Question
/* * File: calendar.cpp * ------------------ * This file implements the calendar.h interface */ #include #include P3calendar.h #include error.h #include strlib.h using namespace std; /*

/* * File: calendar.cpp * ------------------ * This file implements the calendar.h interface */
#include
/* * Implementation notes: monthToString * ----------------------------------- * The monthToString function must return some value if the month does not * match any of the enumeration constants. Here, as in the Direction * type, the function returns ???. */ namespace P3 { string monthToString(Month month) { switch (month) { case JANUARY: return "JANUARY"; case FEBRUARY: return "FEBRUARY"; case MARCH: return "MARCH"; case APRIL: return "APRIL"; case MAY: return "MAY"; case JUNE: return "JUNE"; case JULY: return "JULY"; case AUGUST: return "AUGUST"; case SEPTEMBER: return "SEPTEMBER"; case OCTOBER: return "OCTOBER"; case NOVEMBER: return "NOVEMBER"; case DECEMBER: return "DECEMBER"; default: return "???"; } }
Month operator++(Month & month, int) { Month old = month; month = Month(month + 1); return old; }
/* * Implementation notes: Constructors * ---------------------------------- * There are three constructors for the Date class. The default * constructor creates a Date with a zero internal value that must * be assigned a new value before it is used. The others initialize * the date from the arguments by calling the private initDate method. */
Date::Date() { /* Empty */ }
Date::Date(int day, Month month, int year) { initDate(day, month, year); }
Date::Date(Month month, int day, int year) { initDate(day, month, year); }
/* * Implementation notes: getDay, getMonth * -------------------------------------- * In this implementation of the Date class, the day and the month are * not stored explicitly but must instead be computed from the dayInYear * field. */
int Date::getDay() { Month month = JANUARY; int day = dayInYear; while (day > daysInMonth(month, year)) { day -= daysInMonth(month, year); month++; } return day; }
/* * Method: getMonth * Usage: Month month = date.getMonth(); * ------------------------------------- * Returns the month. */
Month Date::getMonth() { Month month = JANUARY; int day = dayInYear; while (day > daysInMonth(month, year)) { day -= daysInMonth(month, year); month++; } return month; }
int Date::getYear() { return year; }
/* * Implementation notes: toString * ------------------------------ * The toString method uses the getters to perform the translation into * day/month/year values. */
string Date::toString() { string day = to_string(getDay()); string month = to_string(getMonth()); string year = to_string(getYear()); return (day + "/" + month + "/" + year); }
string Date::capitalize(string str) { if (str == "") return ""; return toUpperCase(str.substr(0, 1)) + toLowerCase(str.substr(1)); }
void Date::initDate(int day, Month month, int yyyy) { if (day daysInMonth(month, yyyy)) { error("Specified date does not exist in the calendar"); } dayInYear = day; for (Month m = JANUARY; m
ostream & operator
Date operator+(Date date, int delta) { //TO DO; }
Date operator-(Date date, int delta) { return date + -delta; }
int operator-(Date d1, Date d2) { //TO DO; }
Date & operator+=(Date & date, int delta) { return date = date + delta; }
Date & operator-=(Date & date, int delta) { return date = date - delta; }
Date operator++(Date & date) { return date += 1; }
Date operator++(Date & date, int) { //TO DO; }
Date operator--(Date & date) { return date -= 1; }
Date operator--(Date & date, int) { Date old = date; date -= 1; return old; }
bool operator==(Date d1, Date d2) { return d1 - d2 == 0; }
bool operator!=(Date d1, Date d2) { //TO DO; }
bool operator
bool operator
bool operator>(Date d1, Date d2) { return d1 - d2 > 0; }
bool operator>=(Date d1, Date d2) { return d1 - d2 >= 0; }
/* * Implementation notes: daysInMonth * --------------------------------- * This function is a reasonably literal translation of the old rhyme: * * Thirty days has September * April, June, and November * All the rest have 31 * Excepting February alone * Which has 28 in fine * And each leap year 29 */
int daysInMonth(Month month, int year) { if ((month == SEPTEMBER) || (month == APRIL) || (month == JUNE) || (month == NOVEMBER)) { return 30; } else if(month == FEBRUARY) { if(isLeapYear(year)) return 29; else return 28; } else { return 31; } }
/* * Implementation notes: isLeapYear * -------------------------------- * This function simply encodes the rule for determining leap years: * a leap year is any year divisible by 4, except for years ending in 00, * in which case the year must be divisible by 400. */
bool isLeapYear(int year) { return ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0)) || (year % 400 == 0); }
}
/* * File: TestCalendar.cpp * ---------------------- * This file tests the calendar.h interface. */
#include int main(){ cout The code is attached. Please fill in the to-do part and make sure the program can run without bugs. thanks. 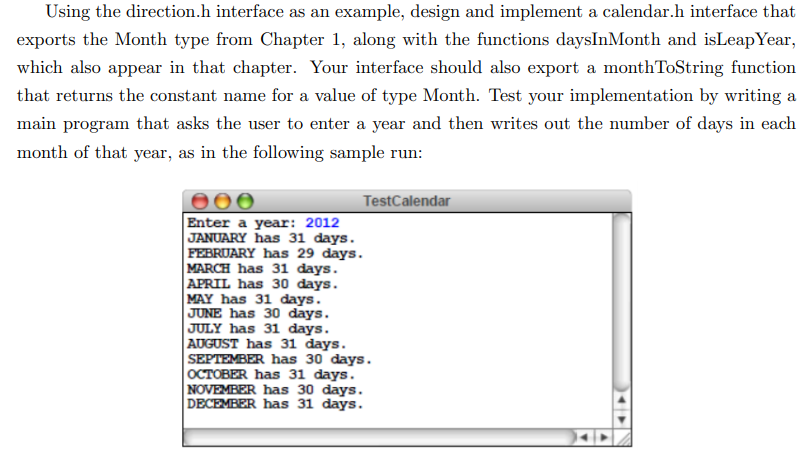


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


