Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Estimating Cost of Capital Measures Sprint Nextel Corporation (S) has $24.3 billion in total debt (which approximates its market value.) Each year this debt
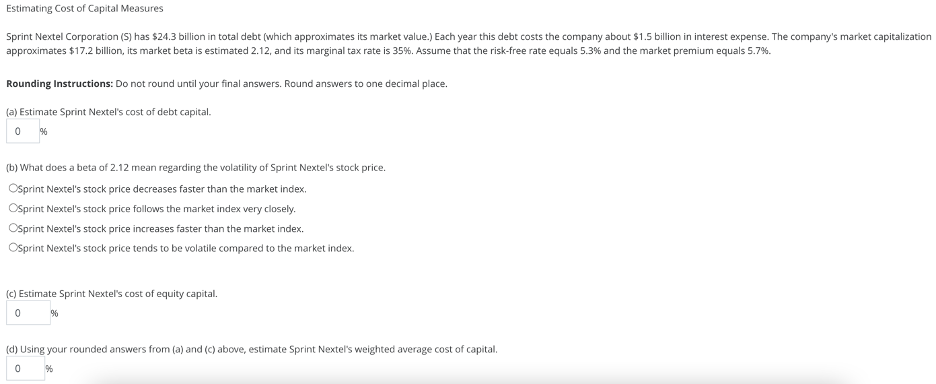

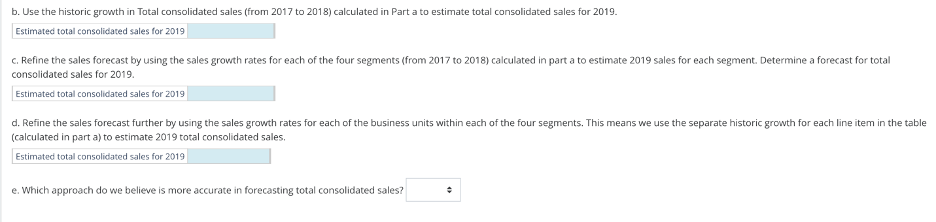



Estimating Cost of Capital Measures Sprint Nextel Corporation (S) has $24.3 billion in total debt (which approximates its market value.) Each year this debt costs the company about $1.5 billion in interest expense. The company's market capitalization approximates $17.2 billion, its market beta is estimated 2.12, and its marginal tax rate is 35%. Assume that the risk-free rate equals 5.3% and the market premium equals 5.7%. Rounding Instructions: Do not round until your final answers. Round answers to one decimal place. (a) Estimate Sprint Nextel's cost of debt capital. 0 % (b) What does a beta of 2.12 mean regarding the volatility of Sprint Nextel's stock price. Osprint Nextel's stock price decreases faster than the market index. OSprint Nextel's stock price follows the market index very closely. OSprint Nextel's stock price increases faster than the market index. Osprint Nextel's stock price tends to be volatile compared to the market index. (c) Estimate Sprint Nextel's cost of equity capital. 0 % (d) Using your rounded answers from (a) and (c) above, estimate Sprint Nextel's weighted average cost of capital. 0 % Estimating Components of both WACC and DDM Analysts estimate the cost of debt capital for Abbott Laboratories (NYSE: ABT) is 2.56% and that its cost of equity capital is 4.1%. Assume that ABT's marginal tax rate is 36%, the risk-free rate is 4.6%, the market risk premium is 5.0%, the ABT market price is $47.73 per common share, and its dividends are $1.18 per common share. (a) Compute ABT's average borrowing rate and its market beta. (Round your answers to one decimal place.) Average borrowing rate = 0 % Market beta = 0 (b) Assume that its dividends continue at the current level in perpetuity. Use the constant perpetuity dividend discount model to infer the market's expected cost of equity capital. (Hint: Use Price per share= Dividends per share/Cost of equity capital.) (Round your answer to one decimal place.) 96 (c) Compare the inferred cost of equity capital from part (b) to the 4.1% estimated cost of equity capital from analysts. OThe inferred cost of equity capital seems high compared to 4.1%, which suggests that the investment has a negative beta. OThe inferred cost of equity capital seems low compared to 4.1%, which suggests that the investment has a negative beta. OThe inferred cost of equity capital seems high compared to 4.1%, which suggests that the investment has a positive beta. OThe inferred cost of equity capital seems low compared to 4.1%, which suggests that the investment has a positive beta. b. Use the historic growth in Total consolidated sales (from 2017 to 2018) calculated in Part a to estimate total consolidated sales for 2019. Estimated total consolidated sales for 2019 c. Refine the sales forecast by using the sales growth rates for each of the four segments (from 2017 to 2018) calculated in part a to estimate 2019 sales for each segment. Determine a forecast for total consolidated sales for 2019. Estimated total consolidated sales for 2019 d. Refine the sales forecast further by using the sales growth rates for each of the business units within each of the four segments. This means we use the separate historic growth for each line item in the table (calculated in part a) to estimate 2019 total consolidated sales. Estimated total consolidated sales for 2019 e. Which approach do we believe is more accurate in forecasting total consolidated sales? = Estimating WACC and Expected Growth in Dividends Model Assume FedEx Corporation (NYSE: FDX) was trading at $107.47 at May 31, 2011. Its dividend per share was $0.36, its market beta was estimated to be 0.7, its average borrowing rate is 9.2%, and its marginal tax rate is 36%. FedEx's market value of equity (market cap) is $32.95 billion and its total market value (enterprise value) is $34.31 billion. Assume a risk-free rate of 5.3% and a market risk premium of 5.7% to answer the following requirements. (a) Estimate FedEx's cost of debt capital, cost of equity capital, and weighted average cost of capital. (Round your answers to one decimal place.) Cost of debt capital = 0 % Cost of equity capital 0 96 Calculate the weighted average cost of capital. (Use rounded answers from above. Do not round until your final answer. Round your final answer to one decimal place.) Weighted average cost of capital = 0 % (b) Using the dividend discount model, and assuming a constant perpetuity for dividends, estimate FedEx's intrinsic value per share. (Use the rounded cost of equity capital calculated in (a). Do not round until your final answer. Round to two decimal places.) $ 0 (c) Using the Gordon growth DDM, and assuming next period's dividends equal $0.36 and grow at a constant rate for each period thereafter, infer the market's expected growth in dividends that are necessary for FedEx's intrinsic value from the model to equal $107.47 per common share. Assume that its cost of equity capital is 9.3%. (Do not round until your final answer. Round to one decimal place.) 0 96 Procter and Gamble (PG) has a June fiscal year-end. On June 30, 2006, analysts expected the company to pay $1.30 dividends per share in fiscal year 2007. The company's market beta is estimated to be 0.7. Assume that the risk-free rate is 4.9% and the market premium is 5%. During fiscal year 2006, the company's sales growth was 20.2%. However, analysis reveals that P&G's fiscal 2006 sales include eight months of sales from Gillette after its acquisition by P&G during 2006. Footnotes report pro forma sales that show what the income statement would have reported had Gillette's full-year sales been included in both 2005 and 2006-specifically, P&G's sales growth would have been 4.4%. (a) Estimate P&G's cost of equity capital using the CAPM model. (Round your answer to one decimal place.) 0 % (b) Using your rounded answer from (a), estimate P&G's intrinsic value using the DDM model assuming that dividends per share are projected at $1.30 per share after 2007. (Hint: Apply the DDM model with constant perpetuity.) (Round your answer to two decimal places.) $ 0 (c) Discuss the appropriateness of the estimate computed in part (b) in light of its assumption for no future dividend growth. The DDM model with a constant perpetuity would correctly estimate P&G's intrinsic value OThe DDM model with a constant perpetuity would likely underestimate P&G's intrinsic value OThe DDM model with a constant perpetuity would likely overestimate P&G's intrinsic value (d) If we use the Gordon growth DDM to estimate stock value per share, which sales growth rate should we use (20.2% or 4.4%)? Explain. The 20.2% rate is appropriate. The 4.4% rate would underestimate the growth rate because the 2006 sales does not include sales from Gillette. OThe 4.4% rate is appropriate. The 20.2% rate would overestimate the growth rate because the 2005 sales number does not include sales from Gillette. (e) On June 30, 2006, the stock of P&G was priced at $55.60 per share. Infer the market expectation about the future growth rate of P&Gs dividend using the DDM model with an increasing perpetuity and the rounded cost of equity capital computed in (a). (Do not round until your final answer. Round your answer to one decimal place.) 0 % Comment on the reasonableness of this inferred growth rate. Oinvestors seem to expect P&G to grow at the same rate as the historical number of 4.4%. Oinvestors seem to expect P&G to grow at a slower rate than the historical number of 4.4% Oinvestors seem to expect P&G to grow at a faster rate than the historical number of 4.4%.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Here are the answers to the questions a Using the information provided Sprint Nextels cost of de...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


