Question: Figure Q5 shows a rectangular slab of 12 cm length and 4 cm high with the thermal conductivity of 10 W/m K. The top
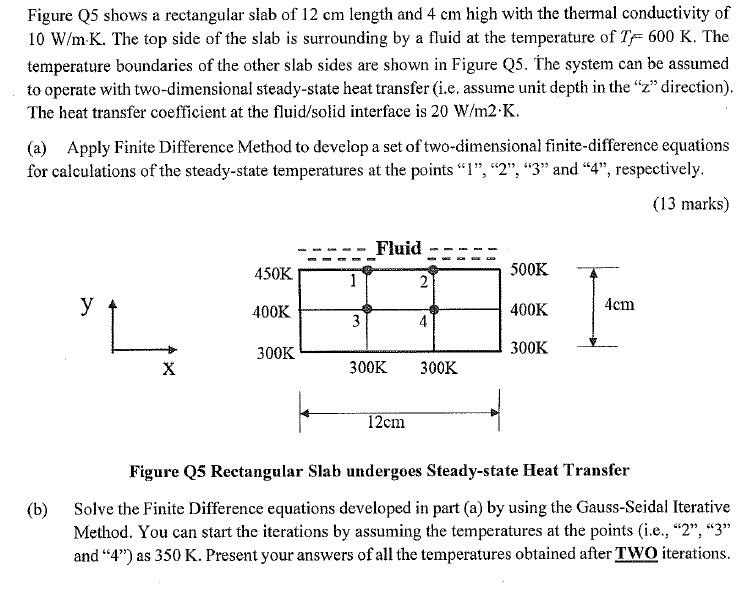
Figure Q5 shows a rectangular slab of 12 cm length and 4 cm high with the thermal conductivity of 10 W/m K. The top side of the slab is surrounding by a fluid at the temperature of T 600 K. The temperature boundaries of the other slab sides are shown in Figure Q5. The system can be assumed to operate with two-dimensional steady-state heat transfer (i.e. assume unit depth in the "z" direction). The heat transfer coefficient at the fluid/solid interface is 20 W/m2.K. (a) Apply Finite Difference Method to develop a set of two-dimensional finite-difference equations for calculations of the steady-state temperatures at the points "1", "2", "3" and "4", respectively. (13 marks) (b) y $4 X Fluid 2 =COD= 3 4 300K 300K 450K 400K 300K 12cm 500K 400K 300K 4cm Figure Q5 Rectangular Slab undergoes Steady-state Heat Transfer Solve the Finite Difference equations developed in part (a) by using the Gauss-Seidal Iterative Method. You can start the iterations by assuming the temperatures at the points (i.e., "2", "3" and "4") as 350 K. Present your answers of all the temperatures obtained after TWO iterations.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a Applying Finite Difference Method to the 2D steadystate ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


