Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
fill in the above using the following table After looking at the projections of the HomeNet project, you decide that they are not realistic It
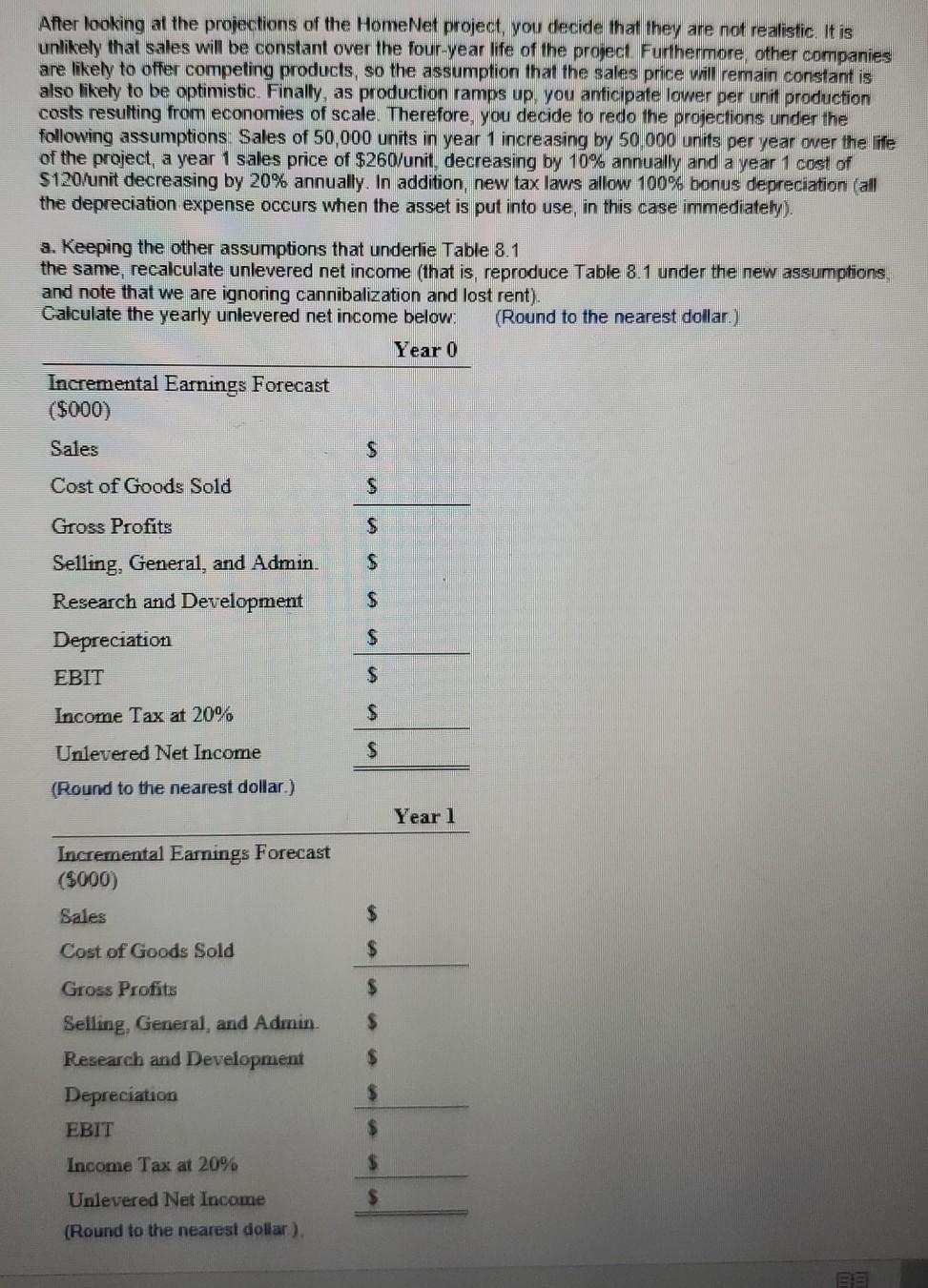
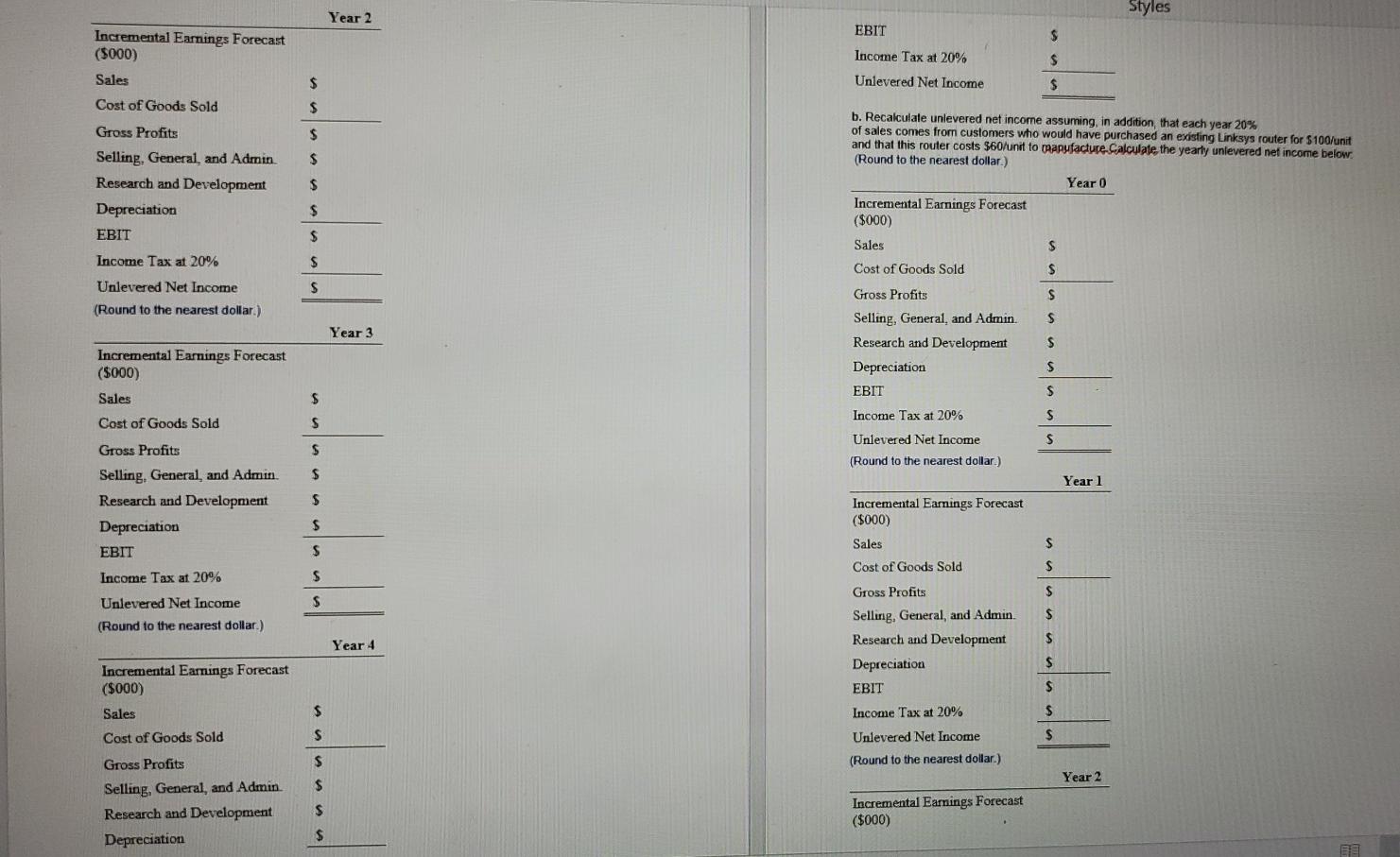
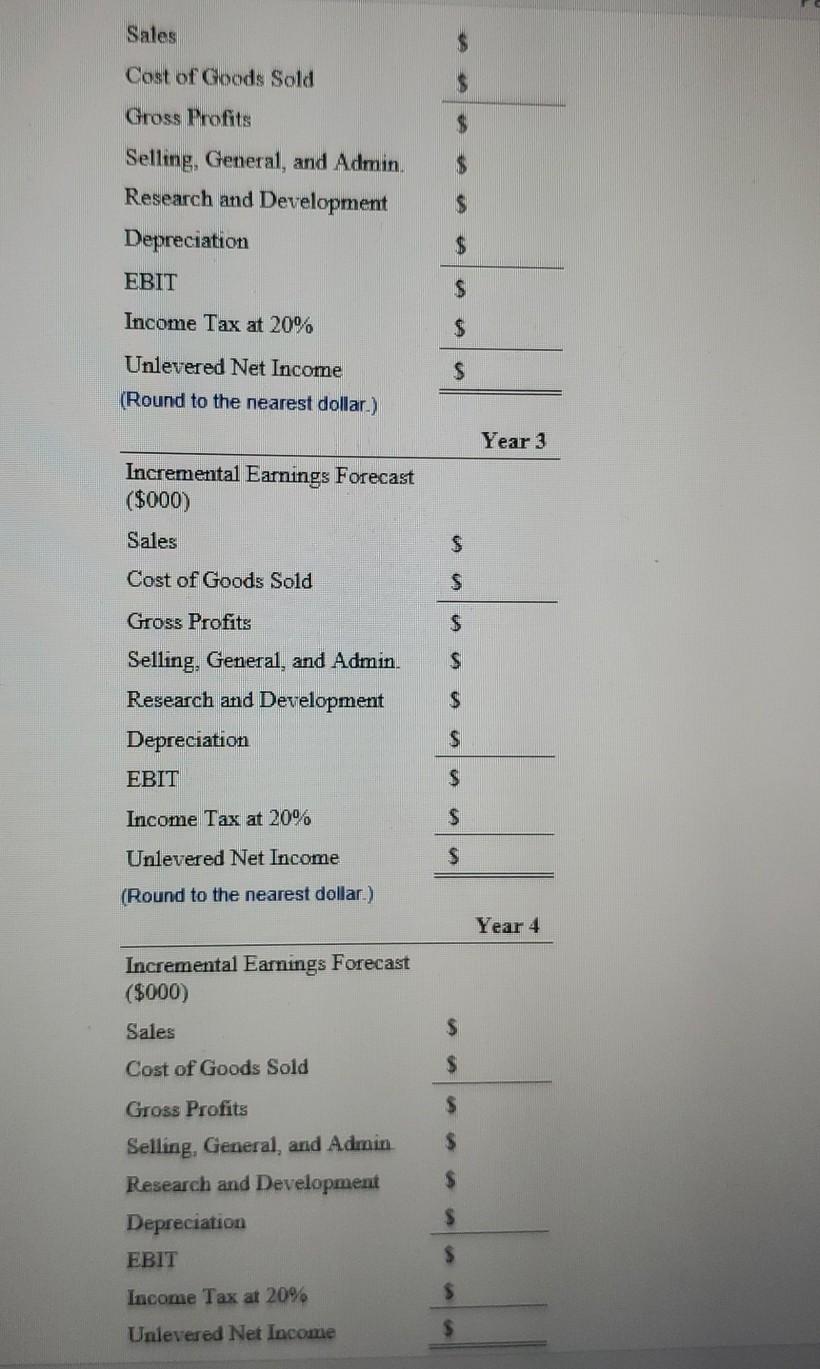
fill in the above using the following table
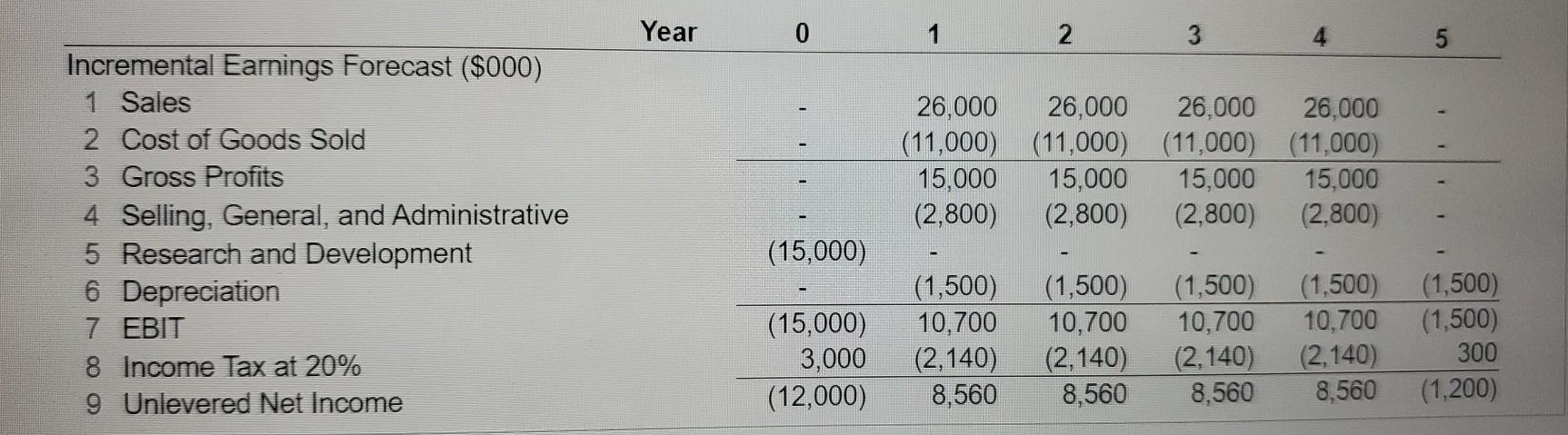
After looking at the projections of the HomeNet project, you decide that they are not realistic It is unlikely that sales will be constant over the four-year life of the project. Furthermore, other companies are likely to offer competing products, so the assumption that the sales price will remain constant is also likely to be optimistic. Finally, as production ramps up, you anticipate lower per unit production costs resulting from economies of scale. Therefore, you decide to redo the projections under the following assumptions Sales of 50,000 units in year 1 increasing by 50,000 units per year over the life of the project, a year 1 sales price of $260/unit, decreasing by 10% annually and a year 1 cost of $120/unit decreasing by 20% annually. In addition, new tax laws allow 100% bonus depreciation (all the depreciation expense occurs when the asset is put into use, in this case immediately). a. Keeping the other assumptions that underlie Table 8.1 the same, recalculate unlevered net income (that is, reproduce Table 8.1 under the new assumptions, and note that we are ignoring cannibalization and lost rent). Calculate the yearly unlevered net income below: (Round to the nearest dollar) Year 0 Incremental Earnings Forecast ($000) Sales $ Cost of Goods Sold S S $ Gross Profits Selling, General, and Admin. Research and Development Depreciation EBIT $ $ $ Income Tax at 20% $ Unlevered Net Income $ (Round to the nearest dollar.) Year 1 Incremental Earnings Forecast (5000) Sales $ Cost of Goods Sold $ $ Gross Profits Selling, General, and Admin Research and Development Depreciation EBIT ... $ $ $ $ Income Tax at 20% $ $ Unlevered Net Income (Round to the nearest dollar). BE Year 2 Styles EBIT $ Incremental Earnings Forecast (5000) Sales Income Tax at 20% $ $ $ Unlevered Net Income Cost of Goods Sold $ $ $ $ Gross Profits Selling, General and Admin Research and Development Depreciation EBIT Income Tax at 20% Unlevered Net Income (Round to the nearest dollar.) $ b. Recalculate unlevered net income assuming, in addition, that each year 20% of sales comes from customers who would have purchased an existing Linksys router for $100/unit and that this router costs $60 unit to manufacture Calculate the yearly unlevered net income below (Round to the nearest dollar.) Year 0 Incremental Earnings Forecast ($000) Sales $ Cost of Goods Sold $ $ $ $ $ $ Year 3 Gross Profits Selling, General, and Admin Research and Development Depreciation EBIT S S $ $ Income Tax at 20% S S S Incremental Earnings Forecast (5000) Sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profits Selling. General, and Admin Research and Development Depreciation EBIT $ Unlevered Net Income (Round to the nearest dollar) $ Year 1 $ S Incremental Earnings Forecast ($000) Sales $ $ Cost of Goods Sold $ Income Tax at 20% S $ $ Unlevered Net Income (Round to the nearest dollar.) S Gross Profits Selling, General, and Admin Research and Development Depreciation EBIT Year 4 $ $ Incremental Earnings Forecast ($000) $ Sales Income Tax at 20% $ $ $ Cost of Goods Sold $ Unlevered Net Income (Round to the nearest dollar.) $ Year 2 $ Gross Profits Selling, General, and Admin Research and Development Depreciation $ Incremental Earnings Forecast ($000) $ Sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profits $ $ $ Selling, General, and Admin. Research and Development Depreciation EBIT $ $ Income Tax at 20% $ $ Unlevered Net Income (Round to the nearest dollar.) Year 3 Incremental Earnings Forecast ($000) Sales $ Cost of Goods Sold $ $ $ Gross Profits Selling, General, and Admin. Research and Development Depreciation EBIT $ $ $ Income Tax at 20% $ Unlevered Net Income $ (Round to the nearest dollar.) Year 4 Incremental Earnings Forecast ($000) Sales $ Cost of Goods Sold $ $ $ Gross Profits Selling, General, and Admin Research and Development Depreciation EBIT $ LI $ Income Tax at 20% Unlevered Net Income Year 0 1 2 3 26,000 26,000 26,000 26,000 (11,000) (11,000) (11,000) (11,000) 15,000 15,000 15,000 15,000 (2,800) (2,800) (2,800) (2,800) Incremental Earnings Forecast ($000) 1 Sales 2 Cost of Goods Sold 3 Gross Profits 4 Selling, General, and Administrative 5 Research and Development 6 Depreciation 7 EBIT 8 Income Tax at 20% 9 Unlevered Net Income (15,000) (15,000) 3,000 (12,000) (1,500) 10,700 (2,140) 8,560 (1,500) 10,700 (2,140) 8,560 (1,500) 10,700 (2,140) 8,560 (1,500) 10,700 (2,140) 8,560 (1,500) (1,500) 300 (1,200)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


