Question
Estimate K based on the data Differential equation: dL/dt = K(1-L) using separation of variables 1. We let L (t) be the fraction of the
Estimate K based on the data
Differential equation: dL/dt = K(1-L) using separation of variables
1. We let L(t) be the fraction of the list already committed to memory at time t. So L=0 corresponds to knowing none of the list, and L=1 corresponds to knowing the entire list. The differential equation is dL/dt=k(1-L). Compile your data in a graph with t , the amount of time spent studying, on the horizontal axis, and L, the fraction of the list learned, on the vertical axis.
2. Use this data to approximate your personal k-value and compare your data with the predictions of the model. You may use numeric or analytic methods, but be sure to carefully explain your work. Estimate how long it would take you to learn a list of 50 and 100 three-digit numbers.
3. Repeat the process in Part 1 on two of the other lists and compute your k-value on these lists. Is your personal k-value really constant, or does it improve with practice? If k does improve with practice, how would you modify the model to include this? list 2 and 3 repeat to estimate K.
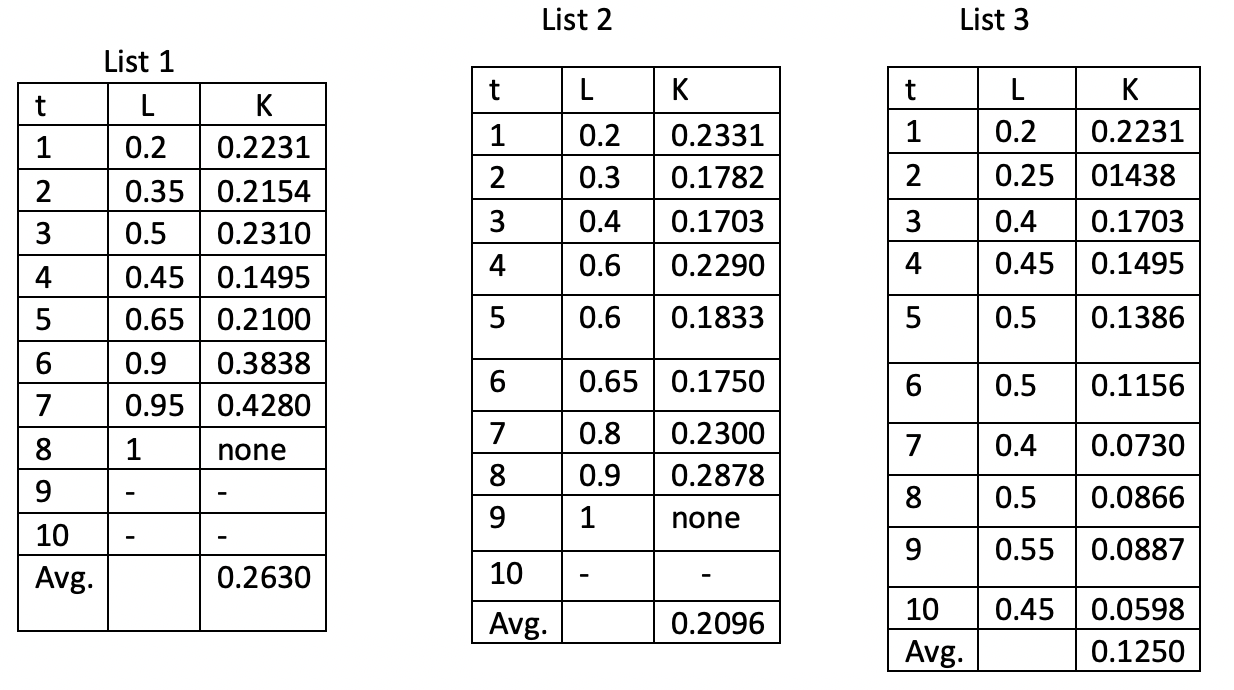
1 23 45 6 7 8 9 10 Avg. List 1 L 0.2 K 0.2231 0.2154 0.2310 0.1495 0.2100 0.9 0.3838 0.95 0.4280 1 none 0.35 0.5 0.45 0.65 0.2630 t 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 List 2 10 Avg. L K 0.2 0.2331 0.3 0.1782 0.4 0.1703 0.6 0.2290 0.6 0.1833 0.65 0.8 0.9 1 - 0.1750 0.2300 0.2878 none 0.2096 t 1 2 List 3 6 7 8 9 L 0.2 0.25 3 0.4 0.1703 4 0.45 0.1495 5 0.5 0.1386 0.5 0.4 0.5 0.55 0.45 10 Avg. K 0.2231 01438 0.1156 0.0730 0.0866 0.0887 0.0598 0.1250
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (145 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


