Question
Figure 1. Four different bonds (W, X, Y, and Z) in a DNA molecule Figure 1 represents a segment of DNA. Radiation can damage the
Figure 1. Four different bonds (W, X, Y, and Z) in a DNA molecule
Figure 1 represents a segment of DNA. Radiation can damage the nucleotides in a DNA molecule. To repair some types of damage, a single nucleotide can be removed from a DNA molecule and replaced with an undamaged nucleotide. Which of the four labeled bonds in Figure 1 could be broken to remove and replace the cytosine nucleotide without affecting the biological information coded in the DNA molecule?
A. Bond X only
B. Bond W only
C. Bonds Y and Z at the same time
D. Bonds W and Z at the same time
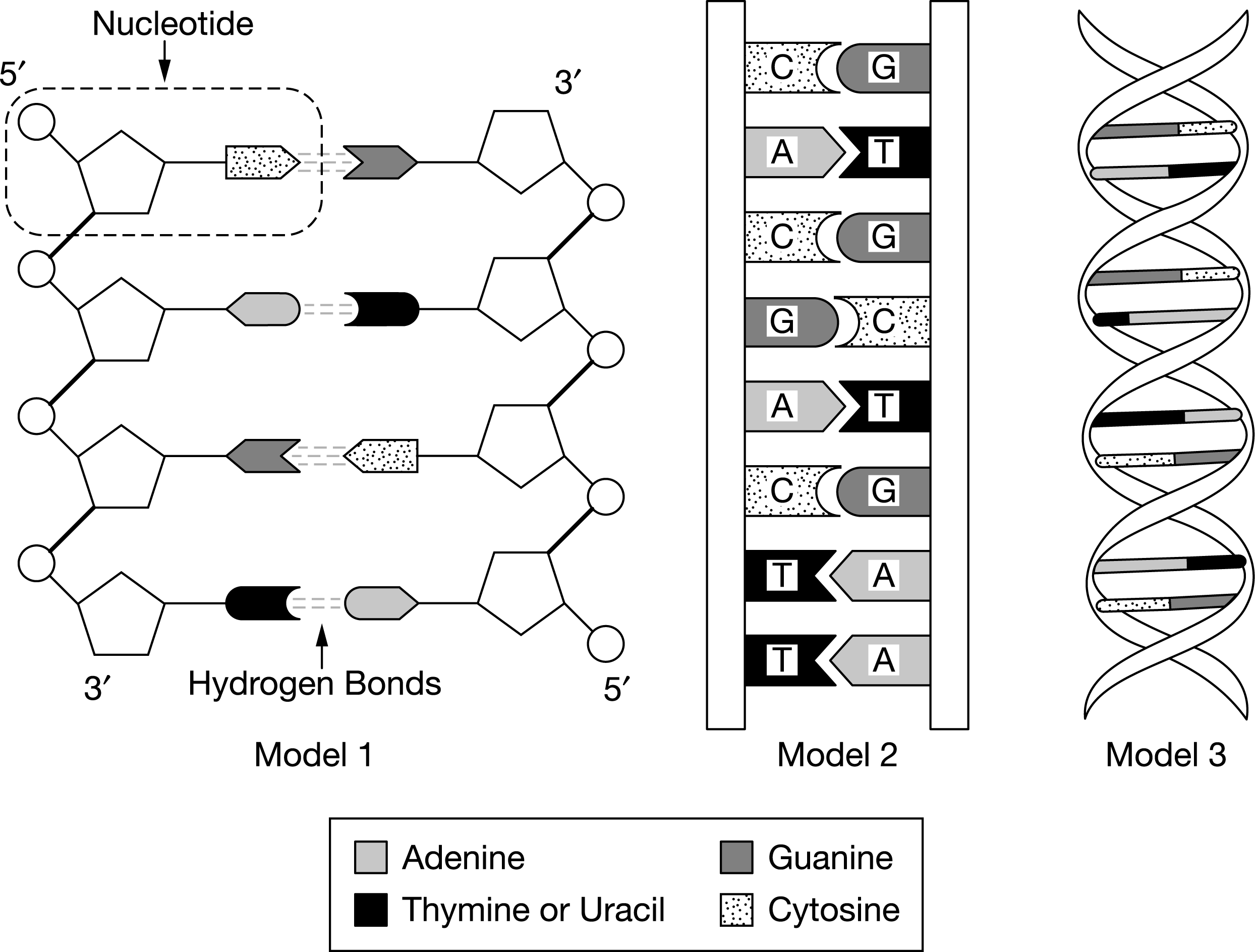
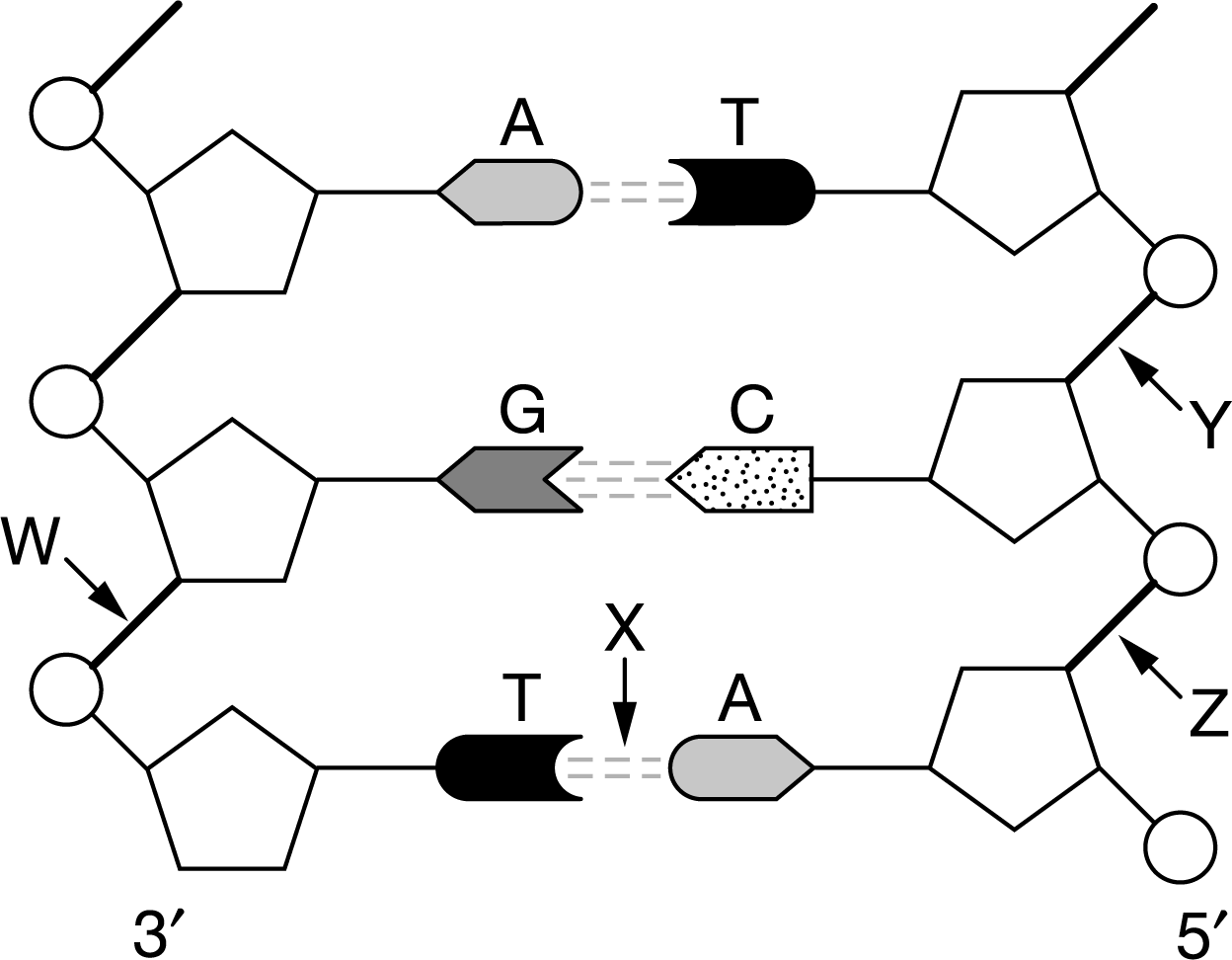
5' Nucleotide 3' +H || || Hydrogen Bonds Model 1 3' 5' Adenine Thymine or Uracil C G A CC G D A T T T G CC T G A A Model 2 Guanine Cytosine XXXXX Model 3 W. 3' A G T == T A Z 5'
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get StartedRecommended Textbook for
The Physical Universe
Authors: Konrad B Krauskopf, Arthur Beiser
16th edition
77862619, 978-0077862619
Students also viewed these Biology questions
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
View Answer in SolutionInn App



