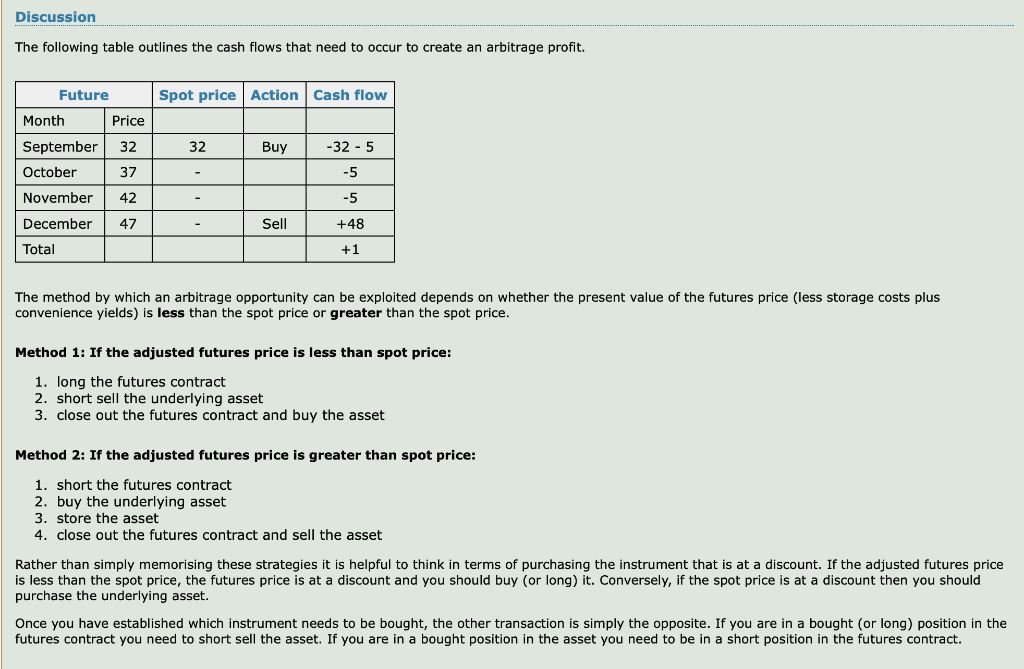
Discussion The following table outlines the cash flows that need to occur to create an arbitrage profit. Future Spot price Action Cash flow Price Month September October 32 32 Buy -32 - 5 37 -5 November 42 -5 47 Sell +48 December Total +1 The method by which an arbitrage opportunity can be exploited depends on whether the present value of the futures price (less storage costs plus convenience yields) is less than the spot price or greater than the spot price. Method 1: If the adjusted futures price is less than spot price: 1. long the futures contract 2. short sell the underlying asset 3. close out the futures contract and buy the asset Method 2: If the adjusted futures price is greater than spot price: 1. short the futures contract 2. buy the underlying asset 3. store the asset 4. close out the futures contract and sell the asset Rather than simply memorising these strategies it is helpful to think in terms of purchasing the instrument that is at a discount. If the adjusted futures price is less than the spot price, the futures price is at a discount and you should buy (or long) it. Conversely, if the spot price is at a discount then you should purchase the underlying asset. Once you have established which instrument needs to be bought, the other transaction is simply the opposite. If you are in a bought (or long) position in the futures contract you need to short sell the asset. If you are in a bought position in the asset you need to be in a short position in the futures contract. Discussion The following table outlines the cash flows that need to occur to create an arbitrage profit. Future Spot price Action Cash flow Price Month September October 32 32 Buy -32 - 5 37 -5 November 42 -5 47 Sell +48 December Total +1 The method by which an arbitrage opportunity can be exploited depends on whether the present value of the futures price (less storage costs plus convenience yields) is less than the spot price or greater than the spot price. Method 1: If the adjusted futures price is less than spot price: 1. long the futures contract 2. short sell the underlying asset 3. close out the futures contract and buy the asset Method 2: If the adjusted futures price is greater than spot price: 1. short the futures contract 2. buy the underlying asset 3. store the asset 4. close out the futures contract and sell the asset Rather than simply memorising these strategies it is helpful to think in terms of purchasing the instrument that is at a discount. If the adjusted futures price is less than the spot price, the futures price is at a discount and you should buy (or long) it. Conversely, if the spot price is at a discount then you should purchase the underlying asset. Once you have established which instrument needs to be bought, the other transaction is simply the opposite. If you are in a bought (or long) position in the futures contract you need to short sell the asset. If you are in a bought position in the asset you need to be in a short position in the futures contract







