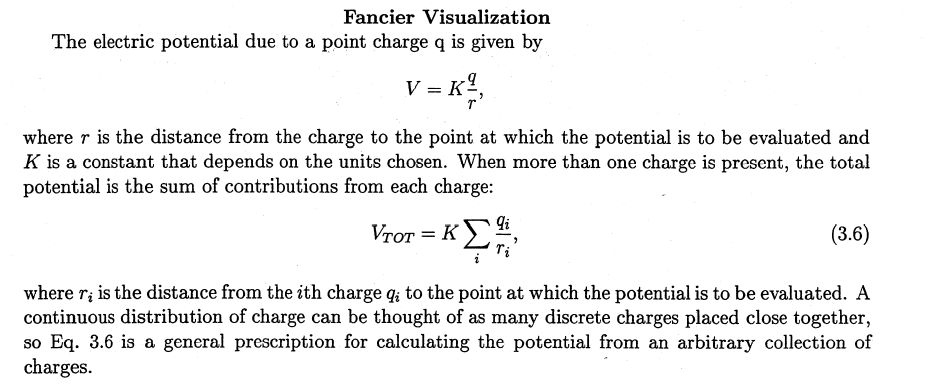
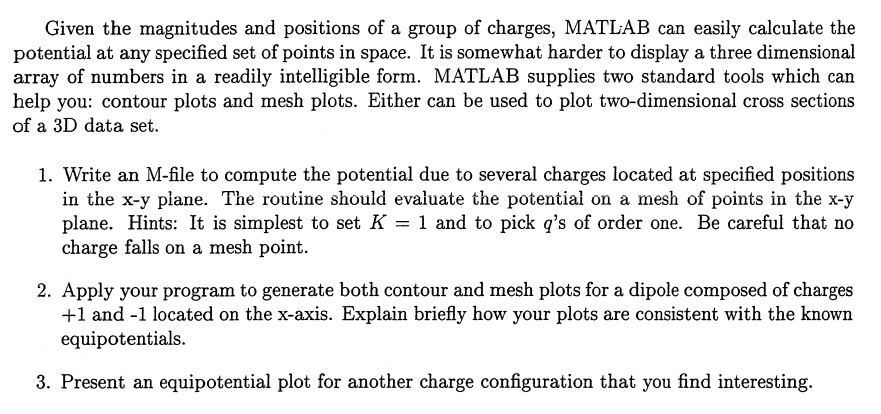
Fancier Visualization The electric potential due to a point charge q is given by V=Krq, where r is the distance from the charge to the point at which the potential is to be evaluated and K is a constant that depends on the units chosen. When more than one charge is present, the total potential is the sum of contributions from each charge: VTOT=Kiriqi, where ri is the distance from the i th charge qi to the point at which the potential is to be evaluated. A continuous distribution of charge can be thought of as many discrete charges placed close together, so Eq. 3.6 is a general prescription for calculating the potential from an arbitrary collection of charges. array of numbers in a readily intelligible form. MATLAB supplies two standard tools which can help you: contour plots and mesh plots. Either can be used to plot two-dimensional cross sections of a 3D data set. 1. Write an M-file to compute the potential due to several charges located at specified positions in the xy plane. The routine should evaluate the potential on a mesh of points in the xy plane. Hints: It is simplest to set K=1 and to pick q 's of order one. Be careful that no charge falls on a mesh point. 2. Apply your program to generate both contour and mesh plots for a dipole composed of charges +1 and 1 located on the x-axis. Explain briefly how your plots are consistent with the known equipotentials. 3. Present an equipotential plot for another charge configuration that you find interesting. Fancier Visualization The electric potential due to a point charge q is given by V=Krq, where r is the distance from the charge to the point at which the potential is to be evaluated and K is a constant that depends on the units chosen. When more than one charge is present, the total potential is the sum of contributions from each charge: VTOT=Kiriqi, where ri is the distance from the i th charge qi to the point at which the potential is to be evaluated. A continuous distribution of charge can be thought of as many discrete charges placed close together, so Eq. 3.6 is a general prescription for calculating the potential from an arbitrary collection of charges. array of numbers in a readily intelligible form. MATLAB supplies two standard tools which can help you: contour plots and mesh plots. Either can be used to plot two-dimensional cross sections of a 3D data set. 1. Write an M-file to compute the potential due to several charges located at specified positions in the xy plane. The routine should evaluate the potential on a mesh of points in the xy plane. Hints: It is simplest to set K=1 and to pick q 's of order one. Be careful that no charge falls on a mesh point. 2. Apply your program to generate both contour and mesh plots for a dipole composed of charges +1 and 1 located on the x-axis. Explain briefly how your plots are consistent with the known equipotentials. 3. Present an equipotential plot for another charge configuration that you find interesting








