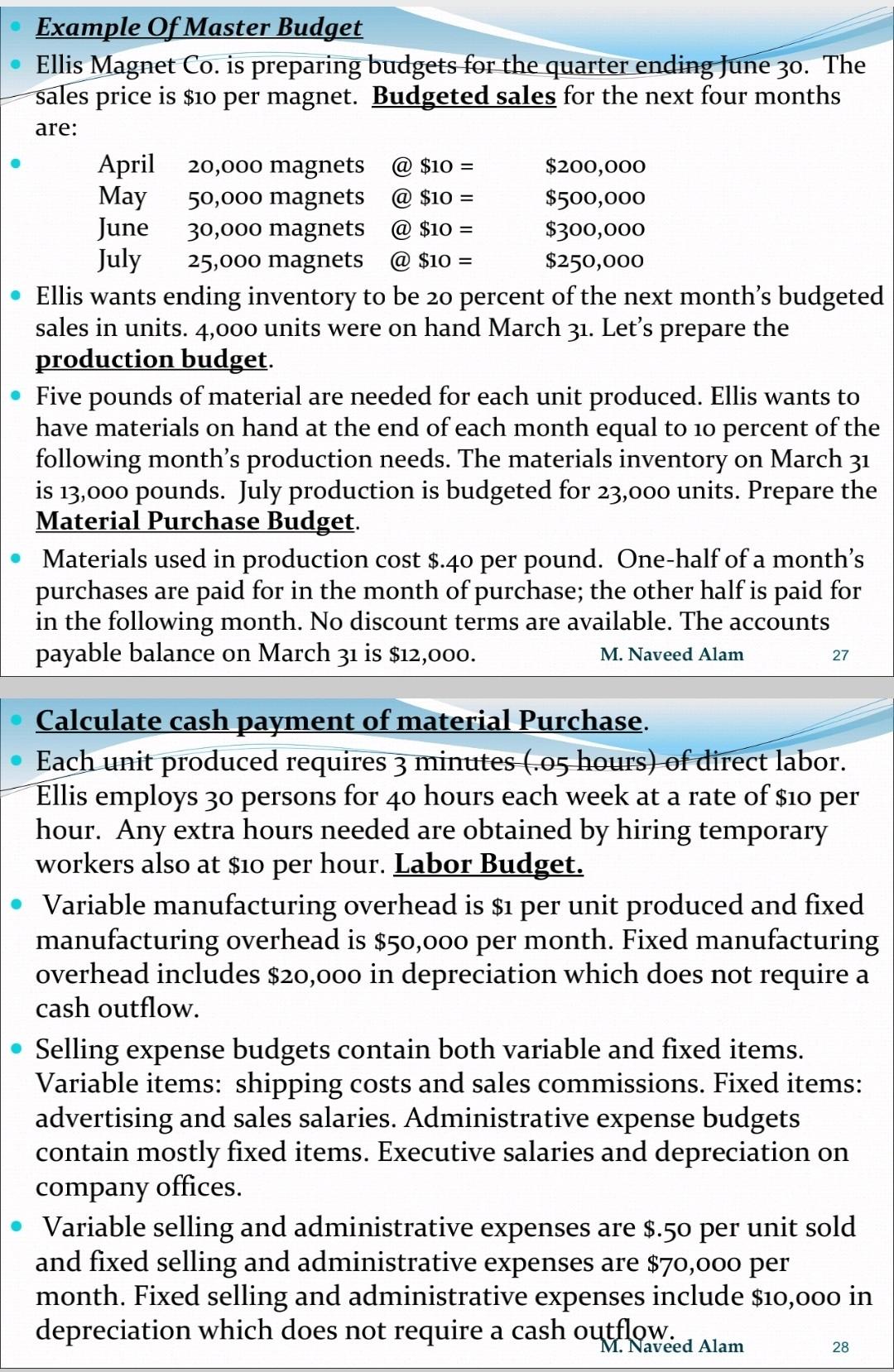

Example Of Master Budget Ellis Magnet Co. is preparing budgets for the quarter ending June 30. The sales price is $10 per magnet. Budgeted sales for the next four months are: @ $10 = @ $10 = @ $10 = @ $10 = April 20,000 magnets $200,000 May 50,000 magnets $500,000 June 30,000 magnets $300,000 July 25,000 magnets $250,000 Ellis wants ending inventory to be 20 percent of the next month's budgeted sales in units. 4,000 units were on hand March 31. Let's prepare the production budget. Five pounds of material are needed for each unit produced. Ellis wants to have materials on hand at the end of each month equal to 10 percent of the following month's production needs. The materials inventory on March 31 is 13,000 pounds. July production is budgeted for 23,000 units. Prepare the Material Purchase Budget. Materials used in production cost $.40 per pound. One-half of a month's purchases are paid for in the month of purchase; the other half is paid for in the following month. No discount terms are available. The accounts payable balance on March 31 is $12,000. M. Naveed Alam 27 Calculate cash payment of material Purchase. Each unit produced requires 3 minutes (.05 hours) of direct labor. Ellis employs 30 persons for 40 hours each week at a rate of $10 per hour. Any extra hours needed are obtained by hiring temporary workers also at $10 per hour. Labor Budget. Variable manufacturing overhead is $i per unit produced and fixed manufacturing overhead is $50,000 per month. Fixed manufacturing overhead includes $20,000 in depreciation which does not require a cash outflow. Selling expense budgets contain both variable and fixed items. Variable items: shipping costs and sales commissions. Fixed items: advertising and sales salaries. Administrative expense budgets contain mostly fixed items. Executive salaries and depreciation on company offices. Variable selling and administrative expenses are $.50 per unit sold and fixed selling and administrative expenses are $70,000 per month. Fixed selling and administrative expenses include $10,000 in depreciation which does not require a cash outflow. M. Naveed Alam 28 All sales are on account. Ellis's collection pattern is: 70 percent collected in month of sale, 25 percent collected in month after sale, 5 percent will be uncollectible , Accounts receivable on March 31 is $30,000, all of which is collectible. Ellis Magnet Company: Has a $100,000 line of credit at its bank, with a zero balance on April 1. Maintains a $30,000 minimum cash balance. Borrows at the beginning of a month and repays at the end of a month. Pays interest at 16 percent when a principal payment is made. Pays a $51,000 cash dividend in April. Purchases equipment costing $143,700 in May and $48,800 in June. Has a $40,000 cash balance on April 1. Ellis reports the following account balances on June 30, prior to preparing its budgeted financial statements: Land - $50,000, Building (net) - $174,500 , Common stock - $200,000, Equipment (net) - $192,500, Retained earnings - $148,150








