Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
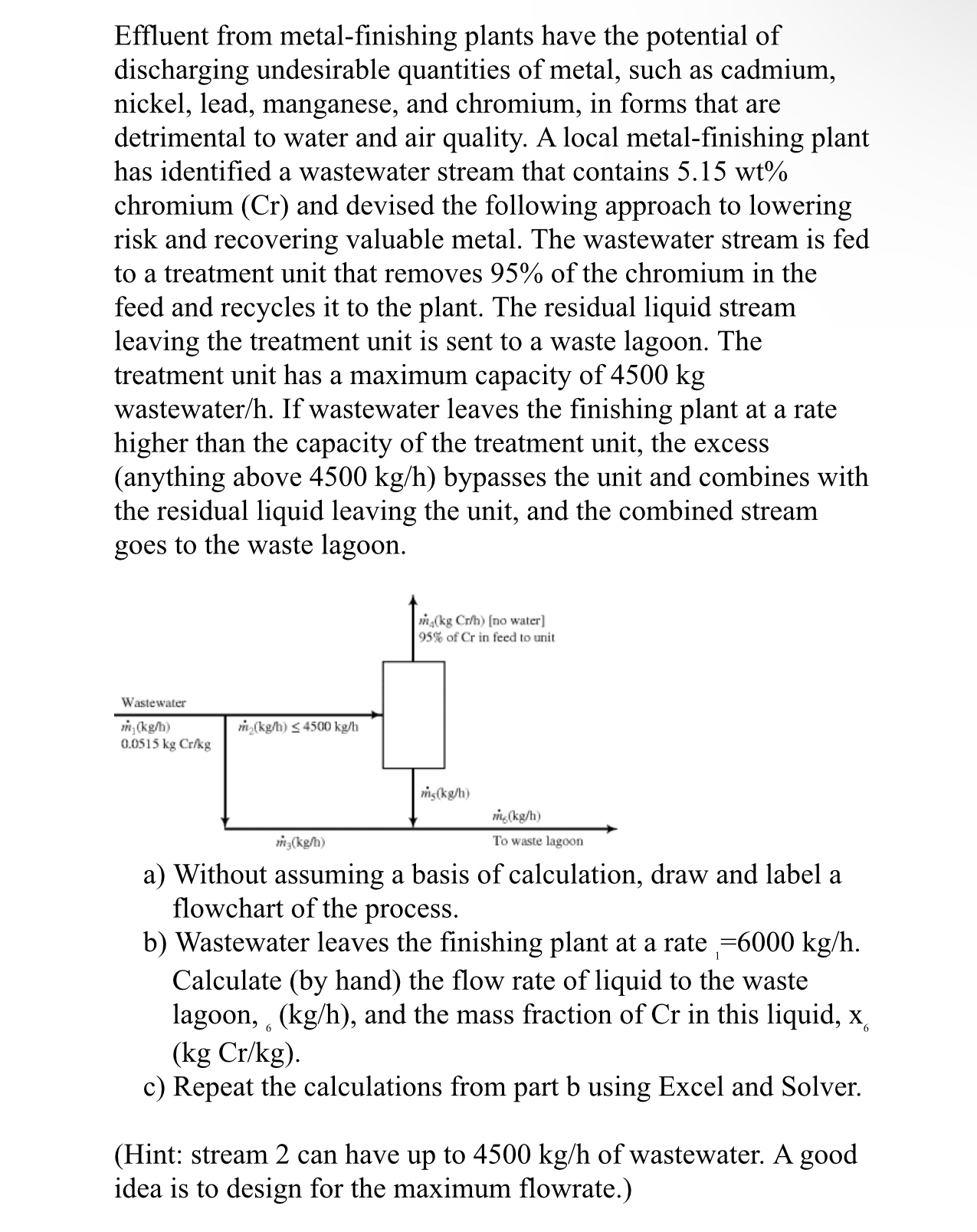
Effluent from metal - finishing plants have the potential of discharging undesirable quantities of metal, such as cadmium, nickel, lead, manganese, and chromium, in forms
Effluent from metalfinishing plants have the potential of discharging undesirable quantities of metal, such as cadmium, nickel, lead, manganese, and chromium, in forms that are detrimental to water and air quality. A local metalfinishing plant has identified a wastewater stream that contains chromium and devised the following approach to lowering risk and recovering valuable metal. The wastewater stream is fed to a treatment unit that removes of the chromium in the feed and recycles it to the plant. The residual liquid stream leaving the treatment unit is sent to a waste lagoon. The treatment unit has a maximum capacity of wastewater If wastewater leaves the finishing plant at a rate higher than the capacity of the treatment unit, the excess anything above bypasses the unit and combines with the residual liquid leaving the unit, and the combined stream goes to the waste lagoon.
a Without assuming a basis of calculation, draw and label a flowchart of the process.
b Wastewater leaves the finishing plant at a rate Calculate by hand the flow rate of liquid to the waste lagoon, and the mass fraction of in this liquid,
c Repeat the calculations from part b using Excel and Solver.
Hint: stream can have up to of wastewater. A good idea is to design for the maximum flowrate.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


