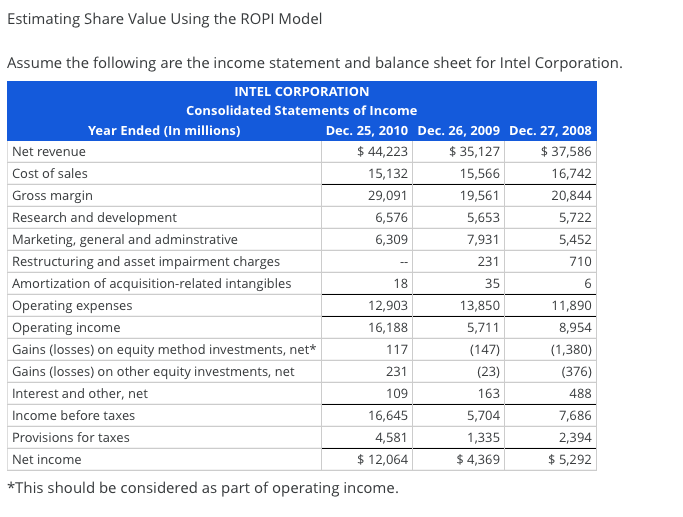
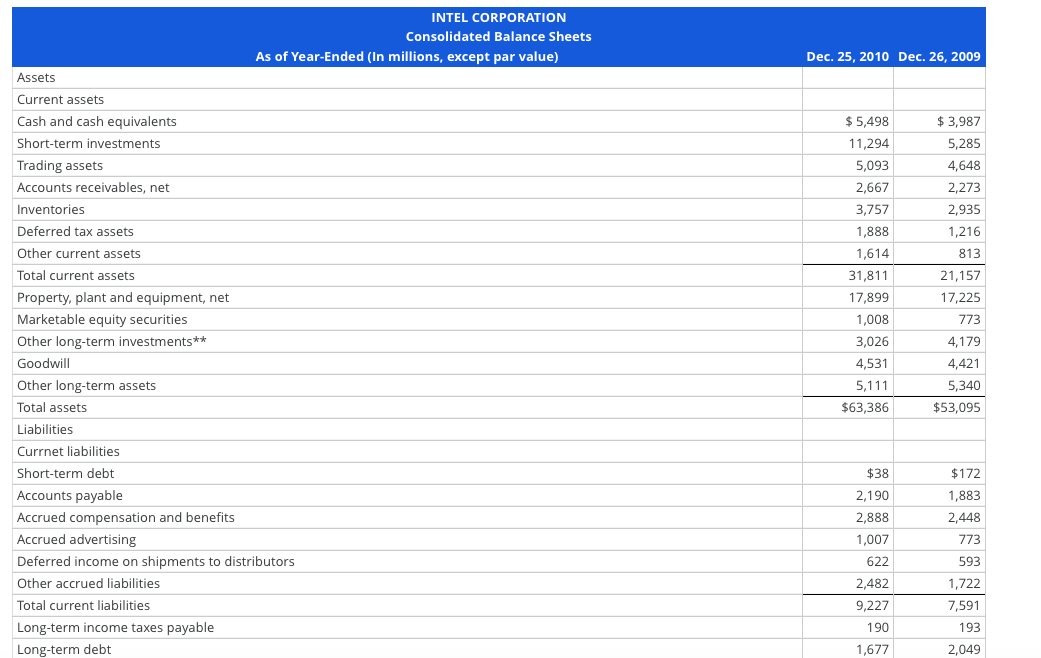
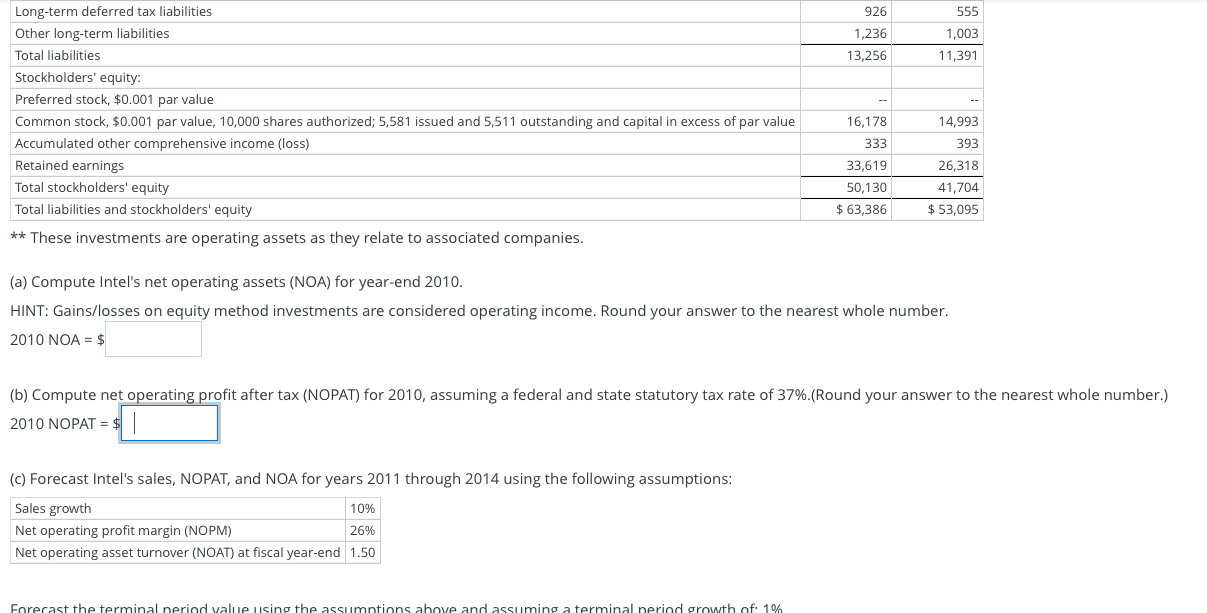
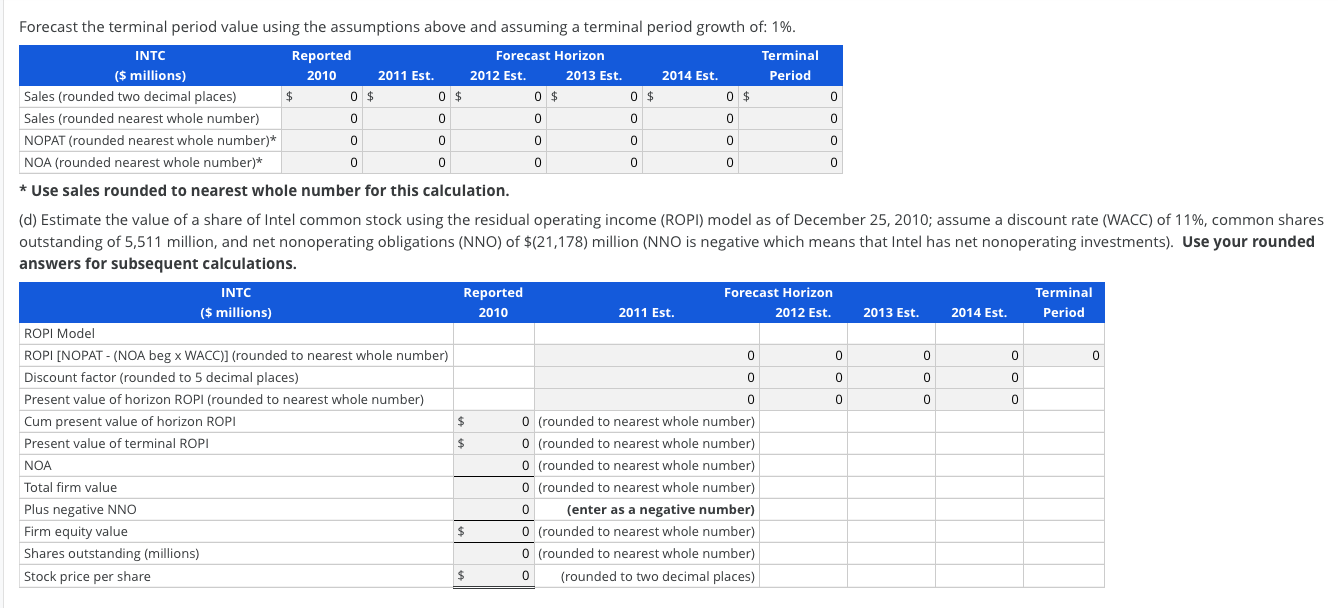
Estimating Share Value Using the ROPI Model Assume the following are the income statement and balance sheet for Intel Corporation. 6,309 18 35 INTEL CORPORATION Consolidated Statements of Income Year Ended (In millions) Dec. 25, 2010 Dec. 26, 2009 Dec. 27, 2008 Net revenue $ 44,223 $35,127 $ 37,586 Cost of sales 15,132 15,566 16,742 Gross margin 29,091 19,561 20,844 Research and development 6,576 5,653 5,722 Marketing, general and adminstrative 7,931 5,452 Restructuring and asset impairment charges 231 710 Amortization of acquisition-related intangibles Operating expenses 12,903 13,850 11,890 Operating income 16,188 5,711 8,954 Gains (losses) on equity method investments, net* 117 (147) (1,380) Gains (losses) on other equity investments, net 231 (23) (376) Interest and other, net 109 163 488 Income before taxes 16,645 5,704 7,686 Provisions for taxes 4,581 1,335 2,394 Net income $ 12,064 $4,369 $5,292 *This should be considered as part of operating income. Dec. 25, 2010 Dec. 26, 2009 $5,498 11,294 5,093 INTEL CORPORATION Consolidated Balance Sheets As of Year-Ended (In millions, except par value) Assets Current assets Cash and cash equivalents Short-term investments Trading assets Accounts receivables, net Inventories Deferred tax assets Other current assets Total current assets Property, plant and equipment, net Marketable equity securities Other long-term investments** Goodwill Other long-term assets Total assets Liabilities Currnet liabilities Short-term debt Accounts payable Accrued compensation and benefits Accrued advertising Deferred income on shipments to distributors Other accrued liabilities Total current liabilities Long-term income taxes payable Long-term debt 2,667 3,757 1,888 1,614 31,811 17,899 1,008 3,026 4,531 5,111 $63,386 $ 3,987 5,285 4,648 2,273 2,935 1,216 813 21,157 17,225 773 4,179 4,421 5,340 $53,095 $38 2,190 2,888 1,007 622 2,482 9,227 190 1,677 $172 1,883 2,448 773 593 1,722 7,591 193 2,049 926 1,236 13,256 555 1,003 11,391 Long-term deferred tax liabilities Other long-term liabilities Total liabilities Stockholders' equity: Preferred stock, $0.001 par value Common stock, $0.001 par value, 10,000 shares authorized; 5,581 issued and 5,511 outstanding and capital in excess of par value Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities and stockholders' equity ** These investments are operating assets as they relate to associated companies. 16,178 333 33,619 50,130 $ 63,386 14,993 393 26,318 41,704 $ 53,095 (a) Compute Intel's net operating assets (NOA) for year-end 2010. HINT: Gains/losses on equity method investments are considered operating income. Round your answer to the nearest whole number. 2010 NOA = $ (b) Compute net operating profit after tax (NOPAT) for 2010, assuming a federal and state statutory tax rate of 37%.(Round your answer to the nearest whole number.) 2010 NOPAT = $ (c) Forecast Intel's sales, NOPAT, and NOA for years 2011 through 2014 using the following assumptions: Sales growth 10% Net operating profit margin (NOPM) 26% Net operating asset turnover (NOAT) at fiscal year-end 1.50 Forecast the terminal nerind value using the assumntions above and assuming a terminal neriod prowth of 1% Forecast the terminal period value using the assumptions above and assuming a terminal period growth of: 1%. INTC Reported Forecast Horizon Terminal ($ millions) 2010 2011 Est. 2012 Est. 2013 Est. 2014 Est. Period Sales (rounded two decimal places) $ 0 $ 0 $ 0 $ Sales (rounded nearest whole number) NOPAT (rounded nearest whole number)* 0 0 NOA (rounded nearest whole number)* 0 $ 0 $ O * Use sales rounded to nearest whole number for this calculation. (d) Estimate the value of a share of Intel common stock using the residual operating income (ROPI) model as of December 25, 2010; assume a discount rate (WACC) of 11%, common shares outstanding of 5,511 million, and net nonoperating obligations (NNO) of $(21,178) million (NNO is negative which means that Intel has net nonoperating investments). Use your rounded answers for subsequent calculations. Reported 2010 Forecast Horizon 2012 Est. Terminal Period 2011 Est. 2013 Est. 2014 Est. 0 0 0 INTC ($ millions) ROPI Model ROPI [NOPAT - (NOA beg x WACC)] (rounded to nearest whole number) Discount factor (rounded to 5 decimal places) Present value of horizon ROPI (rounded to nearest whole number) Cum present value of horizon ROPI Present value of terminal ROPI NOA Total firm value Plus negative NNO Firm equity value Shares outstanding (millions) Stock price per share 0 (rounded to nearest whole number) 0 (rounded to nearest whole number) 0 (rounded to nearest whole number) 0 (rounded to nearest whole number) (enter as a negative number) 0 (rounded to nearest whole number) 0 (rounded to nearest whole number) 0 (rounded to two decimal places) Estimating Share Value Using the ROPI Model Assume the following are the income statement and balance sheet for Intel Corporation. 6,309 18 35 INTEL CORPORATION Consolidated Statements of Income Year Ended (In millions) Dec. 25, 2010 Dec. 26, 2009 Dec. 27, 2008 Net revenue $ 44,223 $35,127 $ 37,586 Cost of sales 15,132 15,566 16,742 Gross margin 29,091 19,561 20,844 Research and development 6,576 5,653 5,722 Marketing, general and adminstrative 7,931 5,452 Restructuring and asset impairment charges 231 710 Amortization of acquisition-related intangibles Operating expenses 12,903 13,850 11,890 Operating income 16,188 5,711 8,954 Gains (losses) on equity method investments, net* 117 (147) (1,380) Gains (losses) on other equity investments, net 231 (23) (376) Interest and other, net 109 163 488 Income before taxes 16,645 5,704 7,686 Provisions for taxes 4,581 1,335 2,394 Net income $ 12,064 $4,369 $5,292 *This should be considered as part of operating income. Dec. 25, 2010 Dec. 26, 2009 $5,498 11,294 5,093 INTEL CORPORATION Consolidated Balance Sheets As of Year-Ended (In millions, except par value) Assets Current assets Cash and cash equivalents Short-term investments Trading assets Accounts receivables, net Inventories Deferred tax assets Other current assets Total current assets Property, plant and equipment, net Marketable equity securities Other long-term investments** Goodwill Other long-term assets Total assets Liabilities Currnet liabilities Short-term debt Accounts payable Accrued compensation and benefits Accrued advertising Deferred income on shipments to distributors Other accrued liabilities Total current liabilities Long-term income taxes payable Long-term debt 2,667 3,757 1,888 1,614 31,811 17,899 1,008 3,026 4,531 5,111 $63,386 $ 3,987 5,285 4,648 2,273 2,935 1,216 813 21,157 17,225 773 4,179 4,421 5,340 $53,095 $38 2,190 2,888 1,007 622 2,482 9,227 190 1,677 $172 1,883 2,448 773 593 1,722 7,591 193 2,049 926 1,236 13,256 555 1,003 11,391 Long-term deferred tax liabilities Other long-term liabilities Total liabilities Stockholders' equity: Preferred stock, $0.001 par value Common stock, $0.001 par value, 10,000 shares authorized; 5,581 issued and 5,511 outstanding and capital in excess of par value Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities and stockholders' equity ** These investments are operating assets as they relate to associated companies. 16,178 333 33,619 50,130 $ 63,386 14,993 393 26,318 41,704 $ 53,095 (a) Compute Intel's net operating assets (NOA) for year-end 2010. HINT: Gains/losses on equity method investments are considered operating income. Round your answer to the nearest whole number. 2010 NOA = $ (b) Compute net operating profit after tax (NOPAT) for 2010, assuming a federal and state statutory tax rate of 37%.(Round your answer to the nearest whole number.) 2010 NOPAT = $ (c) Forecast Intel's sales, NOPAT, and NOA for years 2011 through 2014 using the following assumptions: Sales growth 10% Net operating profit margin (NOPM) 26% Net operating asset turnover (NOAT) at fiscal year-end 1.50 Forecast the terminal nerind value using the assumntions above and assuming a terminal neriod prowth of 1% Forecast the terminal period value using the assumptions above and assuming a terminal period growth of: 1%. INTC Reported Forecast Horizon Terminal ($ millions) 2010 2011 Est. 2012 Est. 2013 Est. 2014 Est. Period Sales (rounded two decimal places) $ 0 $ 0 $ 0 $ Sales (rounded nearest whole number) NOPAT (rounded nearest whole number)* 0 0 NOA (rounded nearest whole number)* 0 $ 0 $ O * Use sales rounded to nearest whole number for this calculation. (d) Estimate the value of a share of Intel common stock using the residual operating income (ROPI) model as of December 25, 2010; assume a discount rate (WACC) of 11%, common shares outstanding of 5,511 million, and net nonoperating obligations (NNO) of $(21,178) million (NNO is negative which means that Intel has net nonoperating investments). Use your rounded answers for subsequent calculations. Reported 2010 Forecast Horizon 2012 Est. Terminal Period 2011 Est. 2013 Est. 2014 Est. 0 0 0 INTC ($ millions) ROPI Model ROPI [NOPAT - (NOA beg x WACC)] (rounded to nearest whole number) Discount factor (rounded to 5 decimal places) Present value of horizon ROPI (rounded to nearest whole number) Cum present value of horizon ROPI Present value of terminal ROPI NOA Total firm value Plus negative NNO Firm equity value Shares outstanding (millions) Stock price per share 0 (rounded to nearest whole number) 0 (rounded to nearest whole number) 0 (rounded to nearest whole number) 0 (rounded to nearest whole number) (enter as a negative number) 0 (rounded to nearest whole number) 0 (rounded to nearest whole number) 0 (rounded to two decimal places)










