Question
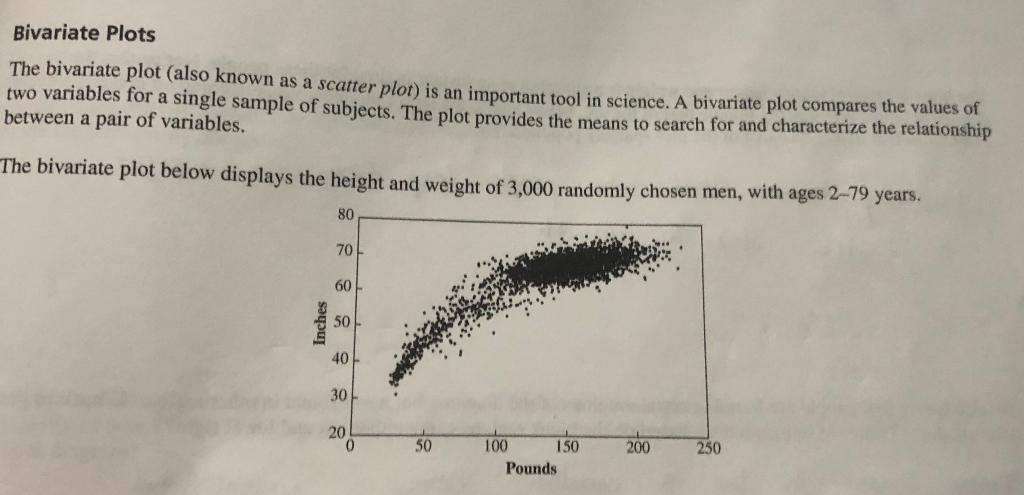
estion: Calculate the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) for PDI. E/V80.00% Cost of equity9.40% Risk-free rate 3.00% Beta 1.28 Market equity risk premium 5.00%

estion:
Calculate the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) for PDI.
E/V80.00%
Cost of equity9.40%
Risk-free rate 3.00%
Beta 1.28
Market equity risk premium 5.00%
D/V20.00%
Cost of debt4.00%
Corporate tax rate40.00%
WACC 80% x 9.40%) + [20% x 4% x (1 - 40%)]= 8.00% WACC = (E/V x Re) + ((D/V x Rd) x (1 - T))
*Cost of equityRisk free rate of return + (Beta * Risk premium) = 3% + (1.28 x 5%) 0.094
Givend the above, I cannot get the following:
Sum of FCF PV =?
Terminal value =?
Present value of terminal value =?
Total value of PDI =?
Assumptions
Discount rate ?
Terminal value ?

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


