finance please help.
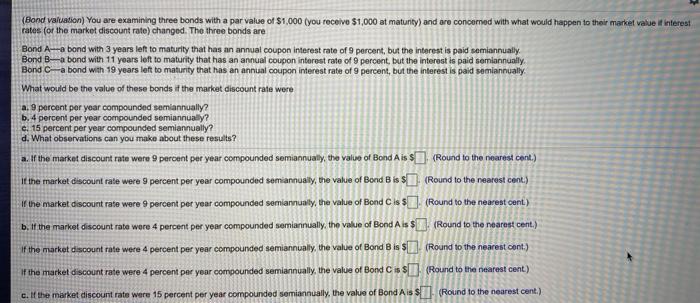
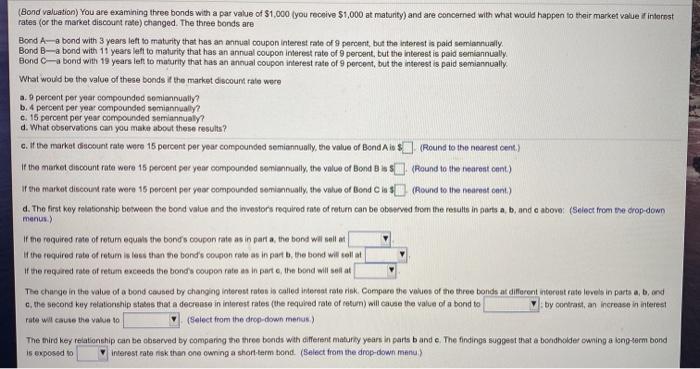
(Bond valuation) You are examining three bonds with a par value of $1,000 (you receivo $1,000 at maturity) and are concerned with what would happen to their market value if interest rates for the market discount rate) changed. The three bonds are Bond A-a bond with 3 years left to maturity that has an annual coupon interest rate of 9 percent, but the interest is paid semiannually Bond B-a bond with 11 years left to maturity that has an annual coupon interest rate of 9 percent, but the interest is paid semiannually Bond C-a bond with 19 years left to maturity that has an annual coupon interest rate of 9 percent, but the interest is paid semiannually What would be the value of these bonds if the market discount rate were a. 9 percent per year compounded semiannually? b. 4 percent per year compounded semiannually? e. 15 percent per year compounded semiannually? d. What observations can you make about these results? a. If the market discount rate were 9 percent per year compounded semiannually, the value of Bond Ais $(Round to the nearest cont.) If the market discount rate were 9 percent per year compounded semiannually, the value of Bond B is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) W the market discount rate were 9 percent per year compounded semiannualy, the value of Bond Ciss (Round to the nearest cent) b. If the market discount rate were 4 percent per your compounded semiannually, the value of Bond Ais $(Round to the nearest cent) If the market discount rate were 4 percent per year compounded semiannually, the value of Bond Bis $ (Round to the nearest cont.) If the market discount rate were 4 percent per year compounded semiannually, the value of Bond Ciss (Round to the nearest cent.) c. If the market discount rate were 15 percent per year compounded semiannually, the value of Bond Ais (Round to the nearest cent.) (Bond valuation) You are examining three bonds with a par value of $1,000 you receive $1,000 at maturity) and are concerned with what would happen to their market value finterest rates (or the market discount rate) changed. The three bonds are Bond A bond with 3 years left to maturity that has an annual coupon Interest rate of 9 percent, but the interest is paid semiannually Bond B-a bond with 11 years left to maturity that has an annual coupon interest rate of 9 percent, but the interest is paid semiannually Bond C-bond with 19 years left to maturity that has an annual coupon interest rate of 9 percent, but the interest is paid semiannually What would be the value of these bonds if the market discount rate were a. 9 percent per year compounded somiannually? b. 4 percent per year compounded semiannually? c. 15 percent per year compounded semiannually? d. What observations can you make about these results? c. If the market Groount rate wore 15 percent per your compounded semiannually, the value of Bond Air $(Round to the nearest cent.) of the market discount rate were 15 percent per year compounded semiannually, the value of Bonds). (Round to the nearest cont) if the market discount rate were 15 percent per year compounded semiannually, the value of Blond C$ (Round to the nearest cont) d. The first way relationship between the bord value and the Investors required rate of return can be observed from the results in parts a, b, and e above: (Select from the drop-down menus) If the required rate of return equals the bond's coupon rate as in part a, the bond wil sell at If the required rate of return is less than the bond's coupon rate as in part, the bond will tell at of the required rate of retum exceeds the bond's coupon rate as in parte, the bond will solat The change in the value of a bond couned by changing interest raton is called interest rate risk. Compare the values of the three bonds at different interest rate levels in parts a, b, ond c. the second kuy relationship states that a decrease in interest rates (the required rate of return) will cause the value of a bond to by contrast, an increase in interest rate will cause the value to (Select from the drop-down menus) The third key relationship can be observed by comparing the three bonds with different maharly years in parts band e. The findings suggest that a bondholder owning a long-term bond is exposed to interest rate risk than one owning a short-term bond. (Select from the drop-down menu