Question
Do students reduce study time in classes where they achieve a higher midterm score? In a Journal of Economic Education article (Winter 2005), Gregory Krohn
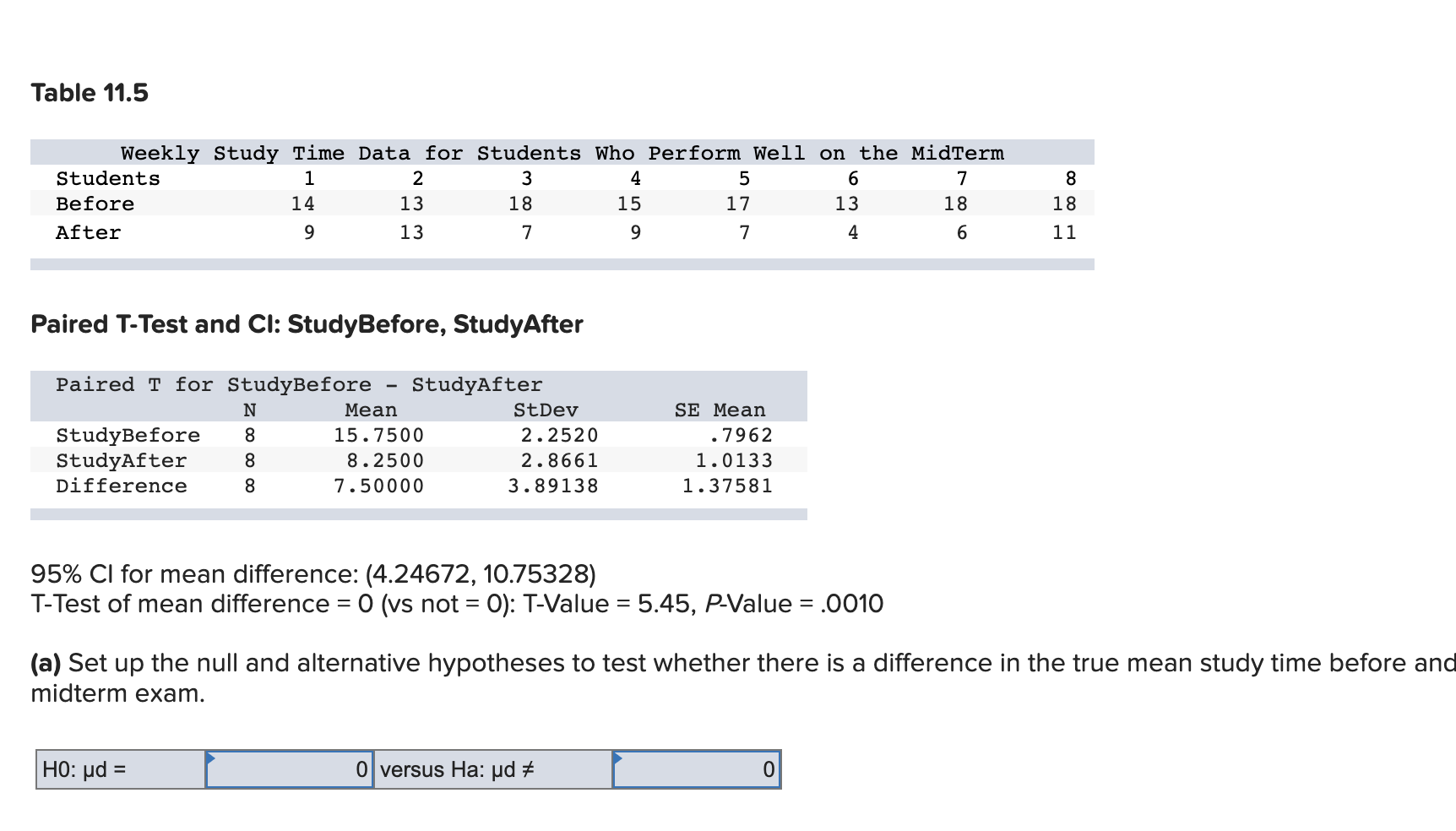
Do students reduce study time in classes where they achieve a higher midterm score? In a Journal of Economic Education article (Winter 2005), Gregory Krohn and Catherine O'Connor studied student effort and performance in a class over a semester. In an intermediate macroeconomics course, they found that "students respond to higher midterm scores by reducing the number of hours they subsequently allocate to studying for the course." Suppose that a random sample of n = 8 students who performed well on the midterm exam was taken and weekly study times before and after the exam were compared. The resulting data are given in Table 11.5. Assume that the population of all possible paired differences is normally distributed.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


