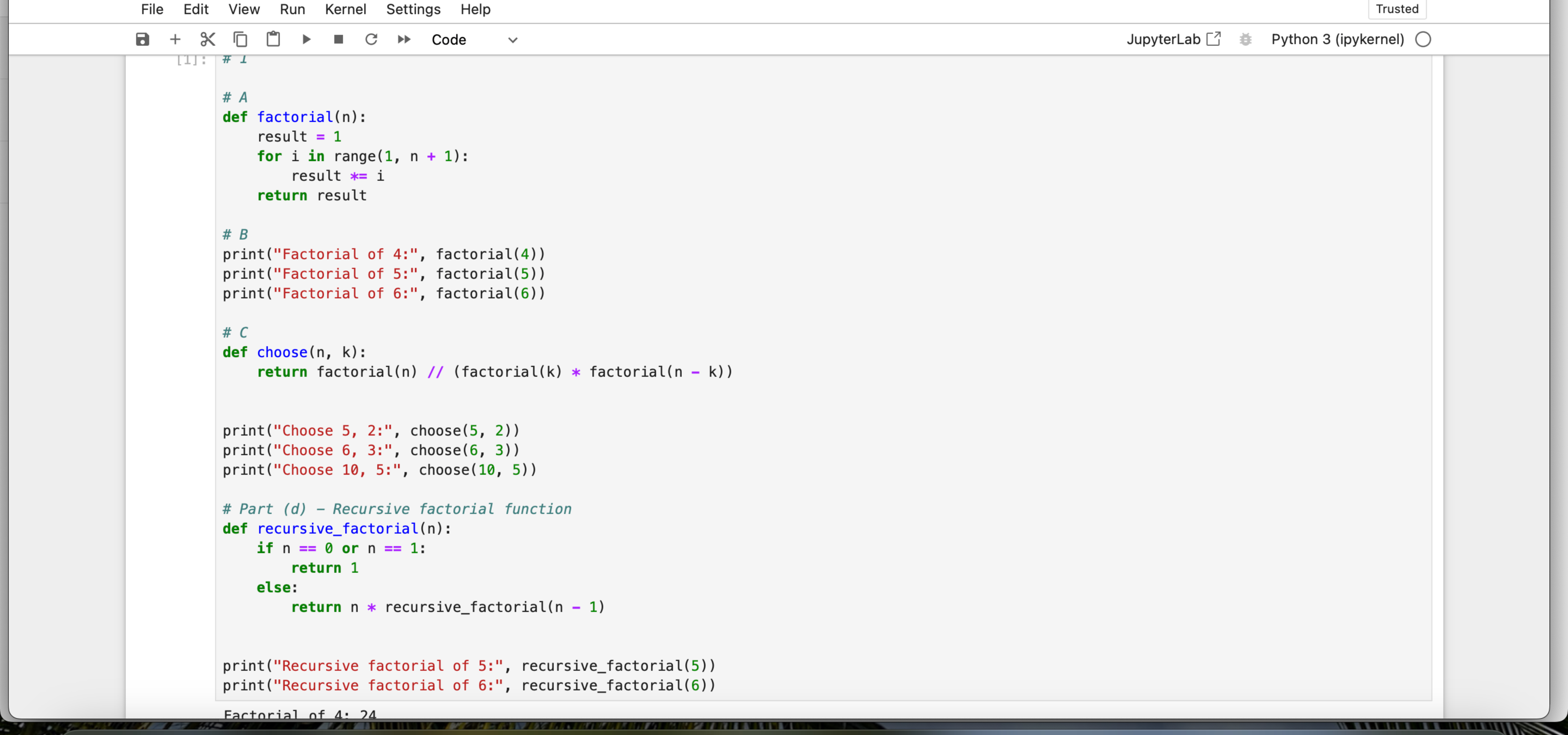
Question: def factorial ( n ) : result = 1 for i in range ( 1 , n + 1 ) : result * = i
def factorialn:
result
for i in range n :
result i
return resultprintFactorial of : factorial
printFactorial of : factorial
printFactorial of : factorialdef choosen k:
return factorialnfactorialk factorialn k
printChoose : choose
printChoose : choose
printChoose : choosedef recursivefactorialn:
if n or n :
return
else:
return n recursivefactorialn
printRecursive factorial of : recursivefactorial
printRecursive factorial of : recursivefactorial
Factorial of : For Homework you had to make two different function to calculate factorials. One
used a for loop, and one used a recursive function that called itsself.
A Which of these function was faster for calculating large factorials? Say You'll
needed to use
import timeit
or something similar to time the two functions.
B What is the largest factorial your functions can calculate as a floating point number,
before they return infinity? You might need to modify your factorial function to return a
float by setting the initial number to
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


