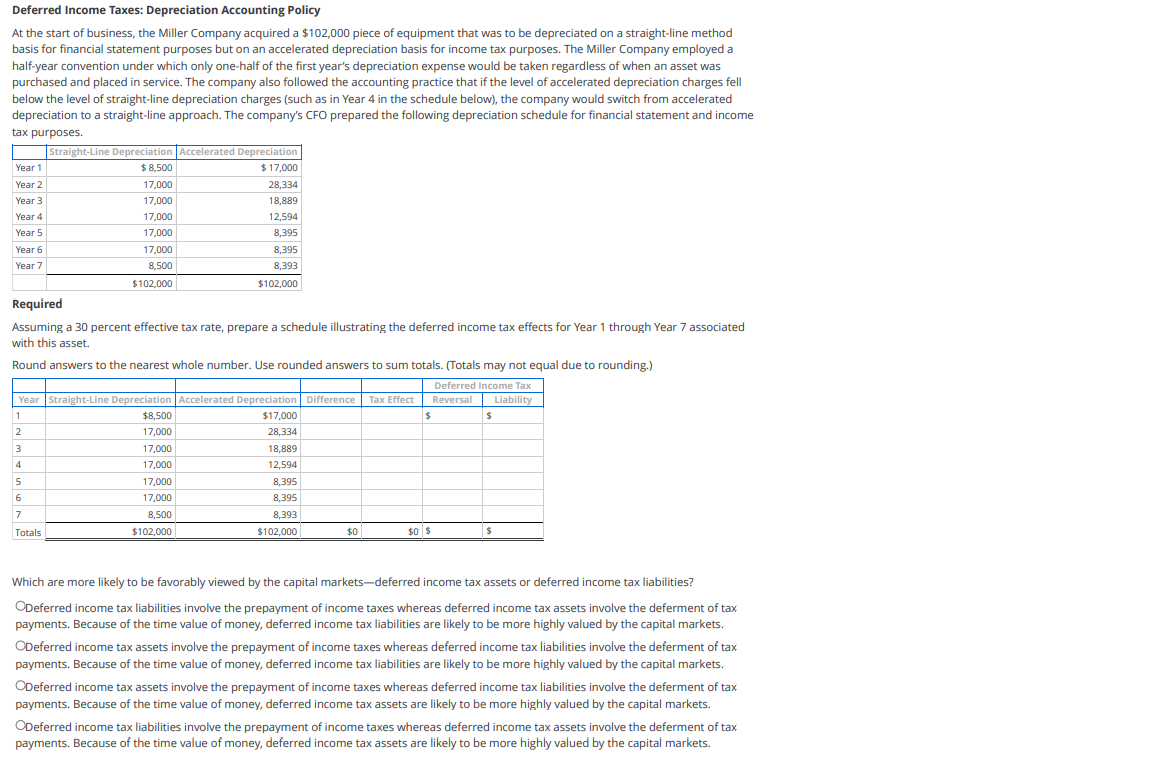
Deferred Income Taxes: Depreciation Accounting Policy At the start of business, the Miller Company acquired a $102,000 piece of equipment that was to be depreciated on a straight-line method basis for financial statement purposes but on an accelerated depreciation basis for income tax purposes. The Miller Company employed a half-year convention under which only one-half of the first year's depreciation expense would be taken regardless of when an asset was purchased and placed in service. The company also followed the accounting practice that if the level of accelerated depreciation charges fell below the level of straight-line depreciation charges (such as in Year 4 in the schedule below), the company would switch from accelerated depreciation to a straight-line approach. The company's CFO prepared the following depreciation schedule for financial statement and income tax purposes. Straight-Line Depreciation Accelerated Depreciation Year 1 $ 8,500 $ 17,000 Year 2 17,000 28,334 Year 3 17,000 18,889 Year 4 17,000 12,594 Year 5 17,000 8,395 Year 6 17,000 8,395 Year 7 8,500 8,393 $102,000 $102,000 Required Assuming a 30 percent effective tax rate, prepare a schedule illustrating the deferred income tax effects for Year 1 through Year 7 associated with this asset. Round answers to the nearest whole number. Use rounded answers to sum totals. (Totals may not equal due to rounding.) Deferred Income Tax Year Straight-Line Depreciation Accelerated Depreciation Difference Tax Effect Reversal Liability $8,500 $17,000 $ 17,000 28,334 3 17,000 18,889 17,000 12,594 17,000 8,395 17,000 8,395 8,500 8,393 Totals $102,000 $102,000 $0 $ 1 $ $ 2. 4 5 6 7 $0 $ Which are more likely to be favorably viewed by the capital markets-deferred income tax assets or deferred income tax liabilities? ODeferred income tax liabilities involve the prepayment of income taxes whereas deferred income tax assets involve the deferment of tax payments. Because of the time value of money, deferred income tax liabilities are likely to be more highly valued by the capital markets. ODeferred income tax assets involve the prepayment of income taxes whereas deferred income tax liabilities involve the deferment of tax payments. Because of the time value of money, deferred income tax liabilities are likely to be more highly valued by the capital markets. ODeferred income tax assets involve the prepayment of income taxes whereas deferred income tax liabilities involve the deferment of tax payments. Because of the time value of money, deferred income tax assets are likely to be more highly valued by the capital markets. ODeferred income tax liabilities involve the prepayment of income taxes whereas deferred income tax assets involve the deferment of tax payments. Because of the time value of money, deferred income tax assets are likely to be more highly valued by the capital markets







