


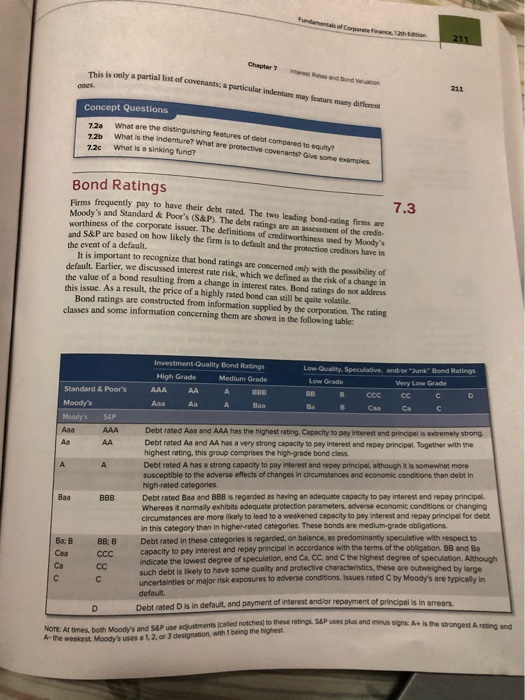

Features of a Microsoft bond Read and make notes from pages 208 to 212 (From topic The Indenture" to "7.3 Bond Ratings"). Based on what you read, and what you learned in class today, make three posts in the following manner A. In the first post answer the following questions 1 to 6. 1. Go to page 207 in your text book and refer to the table titled "Features of a Microsoft Bond' Explain each of the terms amount of issue date of issue, maturity, face value, annual coupon, offer price. coupon payment dates, security, Sinking fund. Call provision, call price, deferred call, and rating in the context of Microsoft Bond. Do not give general definitions. Explain what each term means in this particular bond issue only. (Read the textbook. Each term is very well explained.) 2. Why is it good for the lender to buy a secured bond? Is debenture a secured bond? How is a bond different from a note? (Refer to the text book 3. Why do lenders prefer sinking fund option in a bond? Explain 4. What is a deferred call (refer to the text book please? How will Microsoft decide on the price to buy back if it calls the bond pre-maturedly? Explain 5. What are junk bonds? if you were to buy a bond, would you go for an investment grade bond or speculative bond? Which bond rating is the best? Explain 6. What is a senior debt and what is a subordinate debt? Explain. B. The second and third posts will be responses to atleast two of your classmates. C. The posts and responses have to be original meaningful relevant Insightful analytical and substantial Your posts are due on 28th April 11 59 PM Your posts will be graded based on whether you have submitted all three posts on time, the quality of your responses and usage of correct grammar and spelling PART 3 V tion of future b THE INDENTURE The indenture is the written agreement between the corporate the risors. It is sometimes referred to as the dead of Usually hapa) is appointed by the corporation to represent the bondholders (1) make sure the arms of the indenre are obeyed man Metro described in the following pageland (3) represent the bondholders in de the company defaults on its payments to them. diere is a legal documente care several hundred makes for tedious reading. It is an important document become following provisions: 1. The basic terms of the bonds 2. The total amount of boods issued 3. A description of property used as security 4. The repayment arrangements 5. The call provisions 6. Details of the protective covenants We discuss these features et e gray includes Terms of a Bond Corporate bonds usually have a face value (that isa de of $1,000, although par values of $2.000 like the Microsoft bond have become common Other par values also exist. For example, municipal bonds often have of 5000, and Treasury bonds with par values of $10,000 or $100,000 ure principal e is s ed on the band certificate. So, if a corporation wanted sl million 1.000 bonds would have to be sold. The per value (that is, the initiala value of a bond is almost always the same as the face value, and the terms and changeably in practice Corporate bonds are usually in registered form. For example, the indenture as follows: registered form The form of bonden C hoof each bond payment is made to the owner of record Interest is payable semiannually on July 1 and January 1 of each year to person in whose name the bond is registered at the close of business og June 18 or December 15, respectively. bearer form The form of borde in which the bond issued thout record of the owner's name payment is made to whoever holds the bond This means that the company has a registrar who will record the ownership of and record any changes in ownership. The company will pay the interest and principals check mailed directly to the address of the owner of record. A corporate bond may be ne tered and have attached "coupons." To obtain an interest payment, the owner musste a coupon from the bond certificate and send it to the company registrar (the paying Alternatively, the bond could be in bearer form. This means that the certificate is the basic evidence of ownership, and the corporation will pay the bearer." Ownership is not otherwise recorded, and, as with a registered bond with attached coupons, the holder of the bond certificate detaches the coupons and sends them to the company to receive yol There are two drawbacks to bearer bonds. First, they are difficult to recover if they lost or stolen. Second, because the company does not know who owns its bonds, it can notify bondholders of important events. Bearer bonds were once the dominant pel they are now much less common (in the United States) than registered bonds is Ay the fether bonds The words on agreement or loan contract are usually used for privately placed debt and termom Corporate Finance Chapter Bone www Security Deht to protect the bondholder Collateral is a gener stocks) that are pledged as often involve a pledge of Debt securities are classified according to the collateralmente ed anal is a general term that frequently means securities for example, be d are pledged as security for payment of debt. For example, collateral trust beds wolve a pledge of common stock held by the corporation. Howgst the crm collat al is commonly used to refer to any asset pledged Wartage securities are secured by a mortgage on the real property of the brow a rty involved is usually real estate--for example, land or buildings. The legal ument that describes the mortgage is called a mortgage Instindre or tradend. Cometimes mortgages are on specific property, such as a railroad car More often, blan- ortages are used. A blanket mortgage pledges all the real property owned by the The property involved is usu company." Bonds frequently represent unsecured obligations of the company. A debenture is a debenture secured bond, for which no specific pledge of property is made. The term note is gene r al e lly used for such instruments if the maturity of the unsecured bond is less than 10 years of 10 years or more hen the bond is originally issued. Debenture holders have a claim only on property not note wherwise pledged in other words, the property that remains after mortgages and collat M a t h al trusts are taken into account. The Microsoft bonds in the table are an example of such mature 10 year. an issue. The terminology that we use here and elsewhere in this chapter is standard in the United States. Outside the United States, these same terms can have different meanings. For ex- ample, bonds issued by the British government "gilts") are called treasurystock." Also, in the United Kingdom, a debenture is a secured obligation At the current time, public bonds issued in the United States by industrial and financial companies are typically debentures. Most utility and railroad bonds are secured by a pledge of assets. Seniority In general terms, seniority indicates preference in position over other lend- ers, and debts are sometimes labeled as senior or junior to indicate seniority. Some debt is subordinated, as in, for example, a subordinated debenture. In the event of default, holders of subordinated debt must give preference to other spec- ified creditors. Usually, this means that the subordinated lenders will be paid off only after the specified creditors have been compensated. However, debt cannot be subordinated to equity. The Securities Industry and Financial Markets Association www.sme. Repayment Bonds can be repaid at maturity, at which time the bondholder will re- ceive the stated, or face, value of the bond; or they may be repaid in part or in entirety before maturity. Early repayment in some form is more typical and is often handled through a sinking fund. A sinking fund is an account managed by the bond trustee for the purpose of repaying sinking fund the bonds. The company makes annual payments to the trustee, who then uses the funds to Account managed by the bond rusted for any bond retire a portion of the debt. The trustee does this by either buying up some of the bonds in redemption the market or calling in a fraction of the outstanding bonds. This second option is discussed in the next section. There are many different kinds of sinking fund arrangements, and the details are spelled out in the indenture. For example: 1. Some sinking funds start about 10 years after the initial issuance. 2. Some sinkine funds establish equal payments over the life of the bond. Real property includes land and things "affixed thereto." It does not include cash or inventories of Future Cash Flows PART 3 lity of . 3. Some high-quality bond issues establish payments to the sinking funds ficient to redeem the entire issue. As a consequence, there is the possibile "halloon payment at maturity atebondisse lum. The amount pitially the into the side. This makes cars. Forum call, has become wide tholders receive holders don't sufferal The Call Provision A cal provision allows the company to repunch call provision or all of the hond issue at stated prices over a specific period. Corporate conception callable purchase a at is, the per nd at a specific Generally, the call price is above the bond's stated value that is er Value difference between the call price and the stated value is the call premi the call premium may become smaller over time. One arrangement is to in premium equal to the annual coupon payment and then make it decline price c he per lo date moves closer to the time of maturity. Cal provisions are often not operative during the first part of a bone the call provision less of a worry for bondholders in the bond's early deferred call provision company might be prohibited from calling its bonds for the first 10 years. This is a defen Acal proporting the call provision. During this period of prohibition, the bond is said to be protected company to redning a In recent years, a new type of call provision, a "make-whole" call spread in the corporate bond market. With such a feature, bondhold mately what the bands are worth if they are called. Because bondholdered call protected bond A bond that during a certa in the event of a call, they are made whole pe cannot be redeemed by To determine the make-whole call price, we calculate the present value of interest and principal payments at a rate specified in the indenture. For Our Microsoft issue, we see that the discount rate is "Treasury rate plus means is that we determine the discount rate by first finding a US Treasur same maturity. We calculate the yield to maturity on the Treasury issue and the percent to get the discount rate we use. Notise that with a make-whole call provision, the call price is higher when are lower and vice versa (why?). Also notice that, as is common with a make the Microsoft issue does not have a deferred call feature. Why might in concerned about the absence of this feature? protective covenant Protective Covenants A part of the inderture A protective covenant is that part of the indenture agreement that limits certain actions a company might otherwise wish to take during the certain actions that might be taken during the form of the term of the loan. Protective covenants can be classified into two types: negative con and positive (or affirmative) covenants. alat of the remaining , IS Treasury so with the y issue and then add on 25 ce is higher when interest rates with a make-whole il der's interest A negative covenant is a "thou shall not type of covenant. It limits or prohibits action the company might take. Here are some typical examples: 1. The firm must limit the amount of dividends it pays according to some formula 2. The firm cannot pledge any assets to other lenders. 3. The firm cannot merge with another firm. 4. The firm cannot sell or lease any major assets without approval by the lender 5. The firm cannot issue additional long-term debt. A positive covenant is a "thou shalt type of covenant. It specifies an action the co- puny agrees to take or a condition the company must abide by. Here are some 1. The company must maintain its working capital at or above some specified level. 2. The company must periodically furnish audited financial statements to the che 3. The firm must maintain any collateral or security in good condition. Want detailed information about the amount and terms of the debt issued by a particular firm! Check out ts latest financial statements by seaching SEC filings at www.sec.gov 211 Chapter is is only a partial list of covenants a particular indenture may different Concept Questions 120 2.20 What are the distinguishing features of debt compared to our What is the indendure? What are protective covenants Give some examples 720 What is a sinking fun Bond Ratings s frequently pay to have their debt rated. The two leading bonding firms are Moody's and Standard & Poor's (S&P). The debt ratings are an assessment of the credit arthiness of the corporate issuer. The definitions of creditworthiness used by Moody's S&P are based on how likely the firm is to default and the protection creditors have in the event of a default It is important to recognize that bond ratings are concerned only with the possibility of default. Earlier, we discussed interest rate risk, which we defined as the risk of a change in the value of a bond resulting from a change in interest rates Bond ratings do not address this issue. As a result, the price of a highly rated bond can still be quite volatile. Bond ratings are constructed from information supplied by the corporation. The rating classes and some information concerning them are shown in the following tables Investment-Quality Bond Ratings High Grade Medium Grade AAA AA A BBB Low Quality Speculative and/ or "Junk Bond Ratings Low Grade Very Low Grade B Standard & Poor's Moody's Moody's S&P AAA Debt rated Ass and AAA has the highest rating. Capacity to pay interest and principal is extremely strong Debt rated Aa and AA has a very strong capacity to pay interest and repay principal. Together with the highest rating, this group comprises the high-grade bond class. Debt rated A has a strong capacity to pay interest and repay principal, although it is somewhat more susceptible to the adverse effects of changes in circumstances and economic conditions than debt in high-rated categories Debt rated Baa and BBB is regarded as having an adequate capacity to pay interest and repay principal Whereas normally exhibits adequate protection parameters, adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to lead to a weakened capacity to pay interest and repay principal for det In this category than in higher-rated categories. These bonds are medium-grade obligations Debt rated in these categories is regarded, on balance, as predominantly speculative with respect to capacity to pay interest and repay principal in accordance with the terms of the obligation, BB and Ba Indicate the lowest degree of speculation, and Ca, CC, and the highest degree of speculation. Alhouah such debt is likely to have some quality and protective characteristics, these are outweighed by large uncertainties or major risk exposures to adverse conditions, issues rated C by Moody's are typically in default Doht rated Disin default, and payment of interest andilor repayment of principal is in arrears BBB CCC NOTE: At times, both Moods and supuse adjustments called notches to these ratings. S&Puses plus and minus von notches to these ratings SAP ses plus and minus signs. At is the strongest A rating and A-the weakest Moody's uses at 2. 3 designation with 1 being the highest PART 3 womens the 100 year el to The highest rating a firm's debt can have is AAA or Aaland such des the best quality and to have the lowest degree of risk. For example, the 100 is we discussed earlier was originally rated AAA. This rating is not awarde As of Juary 2018, only two financial US, companies, Johnson & John osoft had AAA ratings. AA or Aa ratings indicate very good quality deht . Mi debt and much or "junk." bonds ated at least BBB by S&P 2016, India-based 10-year shed retailer The Gup more common A large part of corporale borrowing takes the form of low-grade, or these o grade corporate bonds are rated at all, they are rated below investme frade by the major rating agencies, Investment grade bonds are bonds rated at least Baby Moody's Rating species don't always agree. To illustrate, some bonds are known or hands. The reason is that they are rated triple-B (or Baa) by One role y one rating agens de r Ratry another, a "split rating. For example, in February 2016 any and stile and chemical company Standard Industries sold an issue of 10- BBB-by SAP and Baby Moody's A band's credit rating can change as the issue's financial strength improve rules remolc, in May 2016, Fitch Ratings cut the bond rating on alldeleri from BBB B., lowering the company's bond rating from investment hand status Bands that drop into junk territory like this are called fell to jak concerned about the decline in same-store sales and gross margin at the com Credit ratings are important because defaults really do occur, and when the tors can lose heavily. For example, in 2000, AmeriServe Food Distributie 1 sud urants L as Hur king it everything burgers to defaulted on $200 million in junk bonds. After the default, the bonds traded in on the dollar, leaving investors with a loss of more than $160 million Even wone in AmeriServe's case, the bonds had been issued only four months thereby making AmeriServe an NCAA champion. Although that might be a good a college basketball team such as the University of Kentucky Wildcats, in the hood it means "No Coupon At All." and it's not a good thing for investors. lled fallen angels. Finch do occur, and when they do, inves. Usport dont go to org w eb clock tucky Wildcats, in the bond market Concept Questions 238 What does a bond rating say about the risk of fluctuations in a bongs resulting from interest rate changes? 7:36 What is a junk bond? 7.4 Some Different Types of Bonds Thus far we have considered only "plain vanilla corporate bonds. In this section, we briefly look at bonds issued by governments and also at bonds with unusual features GOVERNMENT BONDS The biggest borrower in the world-by a wide marginis everybody's favorite family member, Uncle Sam. In early 2018, the total debt of the U.S. government was $20 milion or about 563,000 per citizen (and growing!). When the government wishes to bor money for more than one year, it sells what are known as Treasury notes and bonds to $3,000 per citirem 2018, the total debe fargin-is everybody's Features of a Microsoft bond Read and make notes from pages 208 to 212 (From topic The Indenture" to "7.3 Bond Ratings"). Based on what you read, and what you learned in class today, make three posts in the following manner A. In the first post answer the following questions 1 to 6. 1. Go to page 207 in your text book and refer to the table titled "Features of a Microsoft Bond' Explain each of the terms amount of issue date of issue, maturity, face value, annual coupon, offer price. coupon payment dates, security, Sinking fund. Call provision, call price, deferred call, and rating in the context of Microsoft Bond. Do not give general definitions. Explain what each term means in this particular bond issue only. (Read the textbook. Each term is very well explained.) 2. Why is it good for the lender to buy a secured bond? Is debenture a secured bond? How is a bond different from a note? (Refer to the text book 3. Why do lenders prefer sinking fund option in a bond? Explain 4. What is a deferred call (refer to the text book please? How will Microsoft decide on the price to buy back if it calls the bond pre-maturedly? Explain 5. What are junk bonds? if you were to buy a bond, would you go for an investment grade bond or speculative bond? Which bond rating is the best? Explain 6. What is a senior debt and what is a subordinate debt? Explain. B. The second and third posts will be responses to atleast two of your classmates. C. The posts and responses have to be original meaningful relevant Insightful analytical and substantial Your posts are due on 28th April 11 59 PM Your posts will be graded based on whether you have submitted all three posts on time, the quality of your responses and usage of correct grammar and spelling PART 3 V tion of future b THE INDENTURE The indenture is the written agreement between the corporate the risors. It is sometimes referred to as the dead of Usually hapa) is appointed by the corporation to represent the bondholders (1) make sure the arms of the indenre are obeyed man Metro described in the following pageland (3) represent the bondholders in de the company defaults on its payments to them. diere is a legal documente care several hundred makes for tedious reading. It is an important document become following provisions: 1. The basic terms of the bonds 2. The total amount of boods issued 3. A description of property used as security 4. The repayment arrangements 5. The call provisions 6. Details of the protective covenants We discuss these features et e gray includes Terms of a Bond Corporate bonds usually have a face value (that isa de of $1,000, although par values of $2.000 like the Microsoft bond have become common Other par values also exist. For example, municipal bonds often have of 5000, and Treasury bonds with par values of $10,000 or $100,000 ure principal e is s ed on the band certificate. So, if a corporation wanted sl million 1.000 bonds would have to be sold. The per value (that is, the initiala value of a bond is almost always the same as the face value, and the terms and changeably in practice Corporate bonds are usually in registered form. For example, the indenture as follows: registered form The form of bonden C hoof each bond payment is made to the owner of record Interest is payable semiannually on July 1 and January 1 of each year to person in whose name the bond is registered at the close of business og June 18 or December 15, respectively. bearer form The form of borde in which the bond issued thout record of the owner's name payment is made to whoever holds the bond This means that the company has a registrar who will record the ownership of and record any changes in ownership. The company will pay the interest and principals check mailed directly to the address of the owner of record. A corporate bond may be ne tered and have attached "coupons." To obtain an interest payment, the owner musste a coupon from the bond certificate and send it to the company registrar (the paying Alternatively, the bond could be in bearer form. This means that the certificate is the basic evidence of ownership, and the corporation will pay the bearer." Ownership is not otherwise recorded, and, as with a registered bond with attached coupons, the holder of the bond certificate detaches the coupons and sends them to the company to receive yol There are two drawbacks to bearer bonds. First, they are difficult to recover if they lost or stolen. Second, because the company does not know who owns its bonds, it can notify bondholders of important events. Bearer bonds were once the dominant pel they are now much less common (in the United States) than registered bonds is Ay the fether bonds The words on agreement or loan contract are usually used for privately placed debt and termom Corporate Finance Chapter Bone www Security Deht to protect the bondholder Collateral is a gener stocks) that are pledged as often involve a pledge of Debt securities are classified according to the collateralmente ed anal is a general term that frequently means securities for example, be d are pledged as security for payment of debt. For example, collateral trust beds wolve a pledge of common stock held by the corporation. Howgst the crm collat al is commonly used to refer to any asset pledged Wartage securities are secured by a mortgage on the real property of the brow a rty involved is usually real estate--for example, land or buildings. The legal ument that describes the mortgage is called a mortgage Instindre or tradend. Cometimes mortgages are on specific property, such as a railroad car More often, blan- ortages are used. A blanket mortgage pledges all the real property owned by the The property involved is usu company." Bonds frequently represent unsecured obligations of the company. A debenture is a debenture secured bond, for which no specific pledge of property is made. The term note is gene r al e lly used for such instruments if the maturity of the unsecured bond is less than 10 years of 10 years or more hen the bond is originally issued. Debenture holders have a claim only on property not note wherwise pledged in other words, the property that remains after mortgages and collat M a t h al trusts are taken into account. The Microsoft bonds in the table are an example of such mature 10 year. an issue. The terminology that we use here and elsewhere in this chapter is standard in the United States. Outside the United States, these same terms can have different meanings. For ex- ample, bonds issued by the British government "gilts") are called treasurystock." Also, in the United Kingdom, a debenture is a secured obligation At the current time, public bonds issued in the United States by industrial and financial companies are typically debentures. Most utility and railroad bonds are secured by a pledge of assets. Seniority In general terms, seniority indicates preference in position over other lend- ers, and debts are sometimes labeled as senior or junior to indicate seniority. Some debt is subordinated, as in, for example, a subordinated debenture. In the event of default, holders of subordinated debt must give preference to other spec- ified creditors. Usually, this means that the subordinated lenders will be paid off only after the specified creditors have been compensated. However, debt cannot be subordinated to equity. The Securities Industry and Financial Markets Association www.sme. Repayment Bonds can be repaid at maturity, at which time the bondholder will re- ceive the stated, or face, value of the bond; or they may be repaid in part or in entirety before maturity. Early repayment in some form is more typical and is often handled through a sinking fund. A sinking fund is an account managed by the bond trustee for the purpose of repaying sinking fund the bonds. The company makes annual payments to the trustee, who then uses the funds to Account managed by the bond rusted for any bond retire a portion of the debt. The trustee does this by either buying up some of the bonds in redemption the market or calling in a fraction of the outstanding bonds. This second option is discussed in the next section. There are many different kinds of sinking fund arrangements, and the details are spelled out in the indenture. For example: 1. Some sinking funds start about 10 years after the initial issuance. 2. Some sinkine funds establish equal payments over the life of the bond. Real property includes land and things "affixed thereto." It does not include cash or inventories of Future Cash Flows PART 3 lity of . 3. Some high-quality bond issues establish payments to the sinking funds ficient to redeem the entire issue. As a consequence, there is the possibile "halloon payment at maturity atebondisse lum. The amount pitially the into the side. This makes cars. Forum call, has become wide tholders receive holders don't sufferal The Call Provision A cal provision allows the company to repunch call provision or all of the hond issue at stated prices over a specific period. Corporate conception callable purchase a at is, the per nd at a specific Generally, the call price is above the bond's stated value that is er Value difference between the call price and the stated value is the call premi the call premium may become smaller over time. One arrangement is to in premium equal to the annual coupon payment and then make it decline price c he per lo date moves closer to the time of maturity. Cal provisions are often not operative during the first part of a bone the call provision less of a worry for bondholders in the bond's early deferred call provision company might be prohibited from calling its bonds for the first 10 years. This is a defen Acal proporting the call provision. During this period of prohibition, the bond is said to be protected company to redning a In recent years, a new type of call provision, a "make-whole" call spread in the corporate bond market. With such a feature, bondhold mately what the bands are worth if they are called. Because bondholdered call protected bond A bond that during a certa in the event of a call, they are made whole pe cannot be redeemed by To determine the make-whole call price, we calculate the present value of interest and principal payments at a rate specified in the indenture. For Our Microsoft issue, we see that the discount rate is "Treasury rate plus means is that we determine the discount rate by first finding a US Treasur same maturity. We calculate the yield to maturity on the Treasury issue and the percent to get the discount rate we use. Notise that with a make-whole call provision, the call price is higher when are lower and vice versa (why?). Also notice that, as is common with a make the Microsoft issue does not have a deferred call feature. Why might in concerned about the absence of this feature? protective covenant Protective Covenants A part of the inderture A protective covenant is that part of the indenture agreement that limits certain actions a company might otherwise wish to take during the certain actions that might be taken during the form of the term of the loan. Protective covenants can be classified into two types: negative con and positive (or affirmative) covenants. alat of the remaining , IS Treasury so with the y issue and then add on 25 ce is higher when interest rates with a make-whole il der's interest A negative covenant is a "thou shall not type of covenant. It limits or prohibits action the company might take. Here are some typical examples: 1. The firm must limit the amount of dividends it pays according to some formula 2. The firm cannot pledge any assets to other lenders. 3. The firm cannot merge with another firm. 4. The firm cannot sell or lease any major assets without approval by the lender 5. The firm cannot issue additional long-term debt. A positive covenant is a "thou shalt type of covenant. It specifies an action the co- puny agrees to take or a condition the company must abide by. Here are some 1. The company must maintain its working capital at or above some specified level. 2. The company must periodically furnish audited financial statements to the che 3. The firm must maintain any collateral or security in good condition. Want detailed information about the amount and terms of the debt issued by a particular firm! Check out ts latest financial statements by seaching SEC filings at www.sec.gov 211 Chapter is is only a partial list of covenants a particular indenture may different Concept Questions 120 2.20 What are the distinguishing features of debt compared to our What is the indendure? What are protective covenants Give some examples 720 What is a sinking fun Bond Ratings s frequently pay to have their debt rated. The two leading bonding firms are Moody's and Standard & Poor's (S&P). The debt ratings are an assessment of the credit arthiness of the corporate issuer. The definitions of creditworthiness used by Moody's S&P are based on how likely the firm is to default and the protection creditors have in the event of a default It is important to recognize that bond ratings are concerned only with the possibility of default. Earlier, we discussed interest rate risk, which we defined as the risk of a change in the value of a bond resulting from a change in interest rates Bond ratings do not address this issue. As a result, the price of a highly rated bond can still be quite volatile. Bond ratings are constructed from information supplied by the corporation. The rating classes and some information concerning them are shown in the following tables Investment-Quality Bond Ratings High Grade Medium Grade AAA AA A BBB Low Quality Speculative and/ or "Junk Bond Ratings Low Grade Very Low Grade B Standard & Poor's Moody's Moody's S&P AAA Debt rated Ass and AAA has the highest rating. Capacity to pay interest and principal is extremely strong Debt rated Aa and AA has a very strong capacity to pay interest and repay principal. Together with the highest rating, this group comprises the high-grade bond class. Debt rated A has a strong capacity to pay interest and repay principal, although it is somewhat more susceptible to the adverse effects of changes in circumstances and economic conditions than debt in high-rated categories Debt rated Baa and BBB is regarded as having an adequate capacity to pay interest and repay principal Whereas normally exhibits adequate protection parameters, adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to lead to a weakened capacity to pay interest and repay principal for det In this category than in higher-rated categories. These bonds are medium-grade obligations Debt rated in these categories is regarded, on balance, as predominantly speculative with respect to capacity to pay interest and repay principal in accordance with the terms of the obligation, BB and Ba Indicate the lowest degree of speculation, and Ca, CC, and the highest degree of speculation. Alhouah such debt is likely to have some quality and protective characteristics, these are outweighed by large uncertainties or major risk exposures to adverse conditions, issues rated C by Moody's are typically in default Doht rated Disin default, and payment of interest andilor repayment of principal is in arrears BBB CCC NOTE: At times, both Moods and supuse adjustments called notches to these ratings. S&Puses plus and minus von notches to these ratings SAP ses plus and minus signs. At is the strongest A rating and A-the weakest Moody's uses at 2. 3 designation with 1 being the highest PART 3 womens the 100 year el to The highest rating a firm's debt can have is AAA or Aaland such des the best quality and to have the lowest degree of risk. For example, the 100 is we discussed earlier was originally rated AAA. This rating is not awarde As of Juary 2018, only two financial US, companies, Johnson & John osoft had AAA ratings. AA or Aa ratings indicate very good quality deht . Mi debt and much or "junk." bonds ated at least BBB by S&P 2016, India-based 10-year shed retailer The Gup more common A large part of corporale borrowing takes the form of low-grade, or these o grade corporate bonds are rated at all, they are rated below investme frade by the major rating agencies, Investment grade bonds are bonds rated at least Baby Moody's Rating species don't always agree. To illustrate, some bonds are known or hands. The reason is that they are rated triple-B (or Baa) by One role y one rating agens de r Ratry another, a "split rating. For example, in February 2016 any and stile and chemical company Standard Industries sold an issue of 10- BBB-by SAP and Baby Moody's A band's credit rating can change as the issue's financial strength improve rules remolc, in May 2016, Fitch Ratings cut the bond rating on alldeleri from BBB B., lowering the company's bond rating from investment hand status Bands that drop into junk territory like this are called fell to jak concerned about the decline in same-store sales and gross margin at the com Credit ratings are important because defaults really do occur, and when the tors can lose heavily. For example, in 2000, AmeriServe Food Distributie 1 sud urants L as Hur king it everything burgers to defaulted on $200 million in junk bonds. After the default, the bonds traded in on the dollar, leaving investors with a loss of more than $160 million Even wone in AmeriServe's case, the bonds had been issued only four months thereby making AmeriServe an NCAA champion. Although that might be a good a college basketball team such as the University of Kentucky Wildcats, in the hood it means "No Coupon At All." and it's not a good thing for investors. lled fallen angels. Finch do occur, and when they do, inves. Usport dont go to org w eb clock tucky Wildcats, in the bond market Concept Questions 238 What does a bond rating say about the risk of fluctuations in a bongs resulting from interest rate changes? 7:36 What is a junk bond? 7.4 Some Different Types of Bonds Thus far we have considered only "plain vanilla corporate bonds. In this section, we briefly look at bonds issued by governments and also at bonds with unusual features GOVERNMENT BONDS The biggest borrower in the world-by a wide marginis everybody's favorite family member, Uncle Sam. In early 2018, the total debt of the U.S. government was $20 milion or about 563,000 per citizen (and growing!). When the government wishes to bor money for more than one year, it sells what are known as Treasury notes and bonds to $3,000 per citirem 2018, the total debe fargin-is everybody's












