Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
E7-2 (Algo) Inferring Missing Amounts Based on Income Statement Relationships LO7-1 Enter the missing dollar amounts for the income statement for each of the
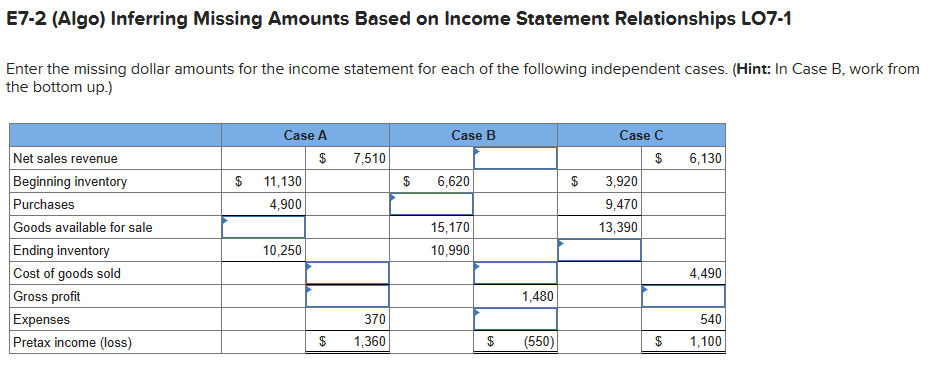
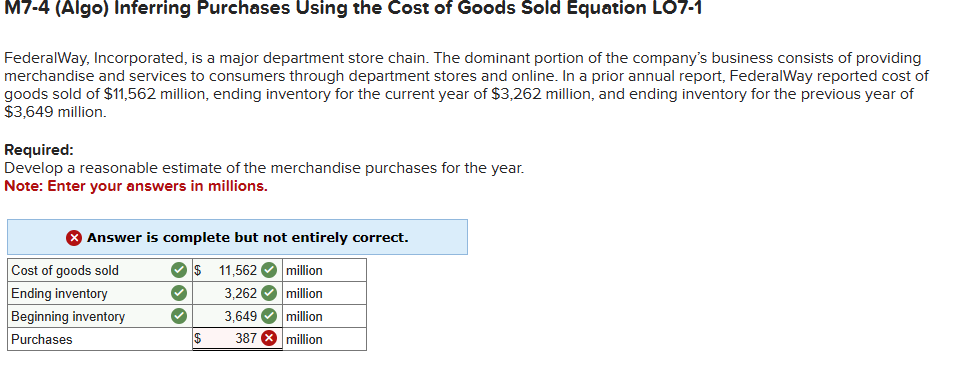
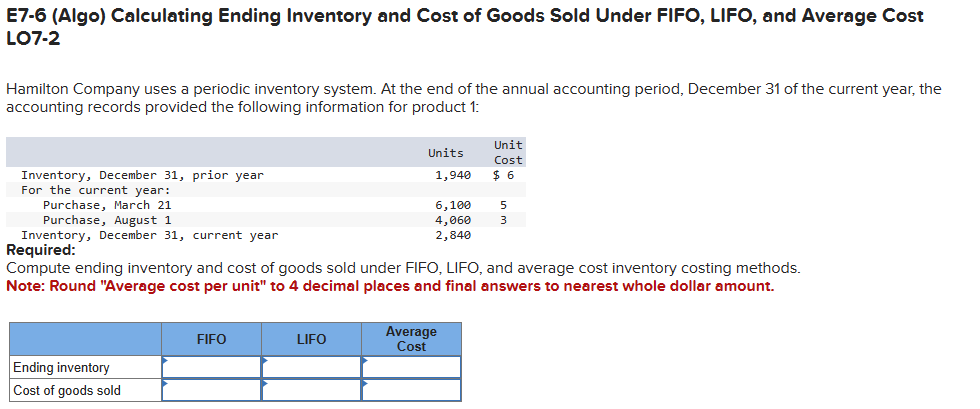

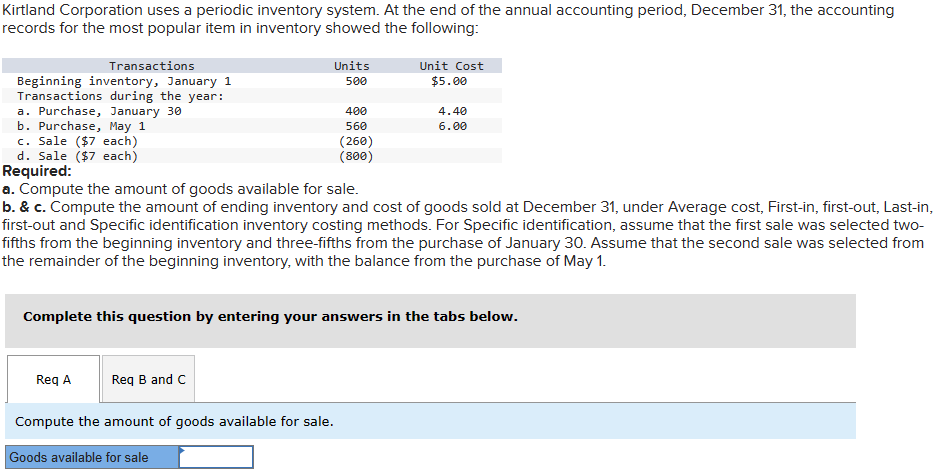
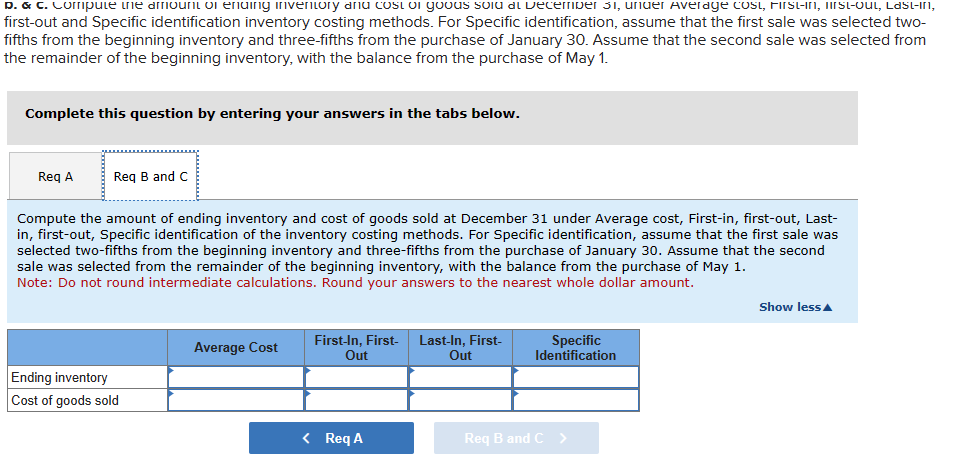
E7-2 (Algo) Inferring Missing Amounts Based on Income Statement Relationships LO7-1 Enter the missing dollar amounts for the income statement for each of the following independent cases. (Hint: In Case B, work from the bottom up.) Net sales revenue Beginning inventory Purchases Case A $ Case B 7,510 $ 11,130 $ 6,620 4,900 Goods available for sale Ending inventory 10,250 15,170 10,990 Cost of goods sold Case C $ 6,130 $ 3,920 9,470 13,390 4,490 Gross profit 1,480 Expenses 370 540 Pretax income (loss) $ 1,360 $ (550) $ 1,100 M7-4 (Algo) Inferring Purchases Using the Cost of Goods Sold Equation LO7-1 Federal Way, Incorporated, is a major department store chain. The dominant portion of the company's business consists of providing merchandise and services to consumers through department stores and online. In a prior annual report, Federal Way reported cost of goods sold of $11,562 million, ending inventory for the current year of $3,262 million, and ending inventory for the previous year of $3,649 million. Required: Develop a reasonable estimate of the merchandise purchases for the year. Note: Enter your answers in millions. Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Cost of goods sold $ 11,562 million Ending inventory 3,262 million Beginning inventory 3,649 million Purchases $ 387 million E7-6 (Algo) Calculating Ending Inventory and Cost of Goods Sold Under FIFO, LIFO, and Average Cost LO7-2 Hamilton Company uses a periodic inventory system. At the end of the annual accounting period, December 31 of the current year, the accounting records provided the following information for product 1: Inventory, December 31, prior year For the current year: Purchase, March 21 Purchase, August 1 Inventory, December 31, current year Required: Unit Units Cost 1,940 $6 6,100 5 4,060 3 2,840 Compute ending inventory and cost of goods sold under FIFO, LIFO, and average cost inventory costing methods. Note: Round "Average cost per unit" to 4 decimal places and final answers to nearest whole dollar amount. Ending inventory Cost of goods sold Average FIFO LIFO Cost E7-4 (Algo) Inferring Merchandise Purchases LO7-1 Harrison and Company is a leading retailer of casual apparel for men, women, and children. Assume that you are employed as a stock analyst and your boss has just completed a review of the new Harrison annual report. She provided you with her notes, but they are missing some information that you need. Her notes show that the ending inventory for Harrison in the current and previous years was $272,322,000 and $233,093,000, respectively. Net sales for the current year were $2,540,306,000. Cost of goods sold was $178,674,000. Income before taxes was $172,255,000. Required: Determine the amount of purchases for the year. (Hint: Use the cost of goods sold equation or the inventory T-account to solve for the needed value.) Amount of purchases Kirtland Corporation uses a periodic inventory system. At the end of the annual accounting period, December 31, the accounting records for the most popular item in inventory showed the following: Transactions Beginning inventory, January 1 Transactions during the year: a. Purchase, January 30 b. Purchase, May 1 c. Sale ($7 each) d. Sale ($7 each) Required: Units 500 Unit Cost $5.00 400 560 4.40 6.00 (260) (800) a. Compute the amount of goods available for sale. b. & c. Compute the amount of ending inventory and cost of goods sold at December 31, under Average cost, First-in, first-out, Last-in, first-out and Specific identification inventory costing methods. For Specific identification, assume that the first sale was selected two- fifths from the beginning inventory and three-fifths from the purchase of January 30. Assume that the second sale was selected from the remainder of the beginning inventory, with the balance from the purchase of May 1. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A Req B and C Compute the amount of goods available for sale. Goods available for sale D. & C. Compute the amount of ending inventory and cost of goods sold at December 31, under Average cost, FIRST-IN, MISt-Out, Last-in, first-out and Specific identification inventory costing methods. For Specific identification, assume that the first sale was selected two- fifths from the beginning inventory and three-fifths from the purchase of January 30. Assume that the second sale was selected from the remainder of the beginning inventory, with the balance from the purchase of May 1. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A Req B and C Compute the amount of ending inventory and cost of goods sold at December 31 under Average cost, First-in, first-out, Last- in, first-out, Specific identification of the inventory costing methods. For Specific identification, assume that the first sale was selected two-fifths from the beginning inventory and three-fifths from the purchase of January 30. Assume that the second sale was selected from the remainder of the beginning inventory, with the balance from the purchase of May 1. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount. Average Cost First-In, First- Out Last-In, First- Out Specific Identification Ending inventory Cost of goods sold < Req A Req B and C > Show less
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
FIFO Method Beginning inventory 500 units at 5 per unit 2500 Purchase January 30 400 units at 440 per unit 1760 Purchase May 1 560 units at 6 per unit 3360 Total goods available 500 400 560 1460 units ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


