Question
Exercise E-1 Identifying asset values for financial statements Required ndicate whether each of the following assets should be valued at fair market value (FMV), lower
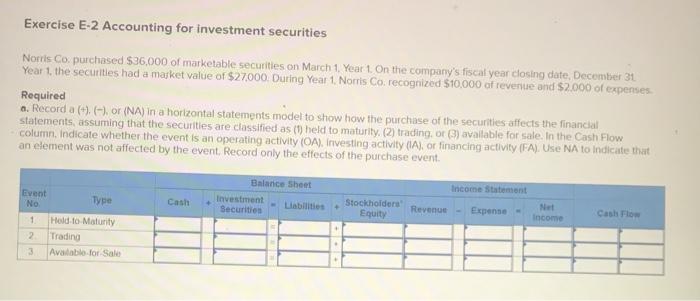
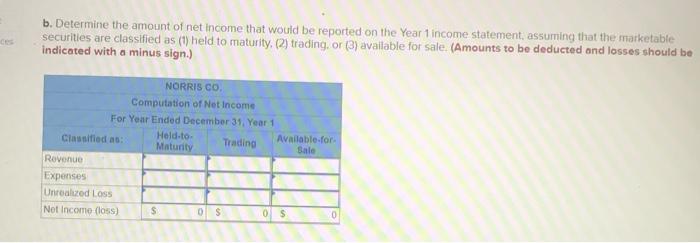
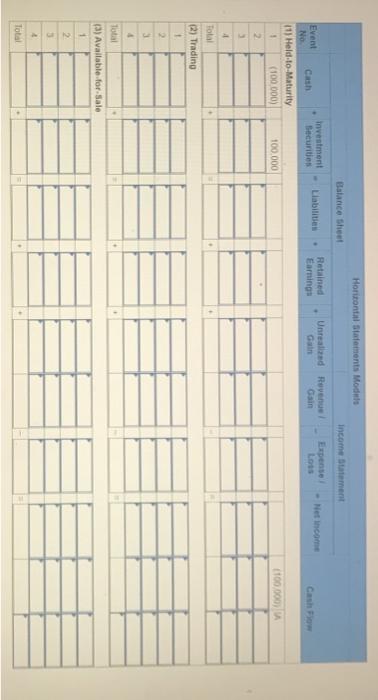
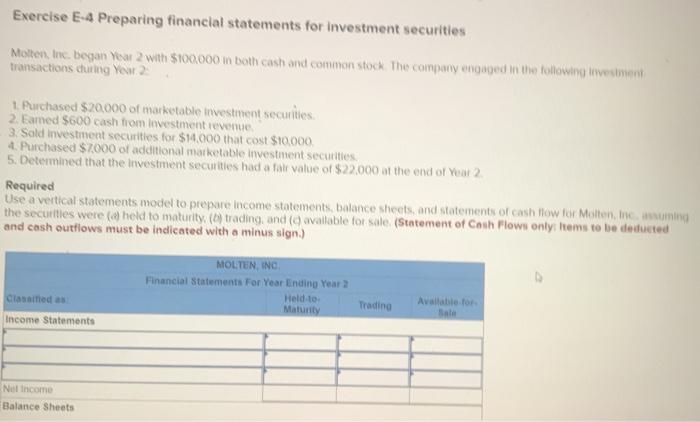
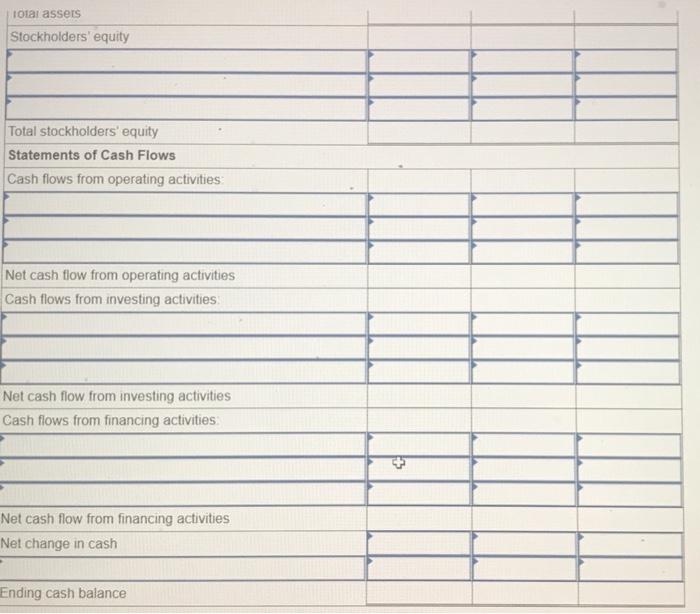
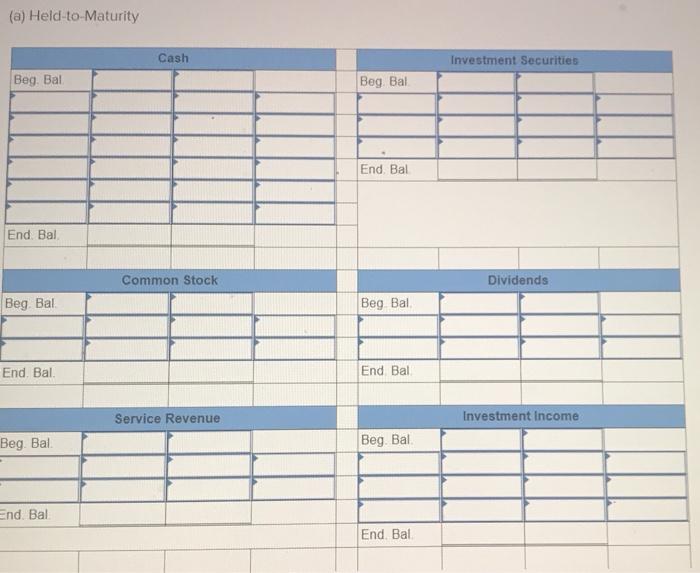
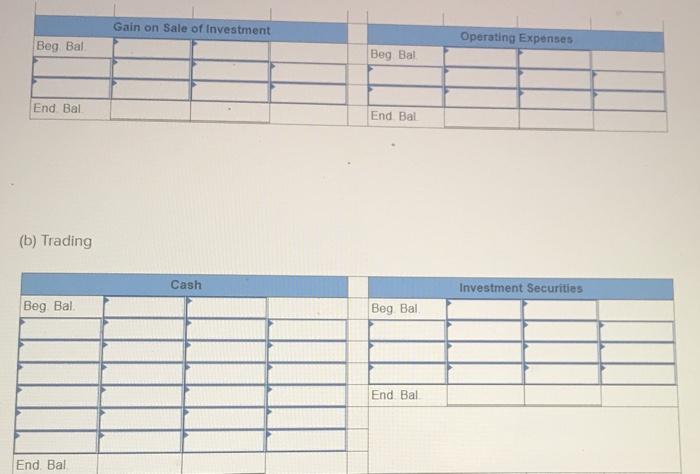
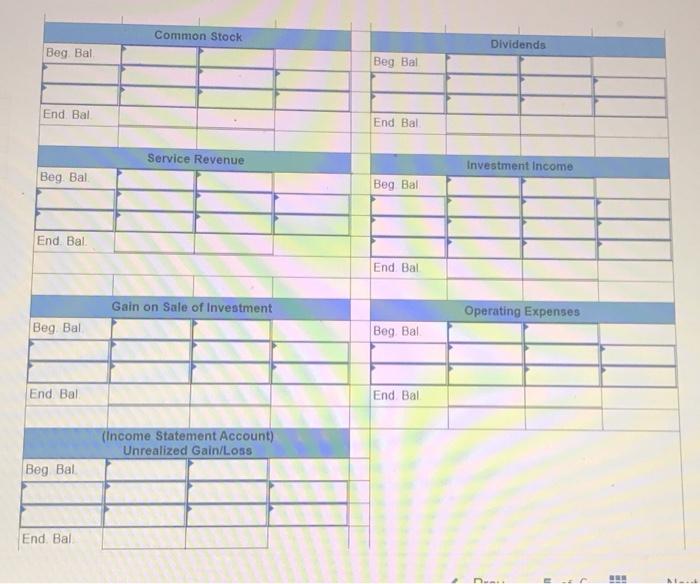
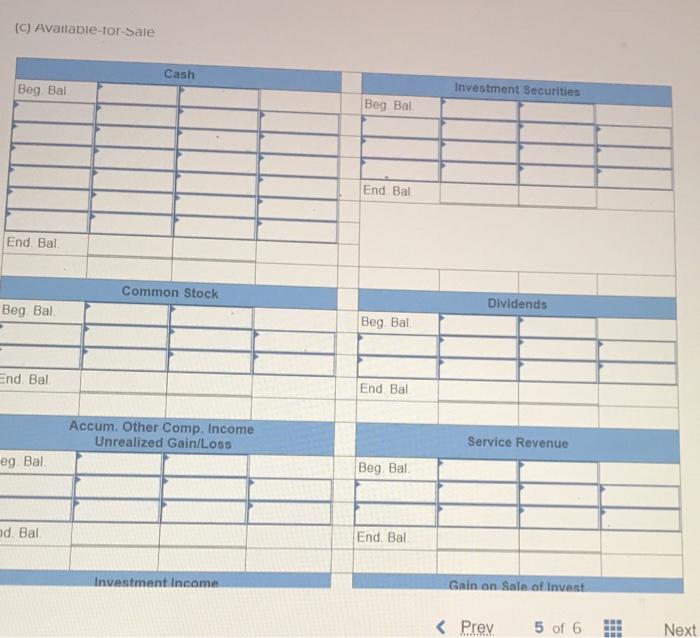
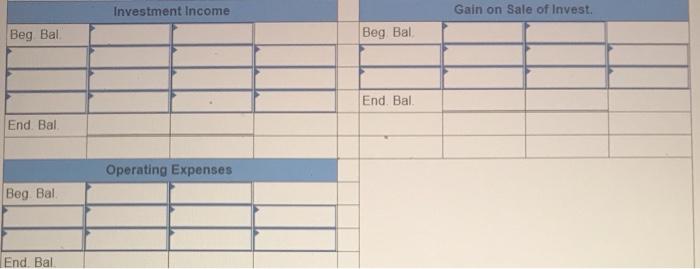
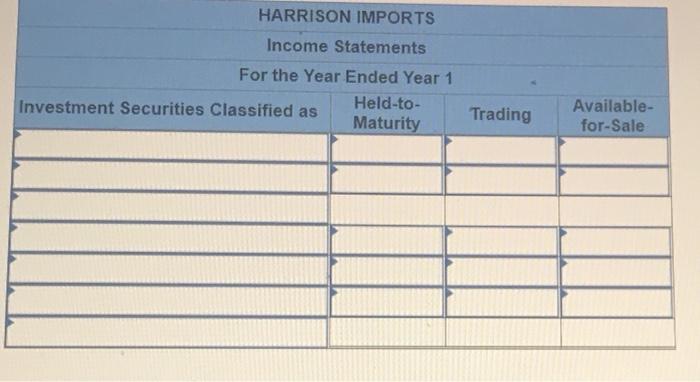
Exercise E-1 Identifying asset values for financial statements Required ndicate whether each of the following assets should be valued at fair market value (FMV), lower of cost or market (LCM), or historical Cost (HC) on the balance sheet. For certain assets, historical cost may be called amortized cost (AC). (Select an "X" in the correct Column and "NA" in all other columns.) Asset FMV LCM HC/AC ces Buildings Available-for-sale securities Office equipment Inventory Supplies Land Trading Securities Intangible Assets Held-to-Maturity Securities Exercise E-2 Accounting for investment securities Norris Co. purchased $36,000 of marketable securities on March 1, Year 1. On the company's fiscal year closing date, December 31 Year 1, the securities had a market value of $27,000. During Year 1, Norris Co. recognized $10,000 of revenue and $2.000 of expenses. Required a. Record a (+). (-), or (NA) in a horizontal statements model to show how the purchase of the securities affects the financial statements, assuming that the securities are classified as (1) held to maturity. (2) trading, or (3) available for sale. In the Cash Flow column. Indicate whether the event is an operating activity (OA), Investing activity (IA), or financing activity (FA). Use NA to Indicate that an element was not affected by the event. Record only the effects of the purchase event. Balance Sheet Income Statement Event No Type Cash Investment Securities Liabilities Stockholders Equity Net Revenue Expense Income 1 Held-to-Maturity 2 Trading 3 Available-for-Sale Cash Flow ces b. Determine the amount of net income that would be reported on the Year 1 income statement, assuming that the marketable securities are classified as (1) held to maturity, (2) trading, or (3) available for sale. (Amounts to be deducted and losses should be indicated with a minus sign.) NORRIS CO. Computation of Net Income For Year Ended December 31, Year 1 Held-to- Maturity Trading Available-for- Sale Classified as: Revenue Expenses Unrealized Loss Net Income (loss) $ $ 0 $ 0 Exercise E-3 Effect of investment securities transactions on financial statements The following information pertains to Botter Supply Co. for Year 1: 1. Purchased $100,000 of marketable investment securities. 2. Earned $10,000 of cash investment revenue. 3. Sold for $30,000 securities that cost $25,000 4. The fair value of the remaining securities at December 31, Year 1, was $89,000. Required a. Record the four events in a statements model like the following one. Use a separate model for each classification: (1) held to maturity, (2) trading, and (3) available for sale. In the Cash Flow column, indicate whether the event is an operating activity (OA). Investing activity (IA), financing activity (FA), or net change in cash (NC). Use NA to indicate that an element was not affected by th event. The first event for the first classification is shown as an example. (Enter any decreases to account balances and cash out Horizontal Statements Models Balance Sheet Income Statement Investment Event Liabilities Cash Securities Retained Earnings Unrealized Revenue/ Gain Gain Expense/ Loss Net income No. Cash Flow (1) Held-to-Maturity (100,000) 100.000 (100,000) A 1 2 3 4 Total (2) Trading 2 3 4 Total (3) Available-for-Sale 1 2 3 4 Total b. What is the amount of net income under each of the three classifications? Held-to-Maturity Trading Available-for-Sale Net Income c. What is the change in cash from operating activities under each of the three classifications? (List any cash outflows with a minus sign.) Operating Activities Held-to-Maturity Trading Available-for-Sale Exercise E-4 Preparing financial statements for investment securities Molten, Inc. began Year 2 with $100,000 in both cash and common stock. The company engaged in the following investment transactions during Year 2 1. Purchased $20,000 of marketable investment securities. 2. Earned $600 cash from Investment revenue. 3. Sold investment securities for $14,000 that cost $10,000. 4. Purchased $7,000 of additional marketable investment securities 5. Determined that the investment securities had a fair value of $22,000 at the end of Year 2 Required Use a vertical statements model to prepare income statements, balance sheets, and statements of cash flow for Molten, Inc., assuming the securities were (a) held to maturity, (b) trading, and (c) available for sale. (Statement of Cash Flows only: Items to be deducted and cash outflows must be indicated with a minus sign.) MOLTEN, INC. Classified as Income Statements Financial Statements For Year Ending Year 2 Held-to- Maturity Nel Income Balance Sheets Available-for- Trading Sale total assets Stockholders' equity Total stockholders' equity Statements of Cash Flows Cash flows from operating activities: Net cash flow from operating activities Cash flows from investing activities: Net cash flow from investing activities Cash flows from financing activities: Net cash flow from financing activities Net change in cash Ending cash balance Exercise E-6 Effect of marketable investment securities transactions on financial statements The following transactions pertain to Harrison Imports for Year 1: Started business by acquiring $30,000 cash from the issue of common stock. 2. Provided $90,000 of services for cash. Invested $35,000 in marketable investment securities. Paid $18,000 of operating expense. Received $500 of investment income from the securities. Invested an additional $16,000 in marketable investment securities. Pald a $2,000 cash dividend to the stockholders. Sold Investment securities that cost $8,000 for $14,000. O. Received another $1,000 in investment income. . Determined the market value of the investment securities at the end of the year was $42,000. Required Use a vertical statements model to prepare a Year 1 income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows, assuming that the marketable investment securities were classified as (a) held to maturity, (b) trading, and (c) available for sale. (Hint: Record the events in accounts prior to preparing the financial statements.) (Record the transactions in the given order. Amounts to be deducted, cash utflows and losses should be indicated with a minus sign.) a) Held to Maturity (a) Held-to-Maturity Beg. Bal End. Bal Cash Investment Securities Beg. Bal. End. Bal Common Stock Dividends Beg. Bal Beg Bal End. Bal. End Bal Service Revenue Investment Income Beg. Bal. Beg. Bal End. Bal End. Bal Gain on Sale of Investment Operating Expenses Beg Bal Beg Bal End Bal (b) Trading End Bal Cash Investment Securities Beg. Bal. Beg Bal. End. Bal End Bal Common Stock Dividends Beg. Bal. Beg Bal End Bal End Bal. Service Revenue Investment Income Beg. Bal Beg Bal End. Bal. End Bal Gain on Sale of Investment Beg Bal Operating Expenses Beg. Bal End Bal Beg Bal End. Bal (Income Statement Account) Unrealized Gain/Loss End. Bal. (c) Available-for-Sale Beg Bal End. Bal. Cash Investment Securities Beg. Bal End Bal Common Stock Dividends Beg. Bal. Beg. Bal. End. Bal End. Bal Accum. Other Comp. Income Unrealized Gain/Loss Service Revenue eg. Bal. Beg Bal. ad. Bal Investment Income End. Bal Gain on Sale of Invest 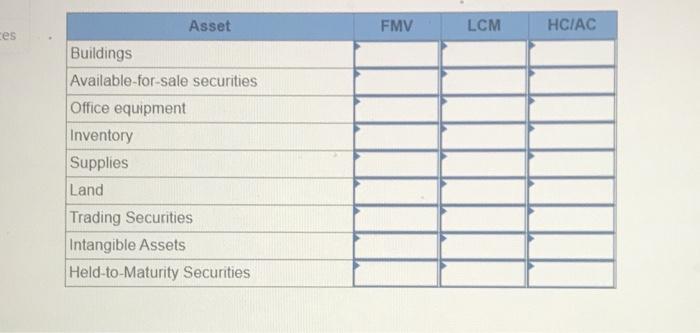



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


