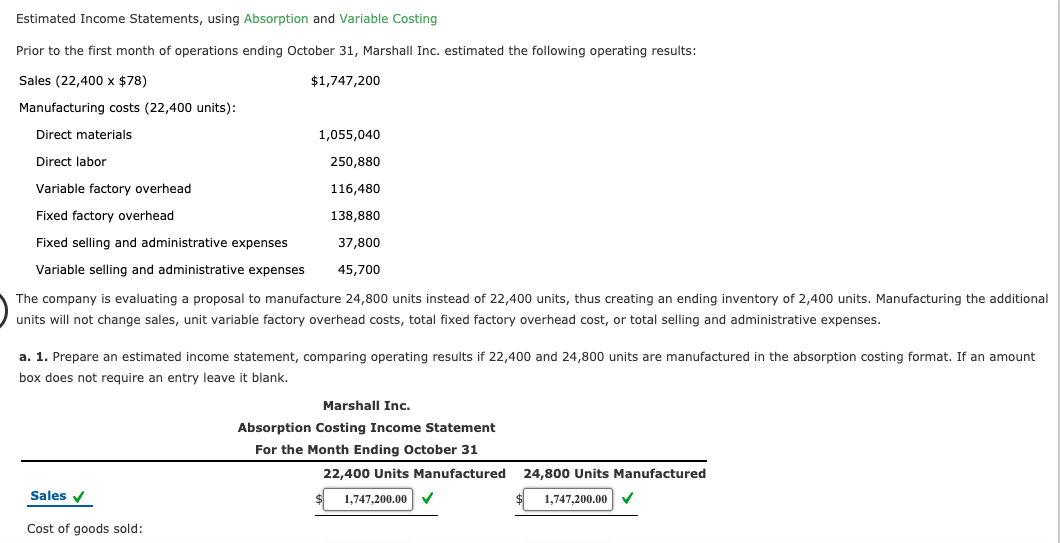
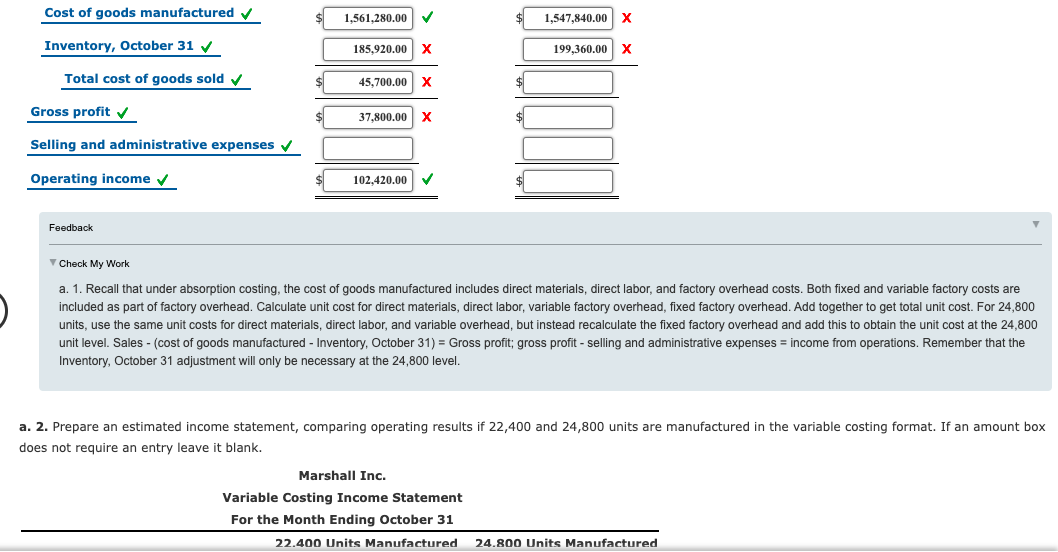

Estimated Income Statements, using Absorption and Variable Costing Prior to the first month of operations ending October 31, Marshall Inc. estimated the following operating results: $1,747,200 Sales (22,400 x $78) Manufacturing costs (22,400 units): Direct materials 1,055,040 Direct labor 250,880 Variable factory overhead 116,480 Fixed factory overhead 138,880 Fixed selling and administrative expenses 37,800 Variable selling and administrative expenses 45,700 The company is evaluating a proposal to manufacture 24,800 units instead of 22,400 units, thus creating an ending inventory of 2,400 units. Manufacturing the additional units will not change sales, unit variable factory overhead costs, total fixed factory overhead cost, or total selling and administrative expenses. a. 1. Prepare an estimated income statement, comparing operating results if 22,400 and 24,800 units are manufactured in the absorption costing format. If an amount box does not require an entry leave it blank. Marshall Inc. Absorption Costing Income Statement For the Month Ending October 31 22,400 Units Manufactured 24,800 Units Manufactured Sales 1,747,200.00 1,747,200.00 Cost of goods sold: Cost of goods manufactured 1,561,280.00 1,547,840.00 X Inventory, October 31 185,920.00 199,360.00x Total cost of goods sold 45,700.00 X Gross profit 37,800.00 X Selling and administrative expenses Operating income 102,420.00 Feedback Check My Work a. 1. Recall that under absorption costing, the cost of goods manufactured includes direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead costs. Both fixed and variable factory costs are included as part of factory overhead. Calculate unit cost for direct materials, direct labor, variable factory overhead, fixed factory overhead. Add together to get total unit cost. For 24,800 units, use the same unit costs for direct materials, direct labor, and variable overhead, but instead recalculate the fixed factory overhead and add this to obtain the unit cost at the 24,800 unit level. Sales - cost of goods manufactured - Inventory, October 31) = Gross profit; gross profit - selling and administrative expenses = income from operations. Remember that the Inventory, October 31 adjustment will only be necessary at the 24,800 level. a. 2. Prepare an estimated income statement, comparing operating results if 22,400 and 24,800 units are manufactured in the variable costing format. If an amount box does not require an entry leave it blank. Marshall Inc. Variable Costing Income Statement For the Month Ending October 31 22.400 Units Manufactured 24.800 Units Manufactured Sales Variable cost of goods sold: Variable cost of goods sold Sales Contribution margin $ $ $ I DO 0000 Fixed costs: Total fixed costs $ $ b. What is the reason for the difference in operating income reported for the two levels of production by the absorption costing income statement? ncon cost over a The increase from operations under absorption costing is caused by tion of over number of units. Thus, the cost of goods sold is The difference can also be explained by the amount of included in the inventory. overhead cost









