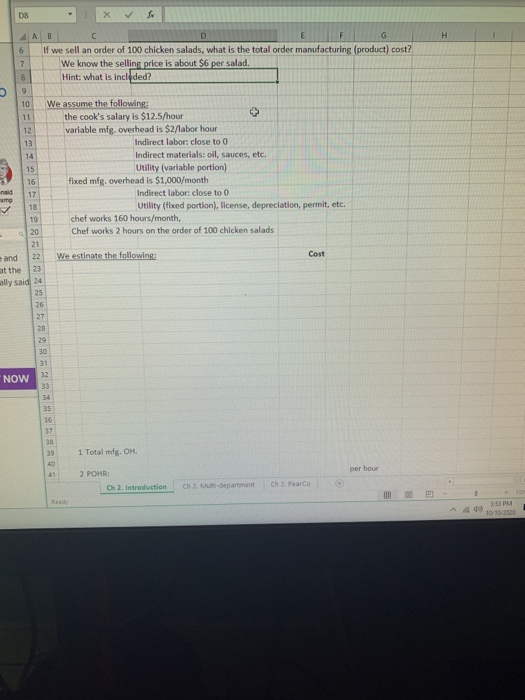
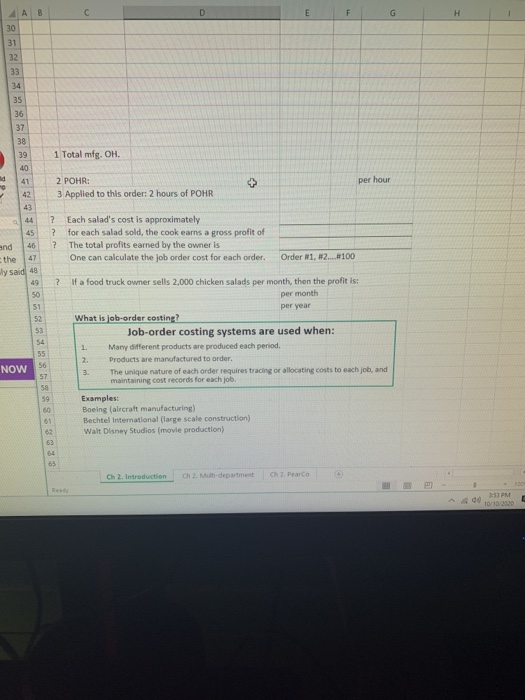
DS 4 AB D E G 6 If we sell an order of 100 chicken salads, what the total order manufacturing (product) cost? 7 We know the selling price is about $6 per salad. 8 Hint: what is included? 9 10 We assume the following: 11 the cook's salary is $12.5/hour 12 variable mig, overhead is $2/labor hour 13 Indirect labor: close to O 14 Indirect materials: oil, sauces, etc. 15 Utility (variable portion) 16 fixed mig, overhead is $1,000/month 17 Indirect labor: close to 0 rum 18 Utility (fixed portion), license, depreciation, permit, etc. 19 chef works 160 hours/month, 20 Chef works 2 hours on the order of 100 chicken salads 21 and 22 We estinate the following: Cost at the 23 ally said 24 25 26 27 23 29 30 31 32 NOW 33 34 35 36 20 39 1 Total mig. OH. 41 2 POHR: per hour Ch 2. Introduction Ch 2. Mi-department Ch 2. Parco Rund 2:53 PM 10/10/2020 AB D E F G H 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 1 Total mfg. OH. 40 41 + per hour 2 POHR: 3 Applied to this order: 2 hours of POHR 42 43 44 and 46 the 47 ly said 48 50 51 52 53 ? Each salad's cost is approximately ? for each salad sold, the cook earns a gross profit of ? The total profits earned by the owner is One can calculate the job order cost for each order. Order N1, 2...8100 ? If a food truck owner sells 2,000 chicken salads per month, then the profit is: per month per year What is job-order costing? Job-order costing systems are used when: Many different products are produced each period, 2. Products are manufactured to order. The unique nature of each order requires tracing or allocating costs to each job, and maintaining cost records for each job. Examples: Boeing (alrcraft manufacturing) Bechtel International (large scale construction) Walt Disney Studios (movie production) 1 NOW 3 55 56 57 50 59 60 69 62 63 64 Ch 2. Introduction ChMudepartment 2. Parco RE 2:51 PM 10/10/2010 DS 4 AB D E G 6 If we sell an order of 100 chicken salads, what the total order manufacturing (product) cost? 7 We know the selling price is about $6 per salad. 8 Hint: what is included? 9 10 We assume the following: 11 the cook's salary is $12.5/hour 12 variable mig, overhead is $2/labor hour 13 Indirect labor: close to O 14 Indirect materials: oil, sauces, etc. 15 Utility (variable portion) 16 fixed mig, overhead is $1,000/month 17 Indirect labor: close to 0 rum 18 Utility (fixed portion), license, depreciation, permit, etc. 19 chef works 160 hours/month, 20 Chef works 2 hours on the order of 100 chicken salads 21 and 22 We estinate the following: Cost at the 23 ally said 24 25 26 27 23 29 30 31 32 NOW 33 34 35 36 20 39 1 Total mig. OH. 41 2 POHR: per hour Ch 2. Introduction Ch 2. Mi-department Ch 2. Parco Rund 2:53 PM 10/10/2020 AB D E F G H 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 1 Total mfg. OH. 40 41 + per hour 2 POHR: 3 Applied to this order: 2 hours of POHR 42 43 44 and 46 the 47 ly said 48 50 51 52 53 ? Each salad's cost is approximately ? for each salad sold, the cook earns a gross profit of ? The total profits earned by the owner is One can calculate the job order cost for each order. Order N1, 2...8100 ? If a food truck owner sells 2,000 chicken salads per month, then the profit is: per month per year What is job-order costing? Job-order costing systems are used when: Many different products are produced each period, 2. Products are manufactured to order. The unique nature of each order requires tracing or allocating costs to each job, and maintaining cost records for each job. Examples: Boeing (alrcraft manufacturing) Bechtel International (large scale construction) Walt Disney Studios (movie production) 1 NOW 3 55 56 57 50 59 60 69 62 63 64 Ch 2. Introduction ChMudepartment 2. Parco RE 2:51 PM 10/10/2010