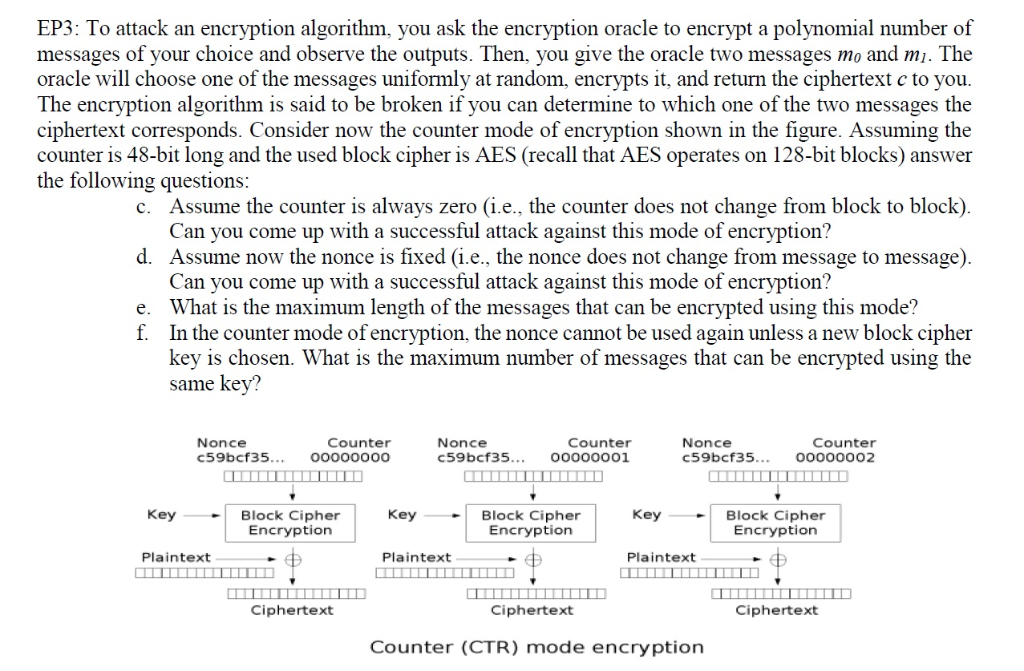
EP3: To attack an encryption algorithm, you ask the encryption oracle to encrypt a polynomial number of messages of your choice and observe the outputs. Then, you give the oracle two messages mo and mi. The oracle will choose one of the messages uniformly at random, encrypts it, and return the ciphertext c to you The encryption algorithm is said to be broken if you can determine to which one of the two messages the ciphertext corresponds. Consider now the counter mode of encryption shown in the figure. Assuming the counter is 48-bit long and the used block cipher is AES (recall that AES operates on 128-bit blocks) answer the following questions: c. Assume the counter is always zero (i.e., the counter does not change from block to block) Can you come up with a successful attack against this mode of encryption? d. Assume now the nonce is fixed (i.e., the nonce does not change from message to message) Can you come up with a successful attack against this mode of encryption? e. What is the maximum length of the messages that can be encrypted using this mode? f. In the counter mode of encryption, the nonce cannot be used again unless a new block cipher kev is chosen. What is the maximum number of messages that can be encrvpted using the same key? Nonce c59bcf35 Counter oo000000 Nonce c59bcf35... oo0oooo1 Counter Nonce c59bcf35... oo0o0002 Counter Block Cipher Encryption Block Cipher Encryption Ke Key Key Block Cipher Encryption Plaintext Plaintext Plaintext Ciphertext Ciphertext Ciphertext Counter (CTR) mode encryption EP3: To attack an encryption algorithm, you ask the encryption oracle to encrypt a polynomial number of messages of your choice and observe the outputs. Then, you give the oracle two messages mo and mi. The oracle will choose one of the messages uniformly at random, encrypts it, and return the ciphertext c to you The encryption algorithm is said to be broken if you can determine to which one of the two messages the ciphertext corresponds. Consider now the counter mode of encryption shown in the figure. Assuming the counter is 48-bit long and the used block cipher is AES (recall that AES operates on 128-bit blocks) answer the following questions: c. Assume the counter is always zero (i.e., the counter does not change from block to block) Can you come up with a successful attack against this mode of encryption? d. Assume now the nonce is fixed (i.e., the nonce does not change from message to message) Can you come up with a successful attack against this mode of encryption? e. What is the maximum length of the messages that can be encrypted using this mode? f. In the counter mode of encryption, the nonce cannot be used again unless a new block cipher kev is chosen. What is the maximum number of messages that can be encrvpted using the same key? Nonce c59bcf35 Counter oo000000 Nonce c59bcf35... oo0oooo1 Counter Nonce c59bcf35... oo0o0002 Counter Block Cipher Encryption Block Cipher Encryption Ke Key Key Block Cipher Encryption Plaintext Plaintext Plaintext Ciphertext Ciphertext Ciphertext Counter (CTR) mode encryption







