Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. In a (very) small community, there are 4 residents who all value access to open space. There is a local plan to develop
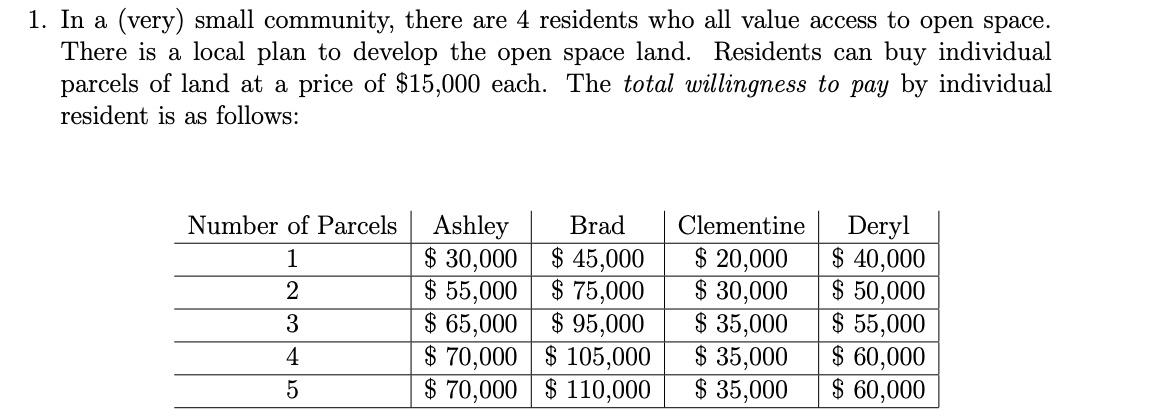

1. In a (very) small community, there are 4 residents who all value access to open space. There is a local plan to develop the open space land. Residents can buy individual parcels of land at a price of $15,000 each. The total willingness to pay by individual resident is as follows: Deryl $ 40,000 $ 50,000 $ 55,000 $ 60,000 $ 60,000 Number of Parcels Ashley Brad Clementine $ 45,000 $ 30,000 $ 55,000 $ 20,000 $ 30,000 $ 35,000 $ 35,000 $ 35,000 1 2 $ 75,000 $ 65,000 $ 95,000 $ 70,000 $ 105,000 $ 70,000 $ 110,000 3 4 (a) What is Ashley's marginal willingness to pay for the 3rd parcel of open space? (Hint: This is his willingness to pay to go from 2 to 3 parcels of open space.) (b) If open space parcels were excludable, so that the residents could only enjoy their own open space and not that of their neighbors, how many parcels would Ashley, Brad, Clementine and Deryl purchase respectively? (c) Under the assumption open space parcels are excludable, draw the each individ- ual's demand function for open space for the community. Keep in mind parcels can only be sold as a whole (i.e. no one can buy 1.5 parcels, only 1 or 2). Find each individual's consumer surplus. (d) If open space parcels are not excludable (such that all users can enjoy a parcel purchased by their neighbor for free), but can only be purchased privately (with no coordination among residents) how many total parcels will be purchased? 1 (e) Draw the aggregate willingness to pay curve for open space as a public good. What is the aggregate consumer surplus from the private provision of public goods in this case? If the residents could coordinate to purchase the efficient amount of open space (i.e. the amount that maximizes total benefits minus total costs) how much would they purchase? What would be the aggregate consumer surplus from this quantity of open space?
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.51 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
d The nonexcludability property of public goods gives rise to the problem called free rider problem ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started