Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
DO NOT USE EXCEL DO NOT SOLVE BY SUMPLY GETTING THE P AND F for eahc year SOLVE USING A, G, g rules if given
DO NOT USE EXCEL
DO NOT SOLVE BY SUMPLY GETTING THE P AND F for eahc year
SOLVE USING A, G, g rules if given gradients
I NEED IT URGENTT
URGENTLY NEEDED
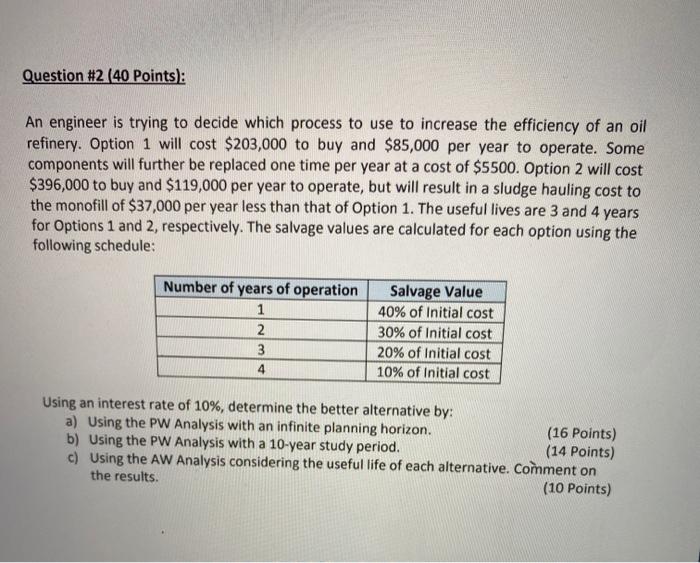
Question #2 (40 Points): An engineer is trying to decide which process to use to increase the efficiency of an oil refinery. Option 1 will cost $203,000 to buy and $85,000 per year to operate. Some components will further be replaced one time per year at a cost of $5500. Option 2 will cost $396,000 to buy and $119,000 per year to operate, but will result in a sludge hauling cost to the monofill of $37,000 per year less than that of Option 1. The useful lives are 3 and 4 years for Options 1 and 2, respectively. The salvage values are calculated for each option using the following schedule: Number of years of operation 1 2 3 4 Salvage Value 40% of Initial cost 30% of Initial cost 20% of Initial cost 10% of Initial cost Using an interest rate of 10%, determine the better alternative by: a) Using the PW Analysis with an infinite planning horizon. (16 Points) b) Using the PW Analysis with a 10-year study period. (14 Points) c) Using the AW Analysis considering the useful life of each alternative. Comment on the results. (10 Points) Question #2 (40 Points): An engineer is trying to decide which process to use to increase the efficiency of an oil refinery. Option 1 will cost $203,000 to buy and $85,000 per year to operate. Some components will further be replaced one time per year at a cost of $5500. Option 2 will cost $396,000 to buy and $119,000 per year to operate, but will result in a sludge hauling cost to the monofill of $37,000 per year less than that of Option 1. The useful lives are 3 and 4 years for Options 1 and 2, respectively. The salvage values are calculated for each option using the following schedule: Number of years of operation 1 2 3 4 Salvage Value 40% of Initial cost 30% of Initial cost 20% of Initial cost 10% of Initial cost Using an interest rate of 10%, determine the better alternative by: a) Using the PW Analysis with an infinite planning horizon. (16 Points) b) Using the PW Analysis with a 10-year study period. (14 Points) c) Using the AW Analysis considering the useful life of each alternative. Comment on the results. (10 Points) Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


