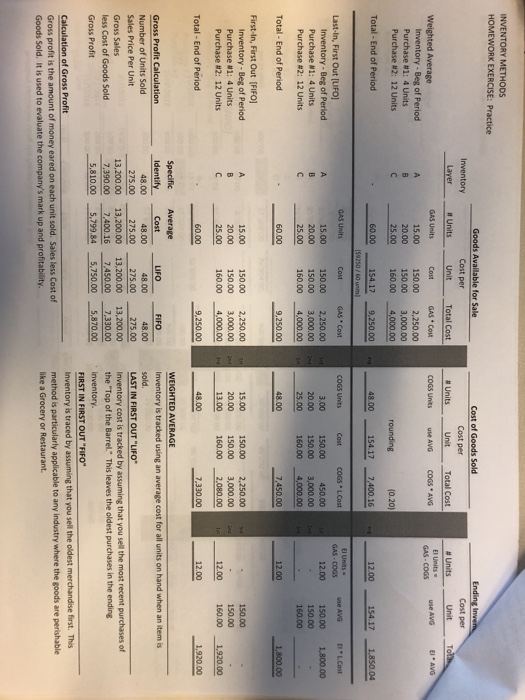
Financial Accounting 2113 Formulas and Definitions Inventory Methods MULAS Gross Sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit-General and Admin Expenses Beg. Inventory Purchases- Ending Inventory Be. Inventory + Purchases Cost of Goods Sold/Average Inventory 365 Days /Average Inventory Turnover Ratio Gross Profit/Gross Sales BEG beginning balance Net Income Pur add purchases GAS goods available for Cost of Goods Sold Cost of Goods Available for sale sale Inventory turnover Ratio -End less ending inventory COGS cost of goods sold # Days in Inventory Gross Profit Percentage KEY CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS Gross Sales Revenues earned from sales of product The cost of the units sold Amount earned per item sold based on cost Expenses of a business not directly related to the product sold Last in First out - Last item purchased is first item sold First in First Out-First purchased is first sold Good for uniform inventory-take an average cost of all items available for sale. identify the exact items purchased/sold. Good for High dollar items or custom Items In periods of rising prices, LIFO gives high cost of goods sold and lower net income resulting in Lower Taxes. Conversely, FIFO puts most recent cost on the Balance Sheet Cost of goods Sold Gross Profit General and Administrative Expenses LIFO FIFO Weighted Average Specific Identification LIFO Income Stmt Approach FIFO Balance Sheet Approach Inventory Cost DOES NOT have to follow the physical flow of inventory Manufacturer vs. Merchandiser Manufacturer builds the items for sale, merchandiser purchases the goods in finished form for resale Raw materials, Work in Processes; Finished Goods Wholesaler is a middle man; Retailer sells to general public Simply stated, it is the difference between LIFO and FIFL costs Inventory Wholesaler versus Retailer Reporting the "LIFO Difference" Periodic Inventory System Perpetual Inventory System Lower of Cost or Market If the Market value of the inventory falls below cost, you must adjust the value of the inventory to the current market value JOUIRNAL ENTRIES Record Purchase of Inventory Perpetual System Inventory Accounts Payable Periodic System Purchases Accounts Payable Record Sales Accounts Receivable/Cash Gross Sales/Sales Revenue Record cost of Goods Sold Cost of Goods Sold Inventory NOTE: Perpetual Inventory System vs. Periodic System changes the timing of this entry Financial Accounting 2113 Formulas and Definitions Inventory Methods MULAS Gross Sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit-General and Admin Expenses Beg. Inventory Purchases- Ending Inventory Be. Inventory + Purchases Cost of Goods Sold/Average Inventory 365 Days /Average Inventory Turnover Ratio Gross Profit/Gross Sales BEG beginning balance Net Income Pur add purchases GAS goods available for Cost of Goods Sold Cost of Goods Available for sale sale Inventory turnover Ratio -End less ending inventory COGS cost of goods sold # Days in Inventory Gross Profit Percentage KEY CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS Gross Sales Revenues earned from sales of product The cost of the units sold Amount earned per item sold based on cost Expenses of a business not directly related to the product sold Last in First out - Last item purchased is first item sold First in First Out-First purchased is first sold Good for uniform inventory-take an average cost of all items available for sale. identify the exact items purchased/sold. Good for High dollar items or custom Items In periods of rising prices, LIFO gives high cost of goods sold and lower net income resulting in Lower Taxes. Conversely, FIFO puts most recent cost on the Balance Sheet Cost of goods Sold Gross Profit General and Administrative Expenses LIFO FIFO Weighted Average Specific Identification LIFO Income Stmt Approach FIFO Balance Sheet Approach Inventory Cost DOES NOT have to follow the physical flow of inventory Manufacturer vs. Merchandiser Manufacturer builds the items for sale, merchandiser purchases the goods in finished form for resale Raw materials, Work in Processes; Finished Goods Wholesaler is a middle man; Retailer sells to general public Simply stated, it is the difference between LIFO and FIFL costs Inventory Wholesaler versus Retailer Reporting the "LIFO Difference" Periodic Inventory System Perpetual Inventory System Lower of Cost or Market If the Market value of the inventory falls below cost, you must adjust the value of the inventory to the current market value JOUIRNAL ENTRIES Record Purchase of Inventory Perpetual System Inventory Accounts Payable Periodic System Purchases Accounts Payable Record Sales Accounts Receivable/Cash Gross Sales/Sales Revenue Record cost of Goods Sold Cost of Goods Sold Inventory NOTE: Perpetual Inventory System vs. Periodic System changes the timing of this entry