 8 & 11.28 & 14.86 & 13.86 & & & & \\ \hline 11 & 9 & 38.45 & 15.8 & 13.77 & & & & \\ \hline 12 & 10 & 75.51 & 41.8 & 12.57 & & & & \\ \hline \end{tabular} Data File Available: The purpose of this exercise is to learn how to calculate stock returns for portfolio models using actual stock price data. Ten years worth of stock price data are included the file StockReturns_8_13 for Apple Computer (AAPL), Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), and Oracle Corporation (ORCL). These data contain closing prices that are adjusted for stock dividends and splits. Using these stock price data, we now want to calculate the annual returns for each stock for the Years 1 through 9 . Returns are often calculated using continuous compounding. If the stock prices are adjusted for splits and stock dividends, then the price of stock i in period t+1,p(i,t+1), is given by p(i,t+1)=pi,teri,t where pi,t is the price of stock i in period t and ri,t is the return on stock i in period t. This calculation assumes no cash dividends were paid, which is true of Apple ri,t=ln(pi,tpi,t+1). For example, the Apple Computer adjusted closing price in Year 9 was $38.45. The closing price in Year 10 was $75.51. Thus, the continuously compounded return for Apple Computer from Year 9 to Year 10 is ln(38.4575.51)=0.6749. We use this calculation as our estimate of the annual return for Apple Computer for Year 9 . Take the closing stock prices shown in the table below and calculat returns for Years 1 through 9 for AAPL, AMD, and ORCL using ri,t=ln(pi,tpi,t+1). (Round your answers to four decimal places.) YEARLY RETURNS FOR AAPL, AMD, AND ORCL \begin{tabular}{|r|r|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline & \multicolumn{1}{|c|}{ A } & B & C & D & E & F & G & H \\ \hline 1 & & AAPL & AMD & ORCL & AAPL & AMD & ORCL & \\ \hline 2 & Year & Adj. Close & Adj. Close & Adj. Close & Return & Return & Return & \\ \hline 3 & 1 & 4.16 & 17.57 & 4.32 & & & & \\ \hline 4 & 2 & 4.58 & 10.1 & 3.88 & & & \\ \hline 5 & 3 & 10.3 & 11.47 & 9.23 & & & \\ \hline 6 & 4 & 25.94 & 18 & 24.98 & & & & \\ \hline 7 & 5 & 10.81 & 24.6 & 29.12 & & & & \\ \hline 8 & 6 & 12.36 & 16.05 & 17.26 & & & & \\ \hline 9 & 7 & 7.18 & 5.24 & 12.03 & & & & \\ \hline 10 & 8 & 11.28 & 14.86 & 13.86 & & & & \\ \hline 11 & 9 & 38.45 & 15.8 & 13.77 & & & & \\ \hline 12 & 10 & 75.51 & 41.8 & 12.57 & & & & \\ \hline \end{tabular}









