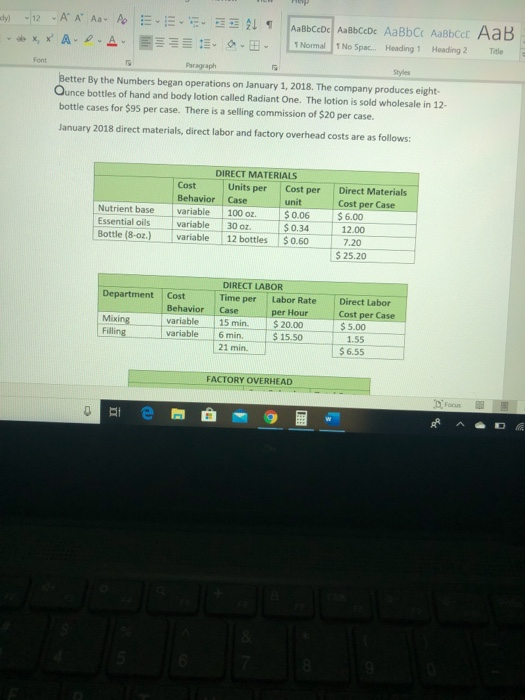
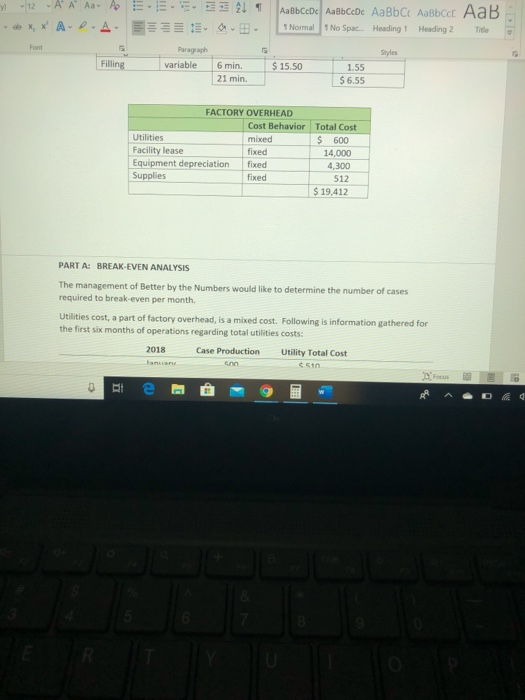
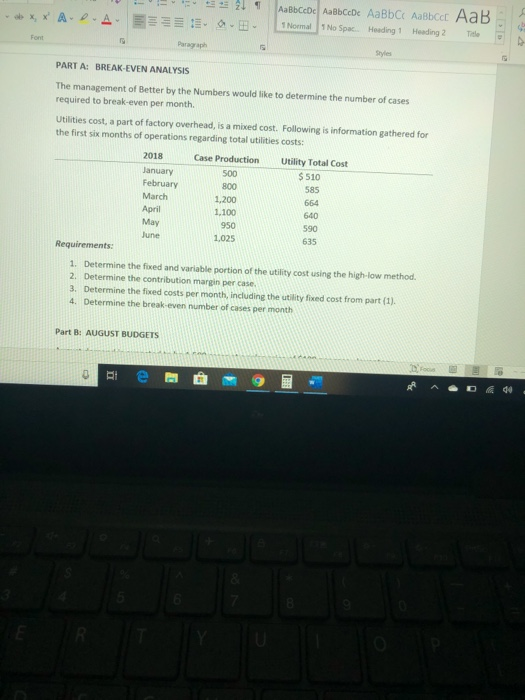
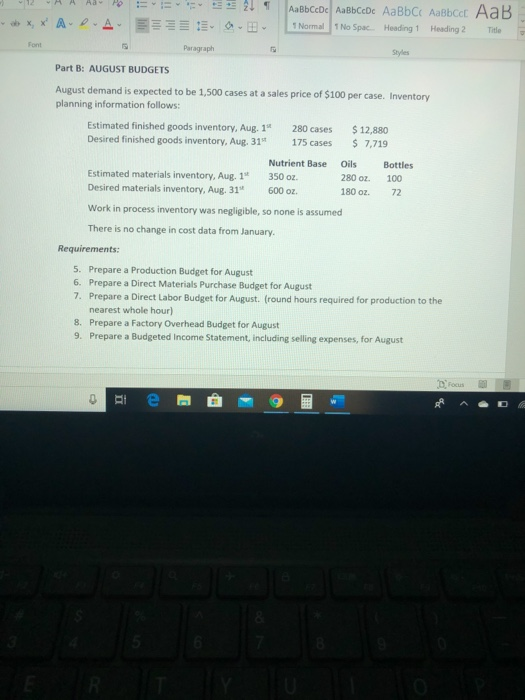
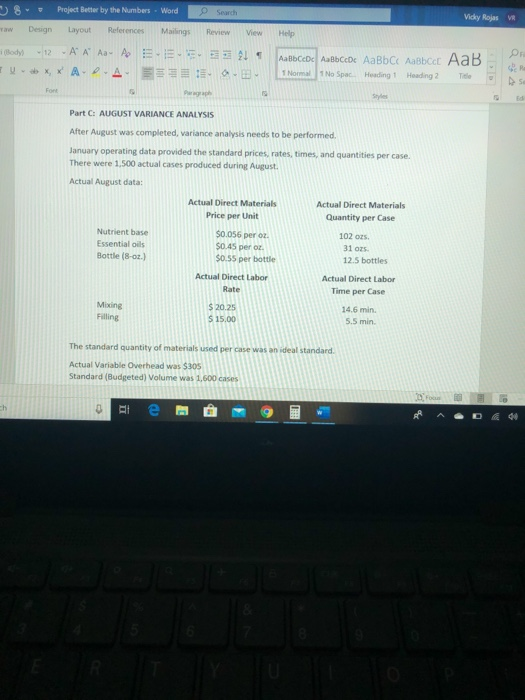
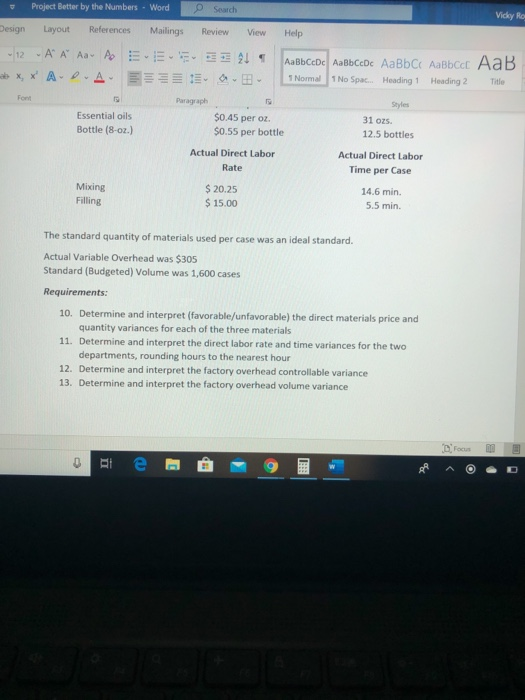
dy - 12A A Aa A X, * A-D-A E 21 AaBbCcDc ABCcDc AaBb C AaBbcc AaB 1 Normal No Spac. Heading 1 Heading 2 Title D- Styles Better By the Numbers began operations on January 1, 2018. The company produces eight- Ounce bottles of hand and body lotion called Radiant One. The lotion is sold wholesale in 12- bottle cases for $95 per case. There is a selling commission of $20 per case. January 2018 direct materials, direct labor and factory overhead costs are as follows: Nutrient base Essential oils Bottle (8-oz.) DIRECT MATERIALS Cost Units per Cost per Behavior Case unit variable 100 oz. $ 0.06 variable 30 OZ. $ 0.34 variable 12 bottles $0.60 Direct Materials Cost per Case $6.00 12.00 7.20 $ 25.20 Department Cost Behavior Mixing variable Filling variable DIRECT LABOR Time per Labor Rate Case per Hour 15 min. $ 20.00 6 min $15.50 21 min. Direct Labor Cost per Case $ 5.00 1.55 $ 6.55 FACTORY OVERHEAD Focus -12 - A A Aav to XX A A 21 1 ABCDe Aa Bb CcDc AaBb C AaBbccc AaB 1 Normal 1 No Spac. Heading 1 Heading 2 Title E EE E Paragraph Styles Filling variable $15.50 6 min. 21 min. 1.55 $ 6.55 FACTORY OVERHEAD Cost Behavior Total Cost Utilities mixed $ 600 Facility lease fixed 14,000 Equipment depreciation fixed 4,300 Supplies 512 $ 19,412 fixed PART A: BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS The management of Better by the Numbers would like to determine the number of cases required to break even per month Utilities cost, a part of factory overhead, is a mixed cost. Following is information gathered for the first six months of operations regarding total utilities costs: 2018 Case Production Utility Total Cost can 510 - 21 T ABbceDe AalbCcDe AaBb C AaBbcc AaB 1 Normal No Spac Heading 1 Heading 2 Title PART A: BREAK-EVEN ANALYSIS The management of Better by the Numbers would like to determine the number of cases required to break-even per month Utilities cost, a part of factory overhead, is a mixed cost. Following is information gathered for the first six months of operations regarding total utilities costs: 2018 Case Production Utility Total Cost January $ 510 February 585 March 1,200 April 1.100 590 500 800 640 May 635 1. Determine the fixed and variable portion of the utility cost using the high-low method. 2. Determine the contribution margin percase 3. Determine the fixed costs per month, including the utility fixed cost from part(1). 4. Determine the break even number of cases per month Part 8: AUGUST BUDGETS 21 - AaBb CcDc AabCcDc AaBbci AaBbcc AaB Normal 1 No Space Heading 1 Heading 2 The E Part B: AUGUST BUDGETS August demand is expected to be 1,500 cases at a sales price of $100 per case. Inventory planning information follows: Estimated finished goods inventory, Aug. 1 280 cases $12,880 Desired finished goods inventory, Aug. 31 175 cases $ 7,719 Estimated materials inventory, Aug. 1 Desired materials inventory, Aug. 314 Nutrient Base 350 02. 600 oz. Oils 280 oz. 180 oz. Bottles 100 72 Work in process inventory was negligible, so none is assumed There is no change in cost data from January. Requirements: 5. Prepare a Production Budget for August 6. Prepare a Direct Materials Purchase Budget for August 7. Prepare a Direct Labor Budget for August. (round hours required for production to the nearest whole hour) 8. Prepare a Factory Overhead Budget for August 9. Prepare a Budgeted Income Statement, including selling expenses, for August RAD 8 - Project Better by the Numbers. Word Search Vicky Rojas VR w Design Layout References Mailings Review View Boys - 12-AA AA EEEE UbX, X A A EEEEE.. bcat Normal 1 No Spac Heading 1 Heading 2 Title Part C. AUGUST VARIANCE ANALYSIS After August was completed, variance analysis needs to be performed January operating data provided the standard prices, rates, times, and quantities per case. There were 1,500 actual cases produced during August Actual Augustdata: Actual Direct Materials Price per Unit Actual Direct Materials Quantity per Case Nutrient base Essential oils Bottle (8-02.) 50.056 per oz. $0.45 per oz. $0.55 per bottle 102 31 os 12.5 bottles Actual Direct Labor Rate Actual Direct Labor Time per Case Moring $ 2025 $15.00 5.5 min The standard quantity of materials used per case was an ideal standard. Actual Variable Overhead was $305 Standard (Budgeted) Volume was 1.500 cases 0 Hi e : 9 Project Better by the Numbers - Word Search Vicky Re esign Layout References Mailings Review View Help 12 AA AB AEEE 21 SABCCDC AaBb CcDc AaBb C Aalbcd AaB XX A-D- A 3399 1 Normal 1 No Spac. Heading 1 Heading 2 Title Paragraph Essential oils Bottle (8-oz.) $0.45 per oz. $0.55 per bottle Styles 31 oz. 12.5 bottles Actual Direct Labor Rate Actual Direct Labor Time per Case Mixing Filling $ 20.25 $15.00 14.6 min. 5.5 min. The standard quantity of materials used per case was an ideal standard. Actual Variable Overhead was $305 Standard (Budgeted) Volume was 1,600 cases Requirements: 10. Determine and interpret (favorable/unfavorable) the direct materials price and quantity variances for each of the three materials 11. Determine and interpret the direct labor rate and time variances for the two departments, rounding hours to the nearest hour 12. Determine and interpret the factory overhead controllable variance 13. Determine and interpret the factory overhead volume variance te - 9 dy - 12A A Aa A X, * A-D-A E 21 AaBbCcDc ABCcDc AaBb C AaBbcc AaB 1 Normal No Spac. Heading 1 Heading 2 Title D- Styles Better By the Numbers began operations on January 1, 2018. The company produces eight- Ounce bottles of hand and body lotion called Radiant One. The lotion is sold wholesale in 12- bottle cases for $95 per case. There is a selling commission of $20 per case. January 2018 direct materials, direct labor and factory overhead costs are as follows: Nutrient base Essential oils Bottle (8-oz.) DIRECT MATERIALS Cost Units per Cost per Behavior Case unit variable 100 oz. $ 0.06 variable 30 OZ. $ 0.34 variable 12 bottles $0.60 Direct Materials Cost per Case $6.00 12.00 7.20 $ 25.20 Department Cost Behavior Mixing variable Filling variable DIRECT LABOR Time per Labor Rate Case per Hour 15 min. $ 20.00 6 min $15.50 21 min. Direct Labor Cost per Case $ 5.00 1.55 $ 6.55 FACTORY OVERHEAD Focus -12 - A A Aav to XX A A 21 1 ABCDe Aa Bb CcDc AaBb C AaBbccc AaB 1 Normal 1 No Spac. Heading 1 Heading 2 Title E EE E Paragraph Styles Filling variable $15.50 6 min. 21 min. 1.55 $ 6.55 FACTORY OVERHEAD Cost Behavior Total Cost Utilities mixed $ 600 Facility lease fixed 14,000 Equipment depreciation fixed 4,300 Supplies 512 $ 19,412 fixed PART A: BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS The management of Better by the Numbers would like to determine the number of cases required to break even per month Utilities cost, a part of factory overhead, is a mixed cost. Following is information gathered for the first six months of operations regarding total utilities costs: 2018 Case Production Utility Total Cost can 510 - 21 T ABbceDe AalbCcDe AaBb C AaBbcc AaB 1 Normal No Spac Heading 1 Heading 2 Title PART A: BREAK-EVEN ANALYSIS The management of Better by the Numbers would like to determine the number of cases required to break-even per month Utilities cost, a part of factory overhead, is a mixed cost. Following is information gathered for the first six months of operations regarding total utilities costs: 2018 Case Production Utility Total Cost January $ 510 February 585 March 1,200 April 1.100 590 500 800 640 May 635 1. Determine the fixed and variable portion of the utility cost using the high-low method. 2. Determine the contribution margin percase 3. Determine the fixed costs per month, including the utility fixed cost from part(1). 4. Determine the break even number of cases per month Part 8: AUGUST BUDGETS 21 - AaBb CcDc AabCcDc AaBbci AaBbcc AaB Normal 1 No Space Heading 1 Heading 2 The E Part B: AUGUST BUDGETS August demand is expected to be 1,500 cases at a sales price of $100 per case. Inventory planning information follows: Estimated finished goods inventory, Aug. 1 280 cases $12,880 Desired finished goods inventory, Aug. 31 175 cases $ 7,719 Estimated materials inventory, Aug. 1 Desired materials inventory, Aug. 314 Nutrient Base 350 02. 600 oz. Oils 280 oz. 180 oz. Bottles 100 72 Work in process inventory was negligible, so none is assumed There is no change in cost data from January. Requirements: 5. Prepare a Production Budget for August 6. Prepare a Direct Materials Purchase Budget for August 7. Prepare a Direct Labor Budget for August. (round hours required for production to the nearest whole hour) 8. Prepare a Factory Overhead Budget for August 9. Prepare a Budgeted Income Statement, including selling expenses, for August RAD 8 - Project Better by the Numbers. Word Search Vicky Rojas VR w Design Layout References Mailings Review View Boys - 12-AA AA EEEE UbX, X A A EEEEE.. bcat Normal 1 No Spac Heading 1 Heading 2 Title Part C. AUGUST VARIANCE ANALYSIS After August was completed, variance analysis needs to be performed January operating data provided the standard prices, rates, times, and quantities per case. There were 1,500 actual cases produced during August Actual Augustdata: Actual Direct Materials Price per Unit Actual Direct Materials Quantity per Case Nutrient base Essential oils Bottle (8-02.) 50.056 per oz. $0.45 per oz. $0.55 per bottle 102 31 os 12.5 bottles Actual Direct Labor Rate Actual Direct Labor Time per Case Moring $ 2025 $15.00 5.5 min The standard quantity of materials used per case was an ideal standard. Actual Variable Overhead was $305 Standard (Budgeted) Volume was 1.500 cases 0 Hi e : 9 Project Better by the Numbers - Word Search Vicky Re esign Layout References Mailings Review View Help 12 AA AB AEEE 21 SABCCDC AaBb CcDc AaBb C Aalbcd AaB XX A-D- A 3399 1 Normal 1 No Spac. Heading 1 Heading 2 Title Paragraph Essential oils Bottle (8-oz.) $0.45 per oz. $0.55 per bottle Styles 31 oz. 12.5 bottles Actual Direct Labor Rate Actual Direct Labor Time per Case Mixing Filling $ 20.25 $15.00 14.6 min. 5.5 min. The standard quantity of materials used per case was an ideal standard. Actual Variable Overhead was $305 Standard (Budgeted) Volume was 1,600 cases Requirements: 10. Determine and interpret (favorable/unfavorable) the direct materials price and quantity variances for each of the three materials 11. Determine and interpret the direct labor rate and time variances for the two departments, rounding hours to the nearest hour 12. Determine and interpret the factory overhead controllable variance 13. Determine and interpret the factory overhead volume variance te - 9