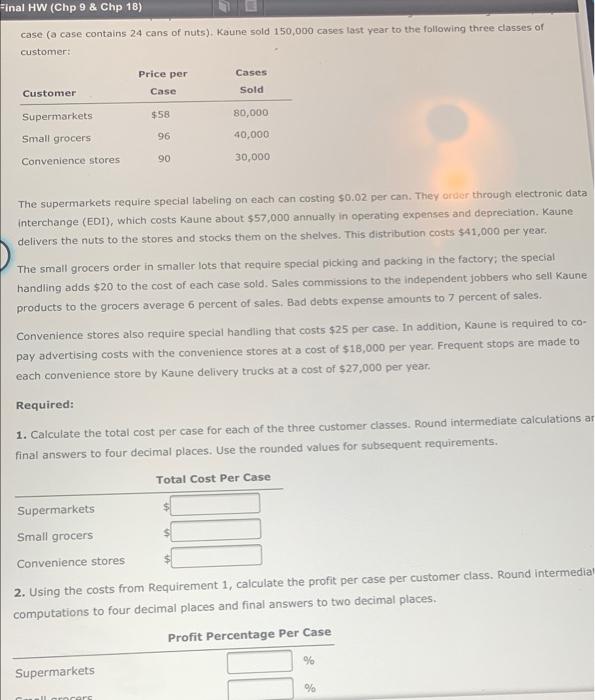
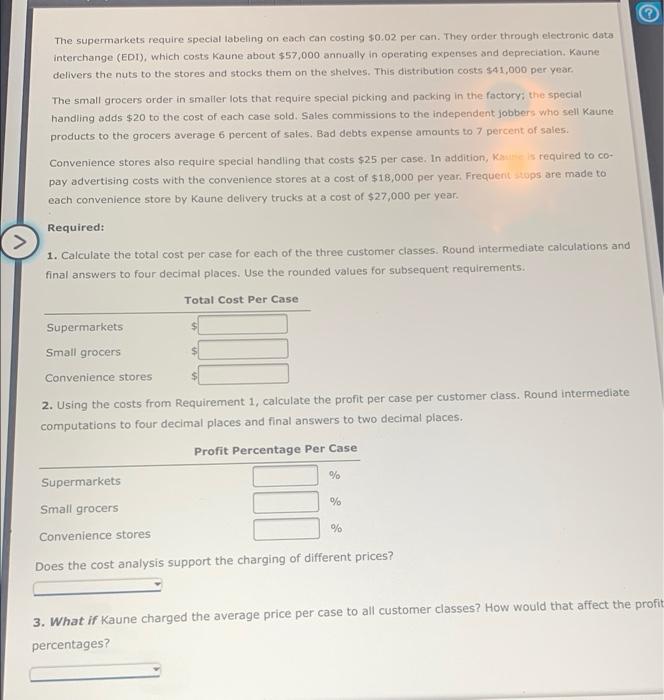
Final HW (Chp 9 & Chp 18) case (a case contains 24 cans of nuts). Kaune sold 150,000 cases last year to the following three classes of customer: Price per Case Cases Sold Customer $58 80,000 Supermarkets Small grocers Convenience stores 96 40,000 90 30,000 The supermarkets require special labeling on each can costing $0.02 per can. They order through electronic data interchange (EDI), which costs Kaune about $57,000 annually in operating expenses and depreciation. Kaune delivers the nuts to the stores and stocks them on the shelves. This distribution costs $41,000 per year. The small grocers order in smaller lots that require special picking and packing in the factory, the special handling adds $20 to the cost of each case sold. Sales commissions to the independent Jobbers who sell Kaune products to the grocers average 6 percent of sales. Bad debts expense amounts to 7 percent of sales. Convenience stores also require special handling that costs $25 per case. In addition, Kaune is required to co- pay advertising costs with the convenience stores at a cost of $18,000 per year. Frequent stops are made to each convenience store by Kaune delivery trucks at a cost of $27,000 per year. Required: 1. Calculate the total cost per case for each of the three customer classes. Round intermediate calculations ar final answers to four decimal places. Use the rounded values for subsequent requirements. Total Cost Per Case Supermarkets Small grocers Convenience stores 2. Using the costs from Requirement 1, calculate the profit per case per customer class. Round intermediar computations to four decimal places and final answers to two decimal places. Profit Percentage Per Case % Supermarkets % llarrers The supermarkets require special labeling on each can costing $0.02 per can. They order through electronic data interchange (EDI), which costs Kaune about $57,000 annually in operating expenses and depreciation, Kaune delivers the nuts to the stores and stocks them on the shelves. This distribution costs $41,000 per year. The small grocers order in smaller lots that require special picking and packing in the factory: the special handling adds $20 to the cost of each case sold. Sales commissions to the independent jobbers who sell Kaune products to the grocers average 6 percent of sales. Bad debts expense amounts to 7 percent of sales. Convenience stores also require special handling that costs $25 per case. In addition, Kis required to co pay advertising costs with the convenience stores at a cost of $18,000 per year. Frequent cups are made to each convenience store by Kaune delivery trucks at a cost of $27,000 per year. Required: 1. Calculate the total cost per case for each of the three customer classes. Round intermediate calculations and final answers to four decimal places. Use the rounded values for subsequent requirements. Total Cost Per Case Supermarkets Small grocers $ Convenience stores 2. Using the costs from Requirement 1, calculate the profit per case per customer class. Round intermediate computations to four decimal places and final answers to two decimal places Profit Percentage Per Case Supermarkets % % Small grocers Convenience stores % Does the cost analysis support the charging of different prices? 3. What if Kaune charged the average price per case to all customer classes? How would that affect the profit percentages? Final HW (Chp 9 & Chp 18) case (a case contains 24 cans of nuts). Kaune sold 150,000 cases last year to the following three classes of customer: Price per Case Cases Sold Customer $58 80,000 Supermarkets Small grocers Convenience stores 96 40,000 90 30,000 The supermarkets require special labeling on each can costing $0.02 per can. They order through electronic data interchange (EDI), which costs Kaune about $57,000 annually in operating expenses and depreciation. Kaune delivers the nuts to the stores and stocks them on the shelves. This distribution costs $41,000 per year. The small grocers order in smaller lots that require special picking and packing in the factory, the special handling adds $20 to the cost of each case sold. Sales commissions to the independent Jobbers who sell Kaune products to the grocers average 6 percent of sales. Bad debts expense amounts to 7 percent of sales. Convenience stores also require special handling that costs $25 per case. In addition, Kaune is required to co- pay advertising costs with the convenience stores at a cost of $18,000 per year. Frequent stops are made to each convenience store by Kaune delivery trucks at a cost of $27,000 per year. Required: 1. Calculate the total cost per case for each of the three customer classes. Round intermediate calculations ar final answers to four decimal places. Use the rounded values for subsequent requirements. Total Cost Per Case Supermarkets Small grocers Convenience stores 2. Using the costs from Requirement 1, calculate the profit per case per customer class. Round intermediar computations to four decimal places and final answers to two decimal places. Profit Percentage Per Case % Supermarkets % llarrers The supermarkets require special labeling on each can costing $0.02 per can. They order through electronic data interchange (EDI), which costs Kaune about $57,000 annually in operating expenses and depreciation, Kaune delivers the nuts to the stores and stocks them on the shelves. This distribution costs $41,000 per year. The small grocers order in smaller lots that require special picking and packing in the factory: the special handling adds $20 to the cost of each case sold. Sales commissions to the independent jobbers who sell Kaune products to the grocers average 6 percent of sales. Bad debts expense amounts to 7 percent of sales. Convenience stores also require special handling that costs $25 per case. In addition, Kis required to co pay advertising costs with the convenience stores at a cost of $18,000 per year. Frequent cups are made to each convenience store by Kaune delivery trucks at a cost of $27,000 per year. Required: 1. Calculate the total cost per case for each of the three customer classes. Round intermediate calculations and final answers to four decimal places. Use the rounded values for subsequent requirements. Total Cost Per Case Supermarkets Small grocers $ Convenience stores 2. Using the costs from Requirement 1, calculate the profit per case per customer class. Round intermediate computations to four decimal places and final answers to two decimal places Profit Percentage Per Case Supermarkets % % Small grocers Convenience stores % Does the cost analysis support the charging of different prices? 3. What if Kaune charged the average price per case to all customer classes? How would that affect the profit percentages