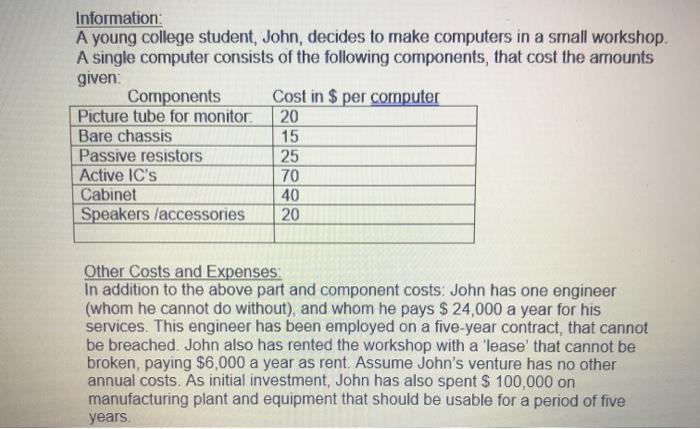
dies basis Q5: Suppose, John prices a computer at $ 230. Then at what level of sales will John make neither a profit or a loss i.e., at what level of sales will John break even? NOTE: This is a standard break even question the break even may be calculated as a break even 'Quantity' or break even "Revenue" level that is just the Break Even Quantity x Price. Q6: Suppose John finds demand to be 1400 computers per year, so he makes this number of computers annually. Now what is his break-even price? NOTE: The break even price at the production level of 1400 computers is obviously simply the per unit (per computer) cost of production when 1400 computers are manufactured Obviously BOTH fixed and variable costs are involved Q7. Assume the production level of 1400 computers per year. John finds that he has to maintain an average component inventory equal to 2 month's production, finished goods in warehouses amount to three month's production, payments are made by dealers and distributors two and a half months after purchase. The annual rate of interest relevant to John's business is 10%. Now what is the break even price for John? NOTE A component inventory of 2 month's production, finished goods in warehouses for there months, and market credit for 25 months are as good as or 'similar to holding an inventory of (2+3+2.5=7.5) month's production valued at the component cost all the time. You have to first calculate the Annual Inventory Holding Cost for this (the interest cost of carrying this inventory) Then you can divide the calculated number by the annual production 1400 to get the per computer cost. The new break even price will be the calculated per computer. Cosi just calculated + the Break Even Price calculated in 0.7 08 John plans to introduce a product in the Florida market - to do this he expects to invest $ 300,000 on a building that has a resale value of S 200.000 after five years his revenues are expected to be $ 100,000 per year and costs are $40,000 by the end of the first year S 45,000 for the next year, and $30,000 per year for the remaining three years. Calculate the Net Present Value of the Florida project if the discount rate or rate of interest is 10% annually Information: A young college student, John, decides to make computers in a small workshop A single computer consists of the following components, that cost the amounts given Components Cost in $ per computer Picture tube for monitor 20 Bare chassis 15 Passive resistors 25 Active IC's 70 Cabinet 40 Speakers /accessories 20 Other Costs and Expenses In addition to the above part and component costs: John has one engineer (whom he cannot do without), and whom he pays $ 24,000 a year for his services. This engineer has been employed on a five-year contract, that cannot be breached. John also has rented the workshop with a 'lease that cannot be broken, paying $6,000 a year as rent. Assume John's venture has no other annual costs. As initial investment, John has also spent $ 100,000 on manufacturing plant and equipment that should be usable for a period of five years