
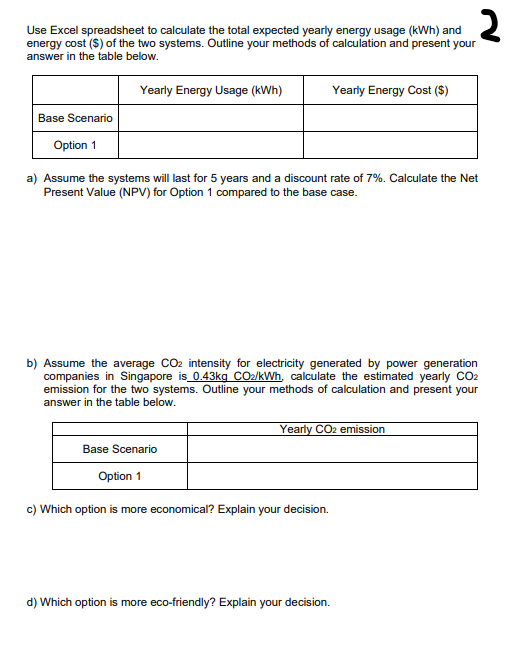

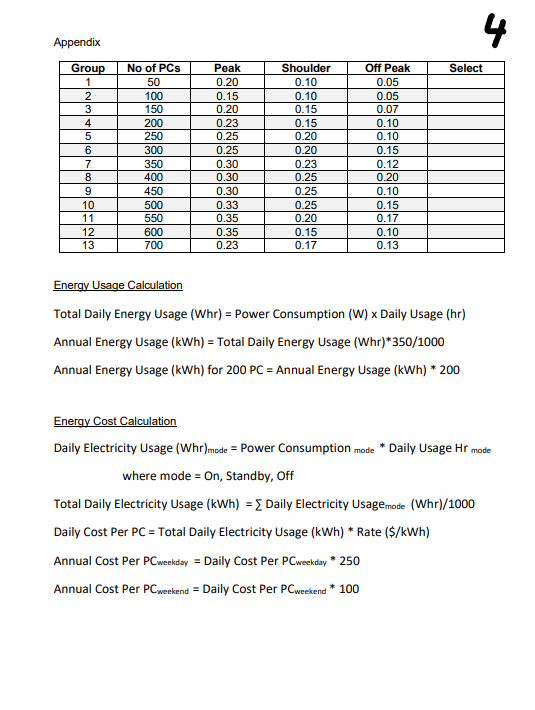

EQUIPMENT 1. Microsoft Excel 2. OptiPlex TM GX280 Mini Tower Datasheet 3. 1704FPVt Screen Datasheet 4. Precision M20 Datasheet Problem Statement: A Case Study on Energy Efficiency With effect from 1 July 2016, electricity consumers in Singapore pay a standard flat electricity tariff for their electricity usage. In an effort to encourage energy saving and to reduce energy demand during peak hours (i.e. reduce peak demand), the Energy Market Authority of Singapore decides to mandate electricity tier tariff package to be offered to all electricity consumers in Singapore by 2020. The objective of tier tariff is to encourage electricity consumers to use electricity during off-peak hours whenever possible. The tier tariff hour structure is tabulated as follows. Please see appendix for tariff rates for each respective group Peak Monday-Friday 2pm to 8pm Shoulder Monday-Friday 7am to 2pm, 8pm to 10pm Saturday-Sunday 7am to 10pm Off Peak All Other Times The School of Engineering is planning to upgrade all the PCs in the laboratories. Please see appendix for the quantity of PCs in the laboratories for each respective group. The options are: Base Scenario (business as usual) OptiPlex GX280 Mini Tower and 1704FPVt Screen (Capital Cost $1500 per computer, Data Sheet provided) Option 1 (saving option if cost effective) Precision M20 laptop (Capital Cost $1600 per computer, Data Sheet provided) The computers will operate 350 days per year (250 weekdays and 100 weekend days). See data sheets provided (see Additional Information.pdf) for energy usage in the three modes of operation namely, On, Standby and Off in table below. Mode of Operation Hours Operating On (Max Power) 10am-6pm (8 hrs per day) Standby (Low Power) 8am-10am & 6pm-8pm (4 hrs per day) Off 8pm-8am (12 hrs per day) 2 Use Excel spreadsheet to calculate the total expected yearly energy usage (kWh) and energy cost ($) of the two systems. Outline your methods of calculation and present your answer in the table below. Yearly Energy Usage (kWh) Yearly Energy Cost ($) Base Scenario Option 1 a) Assume the systems will last for 5 years and a discount rate of 7%. Calculate the Net Present Value (NPV) for Option 1 compared to the base case. b) Assume the average CO2 intensity for electricity generated by power generation companies in Singapore is 0.43kg CO2/kWh, calculate the estimated yearly CO2 emission for the two systems. Outline your methods of calculation and present your answer in the table below. Yearly CO2 emission Base Scenario Option 1 c) Which option is more economical? Explain your decision. d) Which option is more eco-friendly? Explain your decision. e) The electricity prices are expected to rise by 10% per year for the next 5 years. Recalculate the NPV of Option 1 compared to the base case, on this basis. 3 f) In one paragraph, summarise your findings and provide a recommendation with a brief explanation 4 Appendix Group Off Peak Select 1 0.05 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 No of PCs 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600 700 Peak 0.20 0.15 0.20 0.23 0.25 0.25 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.33 0.35 0.35 0.23 Shoulder 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.15 0.20 0.20 0.23 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.17 0.05 0.07 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.12 0.20 0.10 0.15 0.17 0.10 0.13 Energy Usage Calculation Total Daily Energy Usage (Whr) = Power Consumption (W) x Daily Usage (hr) Annual Energy Usage (kWh) = Total Daily Energy Usage (Whr)*350/1000 Annual Energy Usage (kWh) for 200 PC = Annual Energy Usage (kWh)* 200 Energy Cost Calculation Daily Electricity Usage (Whr)mode = Power Consumption mode * Daily Usage Hr mode where mode = On, Standby, Off Total Daily Electricity Usage (kWh) = { Daily Electricity Usagemode (Whr)/1000 Daily Cost Per PC = Total Daily Electricity Usage (kWh)* Rate ($/kWh) Annual Cost Per PCweekday = Daily Cost Per PCweekday 250 Annual Cost Per PCweekend = Daily Cost Per PCweekend * 100 5 Net Present Value Net present value (NPV) is the difference between the present value of cash inflows and the present value of cash outflows over a period of time. NPV is used in capital budgeting to analyse the profitability of a projected investment or project. The NPV is given by: NPV = C + PWF (1.f.n) x S PWF(i,f, n) = (1+f) (1+i) (1+i) (1+f) where, C = capital investment, S = annual saving, n = time period in years, i = discount rate and f = inflation rate. Both rates are percentages and their values are expressed between 0 and 1. Example 10% = 0.1 EQUIPMENT 1. Microsoft Excel 2. OptiPlex TM GX280 Mini Tower Datasheet 3. 1704FPVt Screen Datasheet 4. Precision M20 Datasheet Problem Statement: A Case Study on Energy Efficiency With effect from 1 July 2016, electricity consumers in Singapore pay a standard flat electricity tariff for their electricity usage. In an effort to encourage energy saving and to reduce energy demand during peak hours (i.e. reduce peak demand), the Energy Market Authority of Singapore decides to mandate electricity tier tariff package to be offered to all electricity consumers in Singapore by 2020. The objective of tier tariff is to encourage electricity consumers to use electricity during off-peak hours whenever possible. The tier tariff hour structure is tabulated as follows. Please see appendix for tariff rates for each respective group Peak Monday-Friday 2pm to 8pm Shoulder Monday-Friday 7am to 2pm, 8pm to 10pm Saturday-Sunday 7am to 10pm Off Peak All Other Times The School of Engineering is planning to upgrade all the PCs in the laboratories. Please see appendix for the quantity of PCs in the laboratories for each respective group. The options are: Base Scenario (business as usual) OptiPlex GX280 Mini Tower and 1704FPVt Screen (Capital Cost $1500 per computer, Data Sheet provided) Option 1 (saving option if cost effective) Precision M20 laptop (Capital Cost $1600 per computer, Data Sheet provided) The computers will operate 350 days per year (250 weekdays and 100 weekend days). See data sheets provided (see Additional Information.pdf) for energy usage in the three modes of operation namely, On, Standby and Off in table below. Mode of Operation Hours Operating On (Max Power) 10am-6pm (8 hrs per day) Standby (Low Power) 8am-10am & 6pm-8pm (4 hrs per day) Off 8pm-8am (12 hrs per day) 2 Use Excel spreadsheet to calculate the total expected yearly energy usage (kWh) and energy cost ($) of the two systems. Outline your methods of calculation and present your answer in the table below. Yearly Energy Usage (kWh) Yearly Energy Cost ($) Base Scenario Option 1 a) Assume the systems will last for 5 years and a discount rate of 7%. Calculate the Net Present Value (NPV) for Option 1 compared to the base case. b) Assume the average CO2 intensity for electricity generated by power generation companies in Singapore is 0.43kg CO2/kWh, calculate the estimated yearly CO2 emission for the two systems. Outline your methods of calculation and present your answer in the table below. Yearly CO2 emission Base Scenario Option 1 c) Which option is more economical? Explain your decision. d) Which option is more eco-friendly? Explain your decision. e) The electricity prices are expected to rise by 10% per year for the next 5 years. Recalculate the NPV of Option 1 compared to the base case, on this basis. 3 f) In one paragraph, summarise your findings and provide a recommendation with a brief explanation 4 Appendix Group Off Peak Select 1 0.05 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 No of PCs 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600 700 Peak 0.20 0.15 0.20 0.23 0.25 0.25 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.33 0.35 0.35 0.23 Shoulder 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.15 0.20 0.20 0.23 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.17 0.05 0.07 0.10 0.10 0.15 0.12 0.20 0.10 0.15 0.17 0.10 0.13 Energy Usage Calculation Total Daily Energy Usage (Whr) = Power Consumption (W) x Daily Usage (hr) Annual Energy Usage (kWh) = Total Daily Energy Usage (Whr)*350/1000 Annual Energy Usage (kWh) for 200 PC = Annual Energy Usage (kWh)* 200 Energy Cost Calculation Daily Electricity Usage (Whr)mode = Power Consumption mode * Daily Usage Hr mode where mode = On, Standby, Off Total Daily Electricity Usage (kWh) = { Daily Electricity Usagemode (Whr)/1000 Daily Cost Per PC = Total Daily Electricity Usage (kWh)* Rate ($/kWh) Annual Cost Per PCweekday = Daily Cost Per PCweekday 250 Annual Cost Per PCweekend = Daily Cost Per PCweekend * 100 5 Net Present Value Net present value (NPV) is the difference between the present value of cash inflows and the present value of cash outflows over a period of time. NPV is used in capital budgeting to analyse the profitability of a projected investment or project. The NPV is given by: NPV = C + PWF (1.f.n) x S PWF(i,f, n) = (1+f) (1+i) (1+i) (1+f) where, C = capital investment, S = annual saving, n = time period in years, i = discount rate and f = inflation rate. Both rates are percentages and their values are expressed between 0 and 1. Example 10% = 0.1











