Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
EXTRACT: RoJo Ltd manufactures a range of summerhouses sold in garden centres around the UK. At the beginning of this financial year RoJo Ltd launched
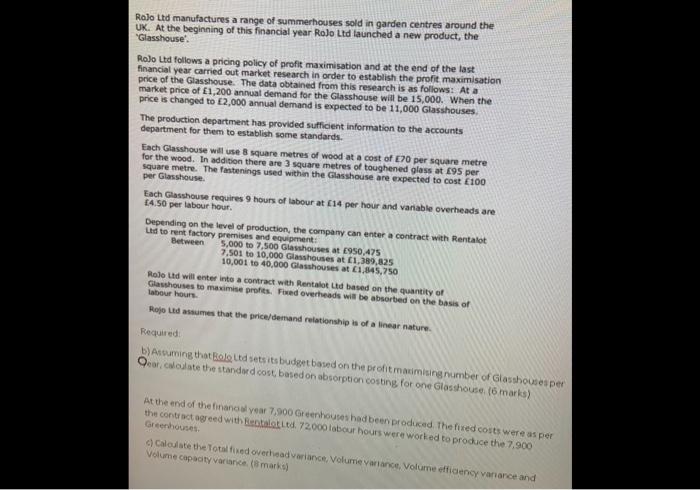

EXTRACT:
RoJo Ltd manufactures a range of summerhouses sold in garden centres around the UK. At the beginning of this financial year RoJo Ltd launched a new product, the Glasshouse.
RoJo Ltd follows a pricing policy of profit maximisation and at the end of the last financial year carried out market research in order to establish the profit maximisation price of the Glasshouse. The data obtained from this research is as follows: At a market price of 1,200 annual demand for the Glasshouse will be 15,000. When the price is changed to 2,000 annual demand is expected to be 11,000 Glasshouses.
The production department has provided sufficient information to the accounts department for them to establish some standards.
Each Glasshouse will use 8 square metres of wood at a cost of 70 per square metre for the wood. In addition there are 3 square metres of toughened glass at 95 per square metre. The fastenings used within the Glasshouse are expected to cost 100 per Glasshouse.
Each Glasshouse requires 9 hours of labour at 14 per hour and variable overheads are 4.50 per labour hour.
Depending on the level of production, the company can enter a contract with Rentalot Ltd to rent factory premises and equipment:
Between
5,000 to 7,500 Glasshouses at 950,475,
7,501 to 10,000 Glasshouses at 1,389,825
10,001 to 40,000 Glasshouses at 1,845,750
RoJo Ltd will enter into a contract with Rentalot Ltd based on the quantity of Glasshouses to maximise profits. Fixed overheads will be absorbed on the basis of labour hours.
Rojo Ltd assumes that the price/demand relationship is of a linear nature.
QUESTION:
1. Assuming that RoJo Ltd sets its budget based on the profit maximising number of Glasshouses per year, calculate the standard cost, based on absorption costing, for one Glasshouse.
2. At the end of the financial year 7,900 Greenhouses had been produced. The fixed costs were as per the contract agreed with Rentalot Ltd. 72,000 labour hours were worked to produce the 7,900 Greenhouses.
Calculate the Total fixed overhead variance, Volume variance, Volume efficiency
variance and Volume capacity variance.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


