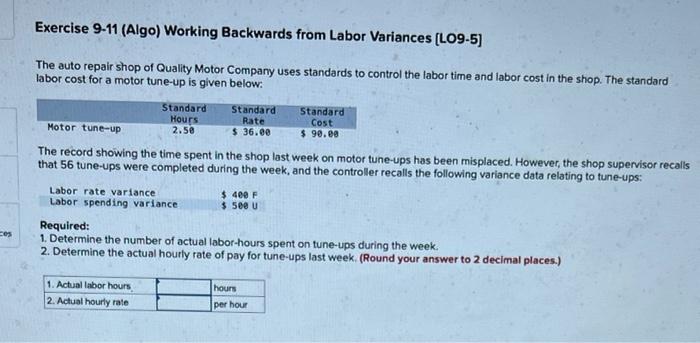
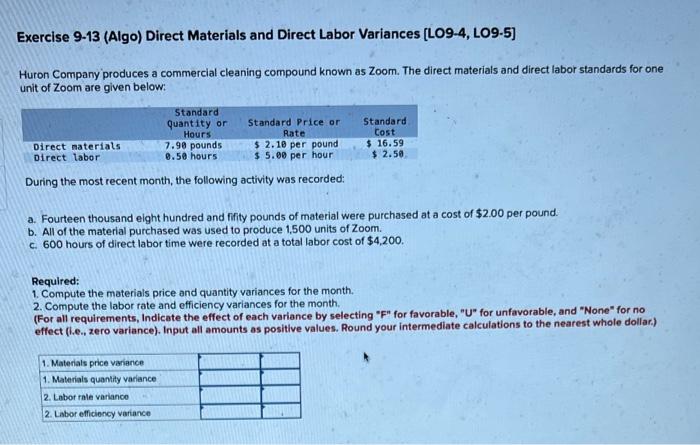
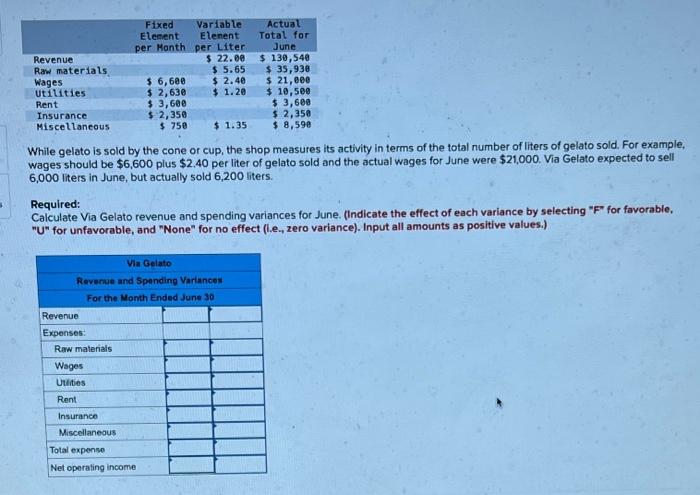
Exercise 9-11 (Algo) Working Backwards from Labor Variances (LO9-5) The auto repair shop of Quality Motor Company uses standards to control the labor time and labor cost in the shop. The standard labor cost for a motor tune-up is given below. Standard Hours 2.50 Motor tune-up Standard Rate $36.00 Standard Cost $ 90.00 The record showing the time spent in the shop last week on motor tune-ups has been misplaced. However, the shop supervisor recalls that 56 tune-ups were completed during the week, and the controller recalls the following variance data relating to tune-ups: Labor rate variance Labor spending variance $ 400 F $500 ces Required: 1. Determine the number of actual labor-hours spent on tune-ups during the week. 2. Determine the actual hourly rate of pay for tune-ups last week. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) 1. Actual labor hours 2. Actual hourly rate hours per hour Exercise 9-13 (Algo) Direct Materials and Direct Labor Variances (L09-4, LO9-5) Huron Company produces a commercial cleaning compound known as Zoom. The direct materials and direct labor standards for one unit of Zoom are given below: Standard Quantity or Hours 7.90 pounds 0.50 hours Standard Price or Rate $ 2.10 per pound $ 5.00 per hour Standard Cost $ 16.59 $ 2.50 Direct materials Direct labor During the most recent month, the following activity was recorded: a. Fourteen thousand eight hundred and nfity pounds of material were purchased at a cost of $2.00 per pound. b. All of the material purchased was used to produce 1500 units of Zoom. c. 600 hours of direct labor time were recorded at a total labor cost of $4,200. Required: 1. Compute the materials price and quantity variances for the month. 2. Compute the labor rate and efficiency variances for the month. (For all requirements, Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values. Round your intermediate calculations to the nearest whole dollar.) 1. Materials price variance 1. Materials quantity variance 2. Laborrie variance 2. Labor efficiency variance Revenue Raw materials Wages Utilities Rent Insurance Miscellaneous Fixed Variable Element Elenent per Month per Liter $ 22.se $ 5.65 $ 6,600 $ 2.40 $ 2,630 $ 1.20 $ 3,600 $ 2,350 $ 750 $ 1.35 Actual Total for June $ 130,540 $ 35,930 $ 21,00 $ 10,500 $ 3,600 $ 2,350 $ 8,590 While gelato is sold by the cone or cup, the shop measures its activity in terms of the total number of liters of gelato sold. For example, wages should be $6,600 plus $2.40 per liter of gelato sold and the actual wages for June were $21,000. Via Gelato expected to sell 6,000 liters in June, but actually sold 6,200 liters. Required: Calculate Via Gelato revenue and spending variances for June. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (l.e.zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values.) Via Gelato Revenue and Spending Variances For the Month Ended June 30 Revenue Expenses Raw materials Wages Utilities Rent Insurance Miscellaneous Total expense Net operating income Exercise 9-16 (Algo) Flexible Budgets in a Cost Center (L09-1, LO9-2] Packaging Solutions Corporation manufactures and sells a wide variety of packaging products. Performance reports are prepared monthly for each department. The planning budget and flexible budget for the Production Department are based on the following formulas, where is the number of labor-hours worked in a month: Direct labor Indirect labor Utilities Supplies Equipment depreciation Factory rent Property taxes Factory administration Cost Formulas $16.189 $4,100 + $1.989 $5,300 + $0.99 $1,600 + $0.289 $18, 100 - $2.469 $8,100 $2,500 $13,400 + $0.500 The Production Department planned to work 4,000 labor hours in March; however, it actually worked 3,800 labor hours during the month. Its actual costs incurred in March are listed below: Direct labor Indirect labor utilities Supplies Equipment depreciation Factory rent Property taxes Factory administration Actual Cost Incurred in March $ 62,720 $10,880 $ 9,290 $ 2,610 $ 27,220 $ 8,500 $ 2,50e $ 14,630 Required: 1. Prepare the Production Department's planning budget for the month. 2. Prepare the Production Department's flexible budget for the month. 3. Calculate the spending variances for all expense items