Error tech has noticed a significant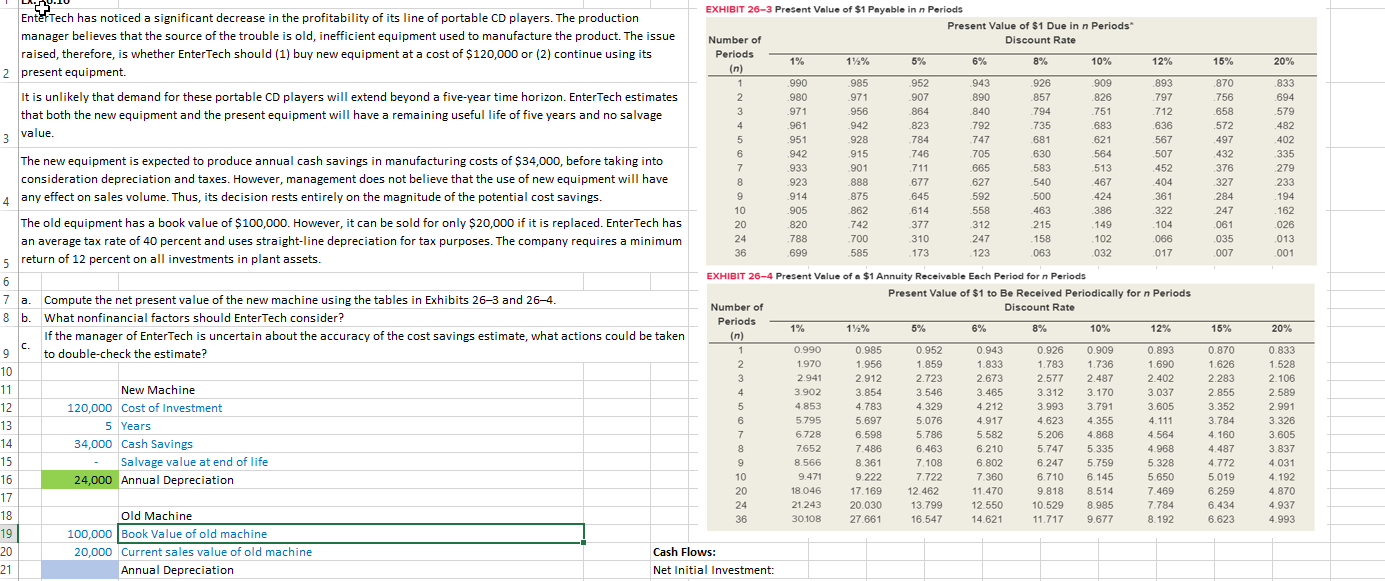
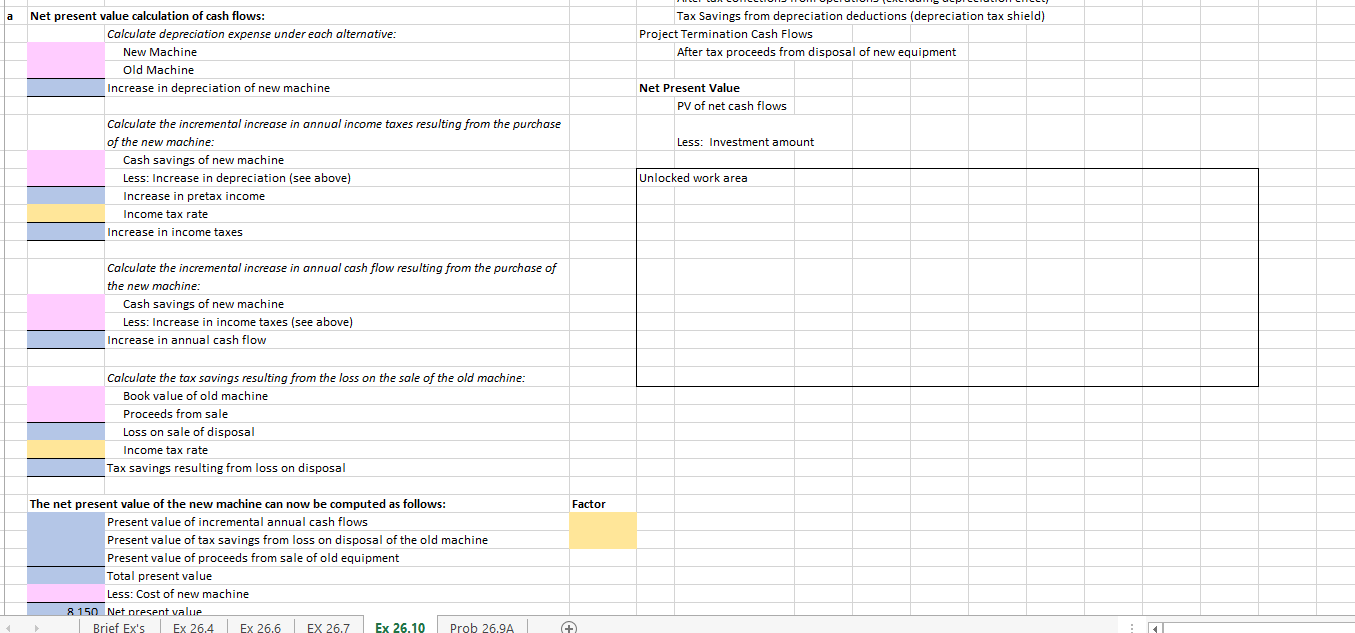
15% 20% 870 756 658 572 497 432 376 327 284 247 .061 .035 007 .833 .694 .579 .482 402 335 279 233 194 . 162 .026 013 001 742 EnterTech has noticed a significant decrease in the profitability of its line of portable CD players. The production EXHIBIT 26-3 Present Value of $1 Payable in n Periods manager believes that the source of the trouble is old, inefficient equipment used to manufacture the product. The issue Present Value of $1 Due in n Periods Number of Discount Rate raised, therefore, is whether EnterTech should (1) buy new equipment at a cost of $120,000 or (2) continue using its Periods 1% 1%% 5% 6% 8% 2 present equipment. 10% 12% (n) 1 990 985 952 943 .926 909 893 It is unlikely that demand for these portable CD players will extend beyond a five-year time horizon. EnterTech estimates 2 980 .971 .907 .890 .857 826 797 that both the new equipment and the present equipment will have a remaining useful life of five years and no salvage 3 .971 .956 864 .840 794 751 .712 4 961 942 823 792 .735 3 value. 683 636 5 951 928 784 747 .681 621 567 6 The new equipment is expected to produce annual cash savings in manufacturing costs of $34,000, before taking into 942 915 746 705 630 564 507 7 933 901 711 .665 .583 513 consideration depreciation and taxes. However, management does not believe that the use of new equipment will have 452 8 .923 .888 677 .627 540 467 404 4 any effect on sales volume. Thus, its decision rests entirely on the magnitude of the potential cost savings. 9 .914 .875 .645 592 500 424 361 10 905 862 614 558 .463 386 322 The old equipment has a book value of $100,000. However, it can be sold for only $20,000 if it is replaced. EnterTech has 20 .820 377 312 215 .149 104 an average tax rate of 40 percent and uses straight-line depreciation for tax purposes. The company requires a minimum 24 .788 700 310 247 158 102 066 36 699 5 return of 12 percent on all investments in plant assets. 585 173 123 063 032 017 6 EXHIBIT 26-4 Present Value of a $1 Annuity Receivable Each Period for n Periods 7 a. Compute the net present value of the new machine using the tables in Exhibits 263 and 26-4. Present Value of $1 to Be Received Periodically for n Periods Number of Discount Rate 8 b. What nonfinancial factors should EnterTech consider? Periods If the manager of EnterTech is uncertain about the accuracy of the cost savings estimate, what actions could be taken 1% 11% 5% 6% 8% (n) 10% 12% C. 9 to double-check the estimate? 1 0.990 0.985 0.952 0.943 0.926 0.909 0.893 10 2 1.970 1.956 1.859 1.833 1.783 1.736 1.690 3 2.941 2.912 2.723 2.673 11 2.577 2.487 2.402 New Machine 4 3.902 3.854 3.546 3.465 3.312 3.170 3.037 12 120,000 Cost of Investment 5 4.853 4.783 4.329 4.212 3.993 3.791 3.605 13 5 Years 6 5.795 5.697 5.076 4.917 4.623 4.355 4.111 7 6.728 14 34,000 Cash Savings 6.598 5.786 5.582 5.206 4.868 4.564 8 7652 7.486 6.463 6.210 5.747 5.335 4.968 15 Salvage value at end of life 9 8.566 8.361 7.108 6.802 6.247 5.759 5.328 16 24,000 Annual Depreciation 10 9.471 9.222 7.722 7.360 6.710 6.145 5.650 17 20 18.046 17.169 12.462 11.470 9.818 8.514 7.469 24 21.243 20.030 13.799 18 12.550 10.529 8.985 Old Machine 7.784 36 30.108 27.661 16.547 14.621 11.717 9.677 8.192 19 100,000 Book Value of old machine 20 20,000 Current sales value of old machine Cash Flows: 21 Annual Depreciation Net Initial Investment: 15% 20% 0.870 1.626 2.283 2.855 3.352 3.784 4.160 4.487 4.772 5.019 6.259 6.434 6.623 0.833 1.528 2.106 2.589 2.991 3.326 3.605 3.837 4.031 4.192 4.870 4.937 4.993 a Net present value calculation of cash flows: Calculate depreciation expense under each alternative: New Machine Old Machine Increase in depreciation of new machine Tax Savings from depreciation deductions (depreciation tax shield) Project Termination Cash Flows After tax proceeds from disposal of new equipment Net Present Value PV of net cash flows Less: Investment amount Calculate the incremental increase in annual income taxes resulting from the purchase of the new machine: Cash savings of new machine Less: Increase in depreciation (see above) Increase in pretax income Income tax rate Increase in income taxes Unlocked work area Calculate the incremental increase in annual cash flow resulting from the purchase of the new machine: Cash savings of new machine Less: Increase in income taxes (see above) Increase in annual cash flow Calculate the tax savings resulting from the loss on the sale of the old machine: Book value of old machine Proceeds from sale Loss on sale of disposal Income tax rate Tax savings resulting from loss on disposal Factor The net present value of the new machine can now be computed as follows: Present value of incremental annual cash flows Present value of tax savings from loss on disposal of the old machine Present value of proceeds from sale of old equipment Total present value Less: Cost of new machine 8150 Net present value Brief Ex's Ex 26,4 Ex 26,6 EX 26.7 Ex 26.10 Prob 26.9A + 15% 20% 870 756 658 572 497 432 376 327 284 247 .061 .035 007 .833 .694 .579 .482 402 335 279 233 194 . 162 .026 013 001 742 EnterTech has noticed a significant decrease in the profitability of its line of portable CD players. The production EXHIBIT 26-3 Present Value of $1 Payable in n Periods manager believes that the source of the trouble is old, inefficient equipment used to manufacture the product. The issue Present Value of $1 Due in n Periods Number of Discount Rate raised, therefore, is whether EnterTech should (1) buy new equipment at a cost of $120,000 or (2) continue using its Periods 1% 1%% 5% 6% 8% 2 present equipment. 10% 12% (n) 1 990 985 952 943 .926 909 893 It is unlikely that demand for these portable CD players will extend beyond a five-year time horizon. EnterTech estimates 2 980 .971 .907 .890 .857 826 797 that both the new equipment and the present equipment will have a remaining useful life of five years and no salvage 3 .971 .956 864 .840 794 751 .712 4 961 942 823 792 .735 3 value. 683 636 5 951 928 784 747 .681 621 567 6 The new equipment is expected to produce annual cash savings in manufacturing costs of $34,000, before taking into 942 915 746 705 630 564 507 7 933 901 711 .665 .583 513 consideration depreciation and taxes. However, management does not believe that the use of new equipment will have 452 8 .923 .888 677 .627 540 467 404 4 any effect on sales volume. Thus, its decision rests entirely on the magnitude of the potential cost savings. 9 .914 .875 .645 592 500 424 361 10 905 862 614 558 .463 386 322 The old equipment has a book value of $100,000. However, it can be sold for only $20,000 if it is replaced. EnterTech has 20 .820 377 312 215 .149 104 an average tax rate of 40 percent and uses straight-line depreciation for tax purposes. The company requires a minimum 24 .788 700 310 247 158 102 066 36 699 5 return of 12 percent on all investments in plant assets. 585 173 123 063 032 017 6 EXHIBIT 26-4 Present Value of a $1 Annuity Receivable Each Period for n Periods 7 a. Compute the net present value of the new machine using the tables in Exhibits 263 and 26-4. Present Value of $1 to Be Received Periodically for n Periods Number of Discount Rate 8 b. What nonfinancial factors should EnterTech consider? Periods If the manager of EnterTech is uncertain about the accuracy of the cost savings estimate, what actions could be taken 1% 11% 5% 6% 8% (n) 10% 12% C. 9 to double-check the estimate? 1 0.990 0.985 0.952 0.943 0.926 0.909 0.893 10 2 1.970 1.956 1.859 1.833 1.783 1.736 1.690 3 2.941 2.912 2.723 2.673 11 2.577 2.487 2.402 New Machine 4 3.902 3.854 3.546 3.465 3.312 3.170 3.037 12 120,000 Cost of Investment 5 4.853 4.783 4.329 4.212 3.993 3.791 3.605 13 5 Years 6 5.795 5.697 5.076 4.917 4.623 4.355 4.111 7 6.728 14 34,000 Cash Savings 6.598 5.786 5.582 5.206 4.868 4.564 8 7652 7.486 6.463 6.210 5.747 5.335 4.968 15 Salvage value at end of life 9 8.566 8.361 7.108 6.802 6.247 5.759 5.328 16 24,000 Annual Depreciation 10 9.471 9.222 7.722 7.360 6.710 6.145 5.650 17 20 18.046 17.169 12.462 11.470 9.818 8.514 7.469 24 21.243 20.030 13.799 18 12.550 10.529 8.985 Old Machine 7.784 36 30.108 27.661 16.547 14.621 11.717 9.677 8.192 19 100,000 Book Value of old machine 20 20,000 Current sales value of old machine Cash Flows: 21 Annual Depreciation Net Initial Investment: 15% 20% 0.870 1.626 2.283 2.855 3.352 3.784 4.160 4.487 4.772 5.019 6.259 6.434 6.623 0.833 1.528 2.106 2.589 2.991 3.326 3.605 3.837 4.031 4.192 4.870 4.937 4.993 a Net present value calculation of cash flows: Calculate depreciation expense under each alternative: New Machine Old Machine Increase in depreciation of new machine Tax Savings from depreciation deductions (depreciation tax shield) Project Termination Cash Flows After tax proceeds from disposal of new equipment Net Present Value PV of net cash flows Less: Investment amount Calculate the incremental increase in annual income taxes resulting from the purchase of the new machine: Cash savings of new machine Less: Increase in depreciation (see above) Increase in pretax income Income tax rate Increase in income taxes Unlocked work area Calculate the incremental increase in annual cash flow resulting from the purchase of the new machine: Cash savings of new machine Less: Increase in income taxes (see above) Increase in annual cash flow Calculate the tax savings resulting from the loss on the sale of the old machine: Book value of old machine Proceeds from sale Loss on sale of disposal Income tax rate Tax savings resulting from loss on disposal Factor The net present value of the new machine can now be computed as follows: Present value of incremental annual cash flows Present value of tax savings from loss on disposal of the old machine Present value of proceeds from sale of old equipment Total present value Less: Cost of new machine 8150 Net present value Brief Ex's Ex 26,4 Ex 26,6 EX 26.7 Ex 26.10 Prob 26.9A +








