Question
Exercise 3-10 (Algo) Applying Overhead; Journal Entries; T-accounts [LO3-1, LO3-2] Dillon Products manufactures various machined parts to customer specifications. The company uses a job-order costing
Exercise 3-10 (Algo) Applying Overhead; Journal Entries; T-accounts [LO3-1, LO3-2]
Dillon Products manufactures various machined parts to customer specifications. The company uses a job-order costing system and applies overhead cost to jobs on the basis of machine-hours. At the beginning of the year, the company used a cost formula to estimate that it would incur $4,377,600 in manufacturing overhead cost at an activity level of 576,000 machine-hours.
The company spent the entire month of January working on a large order for 12,800 custom-made machined parts. The company had no work in process at the beginning of January. Cost data relating to January follow:
- Raw materials purchased on account, $318,000.
- Raw materials used in production, $265,000 (80% direct materials and 20% indirect materials).
- Labor cost accrued in the factory, $171,000 (one-third direct labor and two-thirds indirect labor).
- Depreciation recorded on factory equipment, $62,900.
- Other manufacturing overhead costs incurred on account, $85,100.
- Manufacturing overhead cost was applied to production on the basis of 40,710 machine-hours actually worked during the month.
- The completed job for 12,800 custom-made machined parts was moved into the finished goods warehouse on January 31 to await delivery to the customer. (In computing the dollar amount for this entry, remember that the cost of a completed job consists of direct materials, direct labor, and applied overhead.)
Required:
1. Prepare journal entries to record items (a) through (f) above [ignore item (g) for the moment].
2. Prepare T-accounts for Manufacturing Overhead and Work in Process. Post the relevant items from your journal entries to these T-accounts.
3. Prepare a journal entry for item (g) above.
4. If 10,300 of the custom-made machined parts are shipped to the customer in February, how much of this jobs cost will be included in cost of goods sold for February?
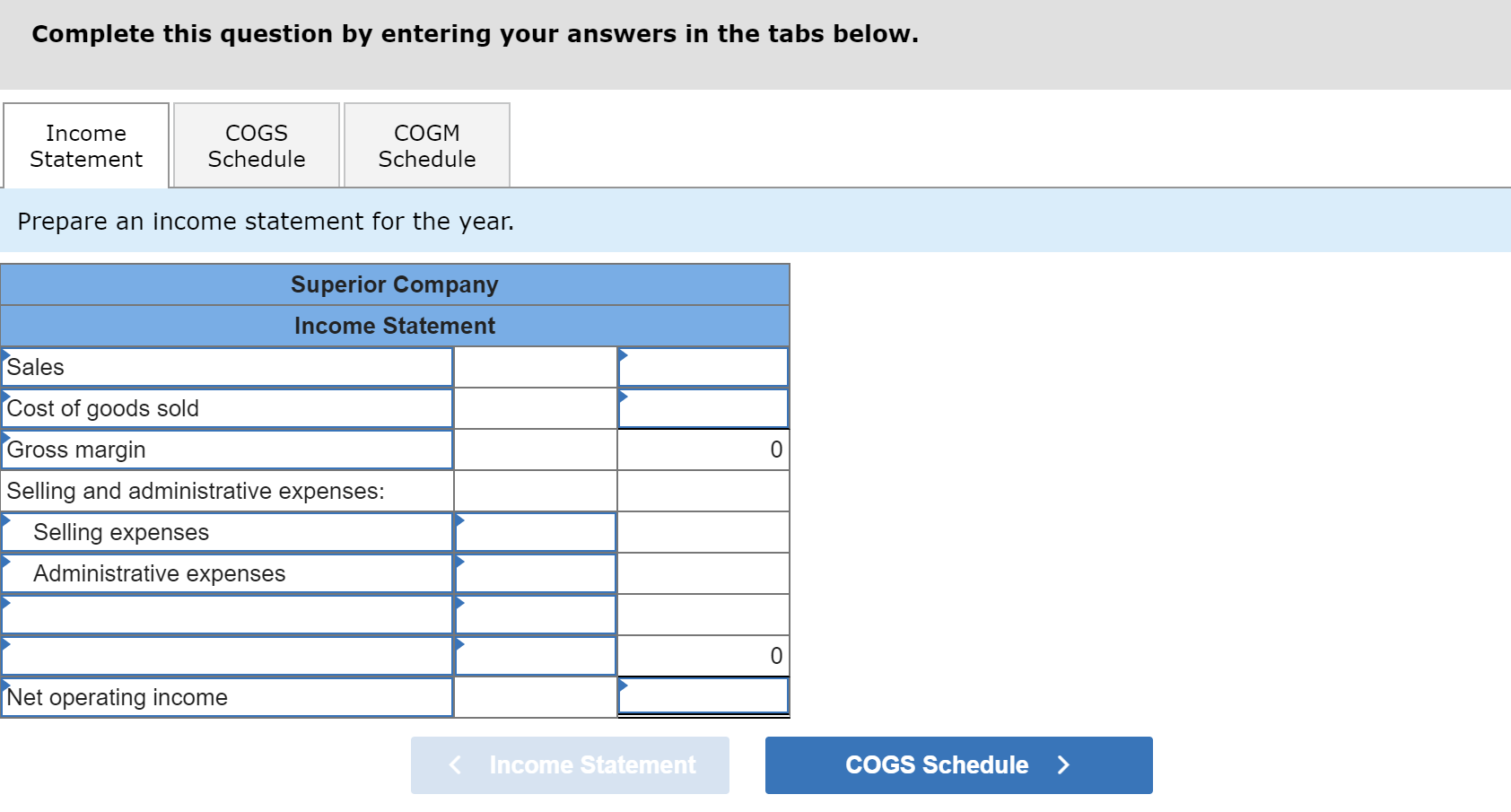
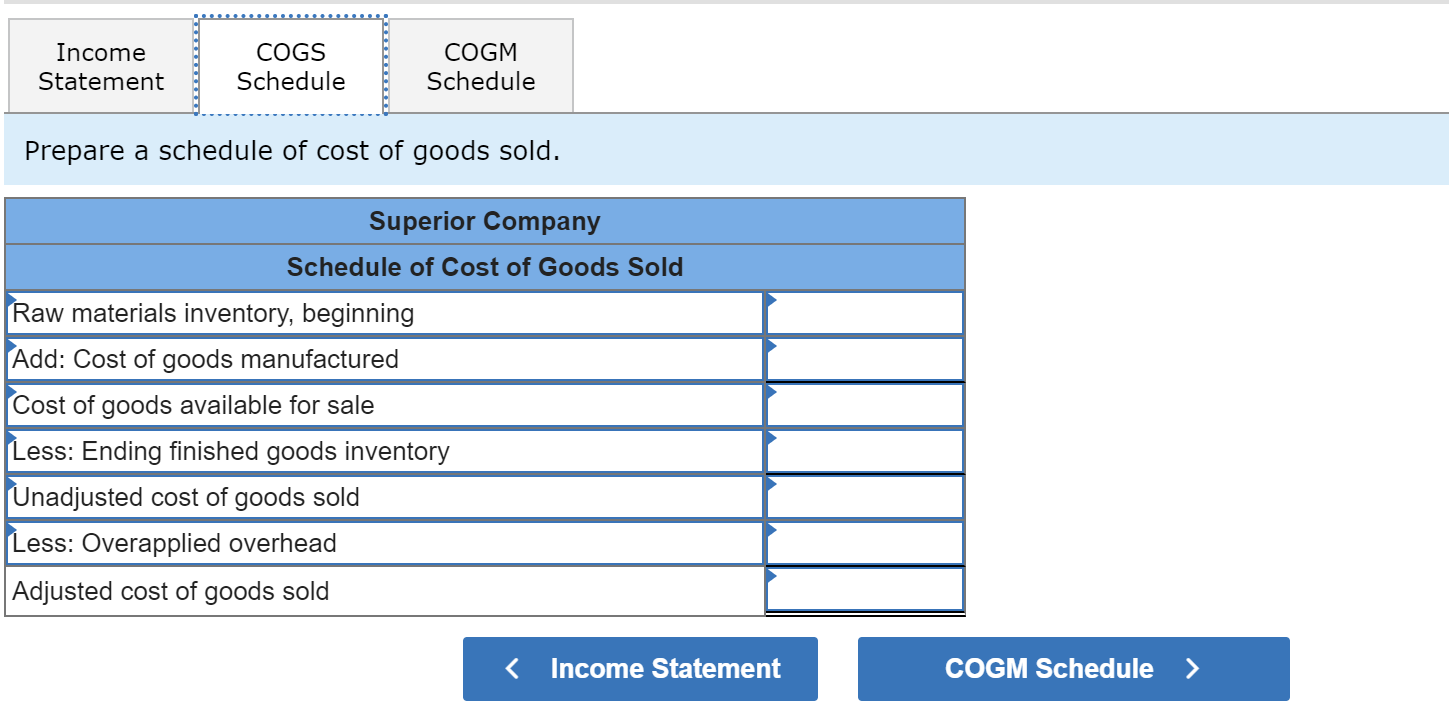
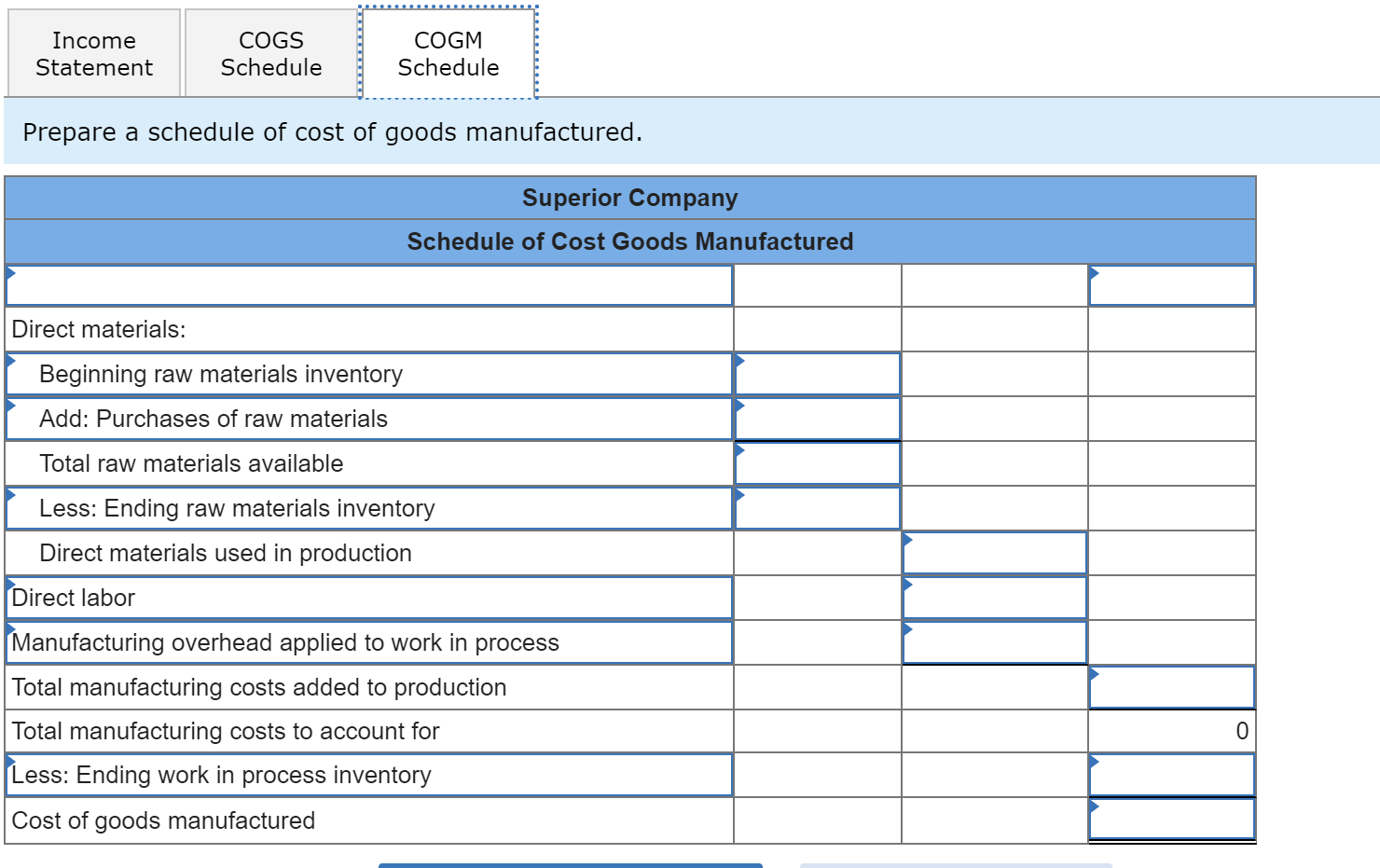
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Income Statement COGS Schedule COGM Schedule Prepare an income statement for the year. Superior Company Income Statement Sales 0 Cost of goods sold Gross margin Selling and administrative expenses: Selling expenses Administrative expenses 0 Net operating income Income Statement COGS Schedule > Income Statement COGS Schedule COGM Schedule Prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold. Superior Company Schedule of Cost of Goods Sold Raw materials inventory, beginning Add: Cost of goods manufactured Cost of goods available for sale Less: Ending finished goods inventory Unadjusted cost of goods sold Less: Overapplied overhead Adjusted cost of goods sold Income Statement COGS Schedule COGM Schedule Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured. Superior Company Schedule of Cost Goods Manufactured Direct materials: Beginning raw materials inventory Add: Purchases of raw materials Total raw materials available Less: Ending raw materials inventory Direct materials used in production Direct labor Manufacturing overhead applied to work in process Total manufacturing costs added to production Total manufacturing costs to account for Less: Ending work in process inventory Cost of goods manufactured 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


