Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Diabetes is a health condition that affects how the body uses glucose to generate energy. One type of diabetes happens when the beta cells
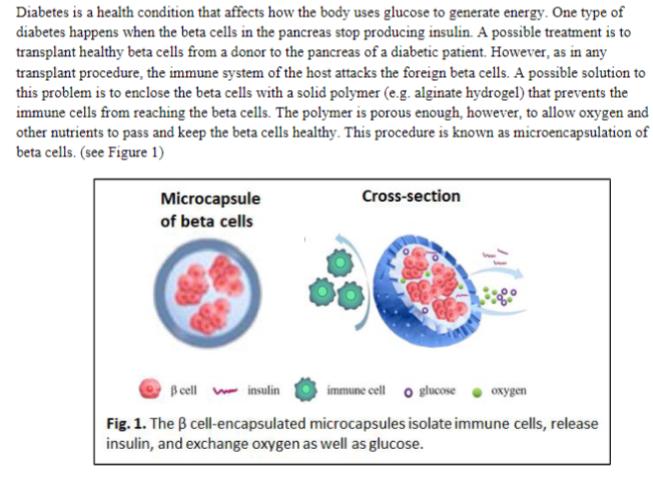

Diabetes is a health condition that affects how the body uses glucose to generate energy. One type of diabetes happens when the beta cells in the pancreas stop producing insulin. A possible treatment is to transplant healthy beta cells from a donor to the pancreas of a diabetic patient. However, as in any transplant procedure, the immune system of the host attacks the foreign beta cells. A possible solution to this problem is to enclose the beta cells with a solid polymer (e.g. alginate hydrogel) that prevents the immune cells from reaching the beta cells. The polymer is porous enough, however, to allow oxygen and other nutrients to pass and keep the beta cells healthy. This procedure is known as microencapsulation of beta cells. (see Figure 1) Microcapsule of beta cells Cross-section B cell insulin immune cell glucose oxygen Fig. 1. The B cell-encapsulated microcapsules isolate immune cells, release insulin, and exchange oxygen as well as glucose. A simplified flowchart of a continuous process for the microencapsulation of beta cells is shown below. There are two inputs to the microencapsulation system: the aqueous cell solution and aqueous alginate solution. The outputs are the solid alginate hydrogel microcapsules (containing beta cells, alginate and water) and a supernatant solution (also with beta cells, alginate and water) The process is at steady-state and there are no chemical reactions occurring. Alginate solution alginate, water Feed (cell solution) 12.6 mg cells ml, water Microencapsulation System Supernatant solution cells, alginate, water Microcapsules (A0 g/min) 10.5 mg cells/g alginate, water The aqueous cell solution input (the Feed) has 12.6 mg beta cells/mL dissolved in water (no alginate) and its specific gravity is 1.05. The aqueous alginate solution input contains 6.5 mass % alginate dissolved in water (no beta cells). The mass flow rates of the input cell solution and input alginate solution are equal. The microcapsules contain 10.5 mg beta cells/g, 4.5 mass % alginate and the rest water. The mass flow rate of the output supernatant is 1.7 times that of the mass flowrate of the microcapsules. It is desired to produce A0 g/min of the microcapsules, where A is the last digit of your ASU ID. For example, if your ASU ID is 1212012345, then A = 5 and A0 g/min = 50 g/min. If the last digit of your ASU ID is 0, use A0 g/min = 100 g/min. a. Draw and label a flowchart for the process. (The one given above is not completely labeled) Note: Please redraw the flowchart by hand. Cutting-and-pasting the above diagram will not be graded b. Write all the possible Material Balance equations applicable to the system in (a). c. Carry out a degree-of-freedom analysis for the system in (a). (Hint: The cells can be considered as one chemical species) Solve for all of the unknowns. d. e. Determine what percent of the beta cells in the feed is left in the output supernatant solution. f. The laboratory process is to be commercialized to produce 5 kg/h of product crystals. What is the scaling factor? g. For (f), determine the required mass flow rates of the feed in kg/h.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


