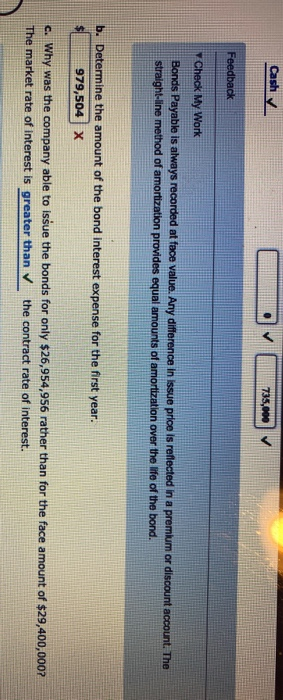
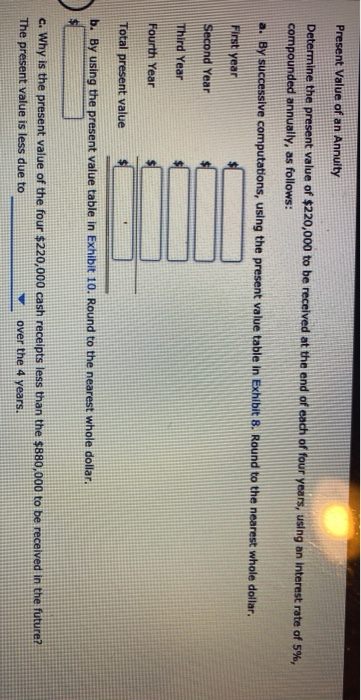
Entries for Issuing Bonds and Amortizing Discount by Straight-Line Method On the first day of its fiscal year, Chin Company issued $29,400,000 of five-year, 5% bonds to winance its operations of producing and selling home improvement products. Interest is payable semiannually. The bonds were issued at a market (effective) Interest rate of 7%, resulting in Chin Company receiving cash of $26,954,956. a. Journalize the entries to record the following: 1. Issuance of the bonds. 2. First semiannual interest payment. The bond discount amortization, using the straight-line method, is combined with the semiannual interest payment. (Round your answer to the nearest dollar.) 3. Second semiannual interest payment. The bond discount amortization, using the straight-line method, is combined with the semiannual interest payment. (Round your answer to the nearest dollar.) For a compound transaction, if an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. Round your answers to the nearest dollar Cash 26,954,956 Discount on Bonds Payable 2,445,044 Bonds Payable 9,400,000 Interest Expense 979,504 Discount on Bonds Payable Cash 735,000 Interest Expense Discount on Bonds Payable 244.504 Cash Ov 735,000 Feedback Check My Work Bonds Payable is always recorded at face value. Any difference in issue price is reflected in a premium or discount account. The straight-line method of amortization provides equal amounts of amortization over the life of the bond. b. Determine the amount of the bond interest expense for the first year. 979,504x c. Why was the company able to issue the bonds for only $26,954,956 rather than for the face amount of $29,400,000? The market rate of interest is greater than the contract rate of interest. Present Value of an Annuity Determine the present value of $220,000 to be received at the end of each of four years, using an interest rate of 5%, compounded annually, as follows: a. By successive computations, using the present value table in Exhibit 8. Round to the nearest whole dollar. First year Second Year Third Year Fourth Year Total present value b. By using the present value table in Exhibit 10. Round to the nearest whole dollar. c. Why is the present value of the four $220,000 cash receipts less than the $880,000 to be received in the future? The present value is less due to over the 4 years