explain with detailed work please tutors.
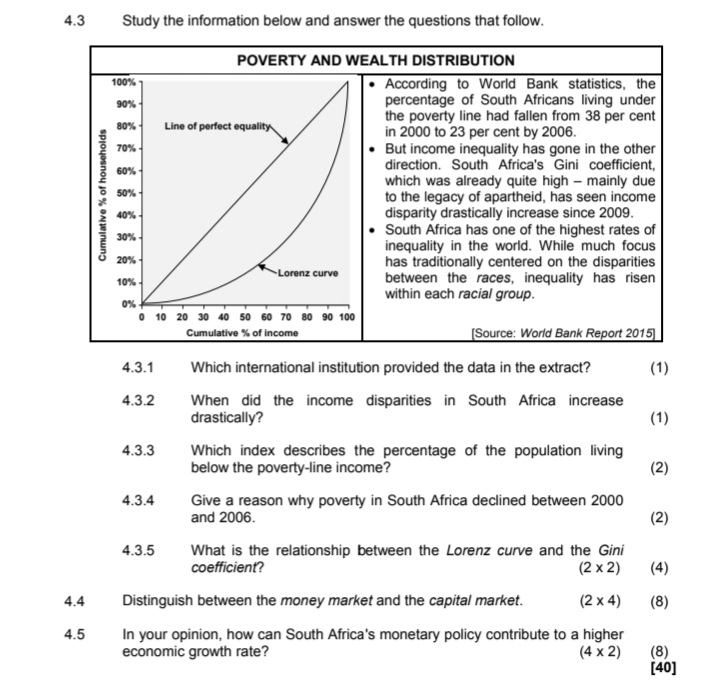
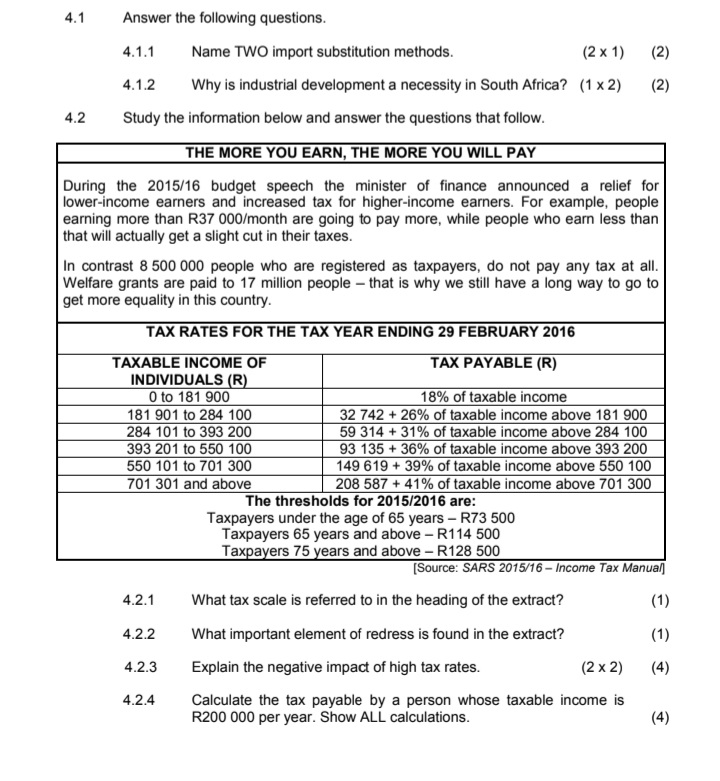
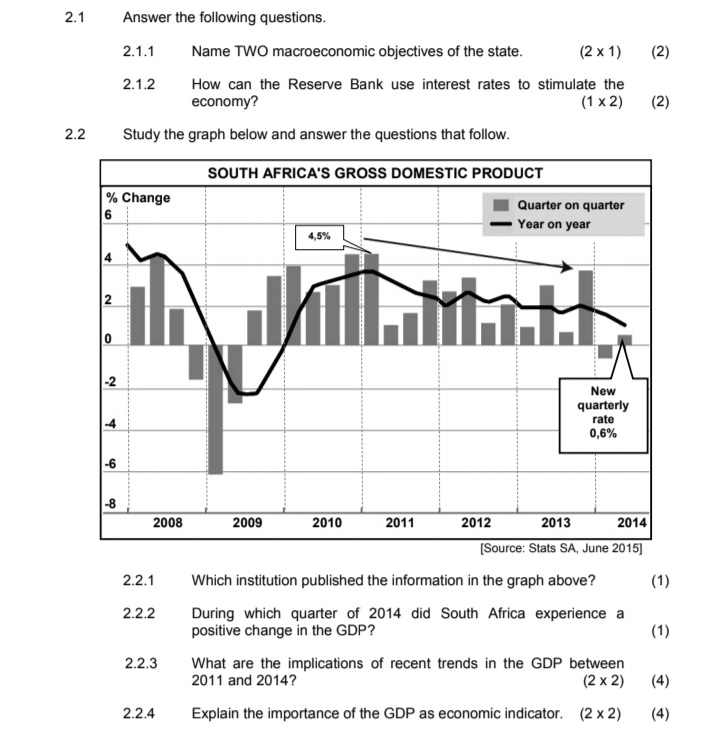
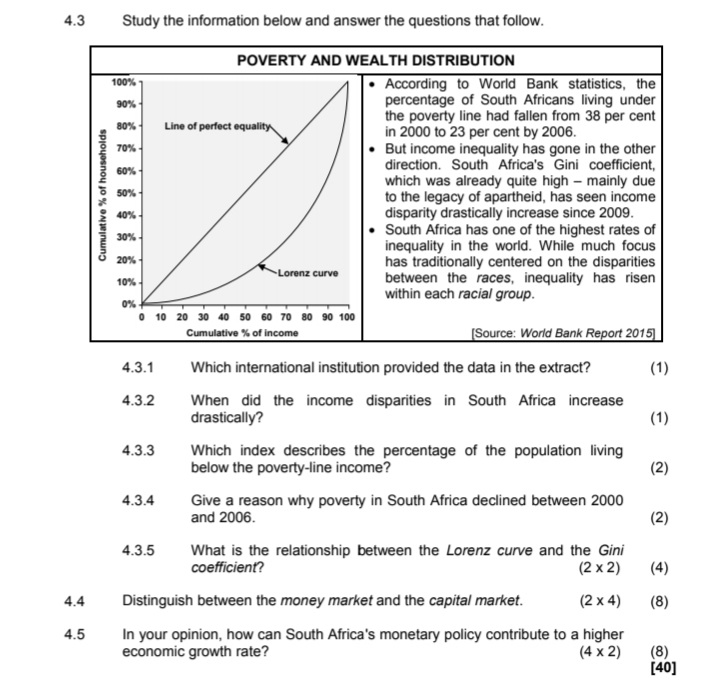
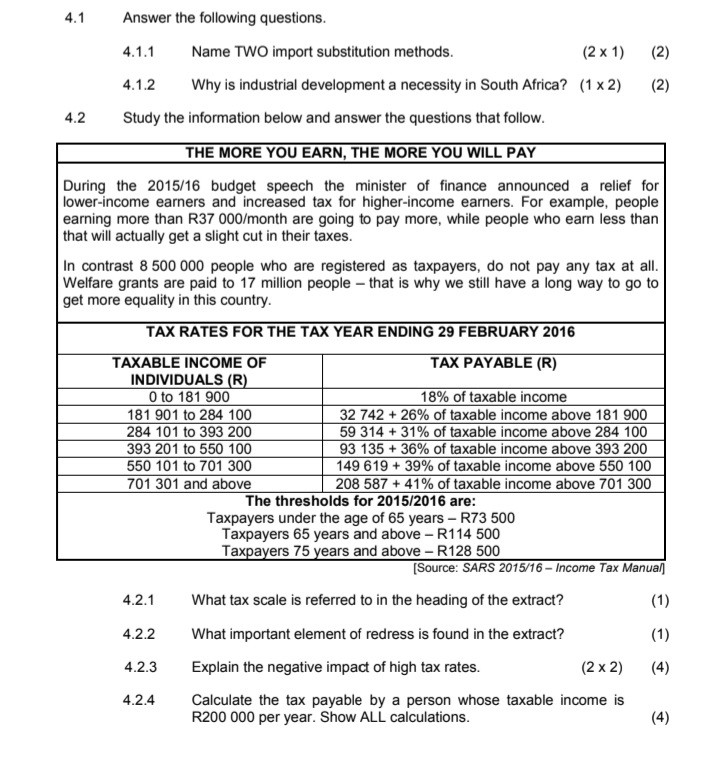
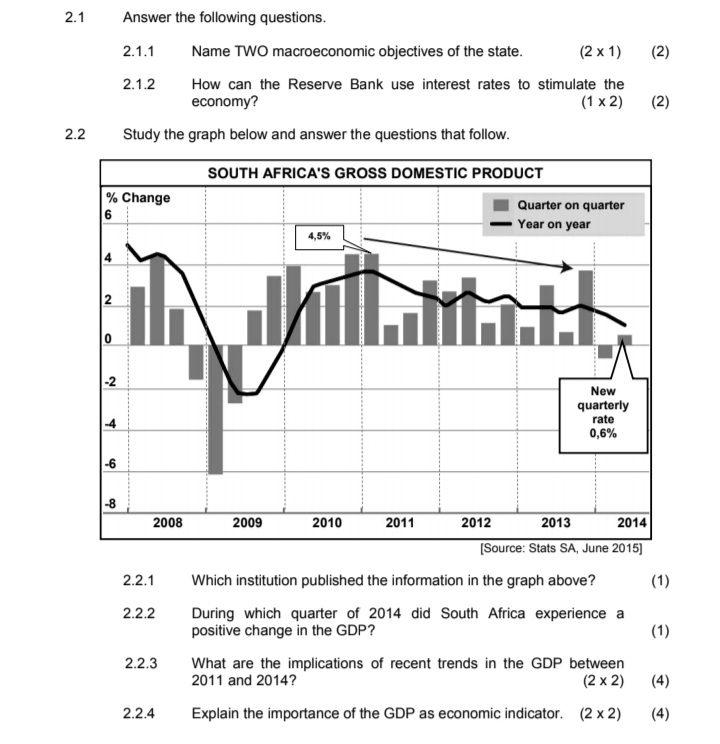
4.3 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow. POVERTY AND WEALTH DISTRIBUTION 100% According to World Bank statistics, the 90% percentage of South Africans living under the poverty line had fallen from 38 per cent 80% Line of perfect equality in 2000 to 23 per cent by 2006. 70% But income inequality has gone in the other 60% direction. South Africa's Gini coefficient, which was already quite high - mainly due 50%% Cumulative % of household to the legacy of apartheid, has seen income 10% disparity drastically increase since 2009. 30% South Africa has one of the highest rates of inequality in the world. While much focus 20% has traditionally centered on the disparities 10%% Lorenz curve between the races, inequality has risen 0% within each racial group. 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Cumulative % of income [Source: World Bank Report 2015] 4.3.1 Which international institution provided the data in the extract? (1) 4.3.2 When did the income disparities in South Africa increase drastically? (1 ) 4.3.3 Which index describes the percentage of the population living below the poverty-line income? (2) 4.3.4 Give a reason why poverty in South Africa declined between 2000 and 2006. (2) 4.3.5 What is the relationship between the Lorenz curve and the Gini coefficient? (2 x2) (4) 4.4 Distinguish between the money market and the capital market. (2 x4) (8) 4.5 In your opinion, how can South Africa's monetary policy contribute to a higher economic growth rate? (4 x 2) (8) [40]4.1 Answer the following questions. 4.1.1 Name TWO import substitution methods. (2 x 1) (2) 4.1.2 Why is industrial development a necessity in South Africa? (1 x 2) (2) 4.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow. THE MORE YOU EARN, THE MORE YOU WILL PAY During the 2015/16 budget speech the minister of finance announced a relief for lower-income earners and increased tax for higher-income earners. For example, people earning more than R37 000/month are going to pay more, while people who earn less than that will actually get a slight cut in their taxes. In contrast 8 500 000 people who are registered as taxpayers, do not pay any tax at all. Welfare grants are paid to 17 million people - that is why we still have a long way to go to get more equality in this country. TAX RATES FOR THE TAX YEAR ENDING 29 FEBRUARY 2016 TAXABLE INCOME OF TAX PAYABLE (R) INDIVIDUALS (R) 0 to 181 900 18% of taxable income 181 901 to 284 100 32 742 + 26% of taxable income above 181 900 284 101 to 393 200 59 314 + 31% of taxable income above 284 100 393 201 to 550 100 93 135 + 36% of taxable income above 393 200 550 101 to 701 300 149 619 + 39% of taxable income above 550 100 701 301 and above 208 587 + 41% of taxable income above 701 300 The thresholds for 2015/2016 are: Taxpayers under the age of 65 years - R73 500 Taxpayers 65 years and above - R114 500 Taxpayers 75 years and above - R128 500 [Source: SARS 2015/16 - Income Tax Manual] 4.2.1 What tax scale is referred to in the heading of the extract? (1) 4.2.2 What important element of redress is found in the extract? (1) 4.2.3 Explain the negative impact of high tax rates. (2 x 2) (4) 4.2.4 Calculate the tax payable by a person whose taxable income is R200 000 per year. Show ALL calculations. (4)2.1 Answer the following questions. 2.1.1 Name TWO macroeconomic objectives of the state. (2 x 1) (2) 2.1.2 How can the Reserve Bank use interest rates to stimulate the economy? (1 x 2) (2) 2.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. SOUTH AFRICA'S GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT % Change 6 Quarter on quarter Year on year 4,5% 2 0 -2 New quarterly -4 rate 0,6% -6 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 (Source: Stats SA, June 2015] 2.2.1 Which institution published the information in the graph above? (1) 2.2.2 During which quarter of 2014 did South Africa experience a positive change in the GDP? (1) 2.2.3 What are the implications of recent trends in the GDP between 2011 and 2014? (2 x 2) ( 4) 2.2.4 Explain the importance of the GDP as economic indicator. (2 x 2) (4)QUESTION 5: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARKS - 40 MINUTES In the global economy countries strive to export more than they import to maximise the benefits of international trade. Examine the supply reasons for international trade. (26) Use a graph and explain how an increase in exports to the USA will affect the value of the rand. (10) [40] QUESTION 6: ECONOMIC PURSUITS 40 MARKS - 40 MINUTES The annual analysis of the economic performances of countries is very important. This is done by international institutions and governments to determine how countries performed in comparison with others. . Analyse the following economic indicators that are used to measure the performance of the economy: > Productivity (maximum 10 marks) >Foreign trade (maximum 16 marks) (26) . Why are comparisons of economic performances of countries important? (10) [40] TOTAL SECTION C: 40 GRAND TOTAL: 150