Question
FINC 3380 Homework 4 Seungho Baek Due: Wednesday, April 1 2020, 6:29 P.M. For this homework assignment, you need to use Excel. Once you done,
FINC 3380 Homework 4
Seungho Baek Due: Wednesday, April 1 2020, 6:29 P.M.
For this homework assignment, you need to use Excel. Once you done, upload your excel file to Blackboard. Do not submit HW4 via email.
Part 1 Reading Assignments Read LN6.
Part 2 Practical Assignments using Excel Consider two annual coupon bonds. Now current market rate of interest (i.e. discount rate) is 7 percent. Bond A has just been issued. Its face value is $1,000, it bears a 7 percent coupon rate and will mature in 10 years. Bond B was issued five years ago, when the interests were higher. This bond has $1,000 face value and bears a 13 percent coupon rate. When issued, this bond had a 15-year maturity, so its remaining maturity is 10 years.
1) Compute the respective bond prices using the above equation.
P=N Ct
(1+r)t
1
Note that this equation is to price a bond with payments Ct, where t=1,2,...,N. Ordinarily,thefirstN1paymentswillbeinterest rates, and CN will be the sum of the repayment of principal and the last interest payment. If the term structure is flat and the discount rate for all of the payment is r.
-
2) Compute the respective Macaulay durations. The Macaulay duration is de- fined as
whereD=1 dP. P dy
-
3) Which bond is more exposure to interest risk? Explain it thoroughly. 1
D= 1
1N tCt P (1+r)t
4) Compute the respective modified durations for two bonds using the below equation and interpret two values.
1 N tCt P 1 (1+r)t
Dmod = 5) Here is another equation to price a bond with a continuously compounding
interest rate of rc.
1+r
N Pc =Cterct
1
-
(1) Using the above equation, calculate the price of the bond.
Note: You need to convert an annual compounding rate to a continuously compounded rate.
(1+r)t = erct rc = ln(1+r)
-
(2) Calculate the Macaulay duration.
Dc = 1 tCterct
P
1
(3) Compare two bond prices from problem 1) and two bond prices from problem 5)and provide your findings. What about the durations (from problem 1) and problem 5))?
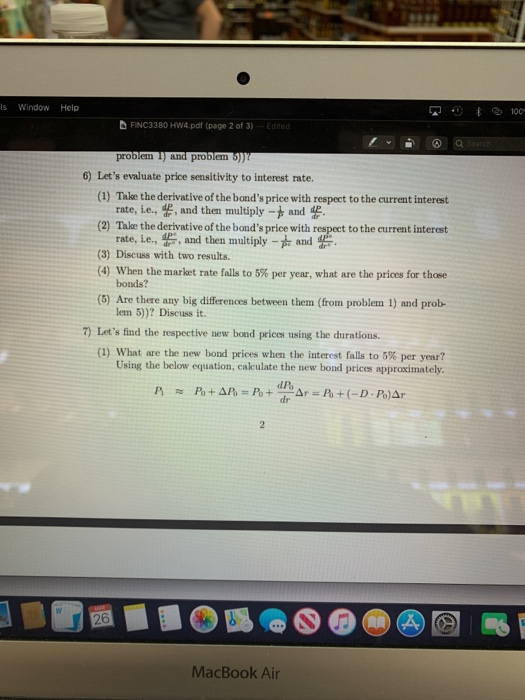
6) Lets evaluate price sensitivity to interest rate. (1) Takethederivativeofthebondspricewithrespecttothecurrentinterest
rate, i.e., dP , and then multiply 1 and dP . dr Pdr
N
(2) Takethederivativeofthebondspricewithrespecttothecurrentinterest rate, i.e., dPc , and then multiply 1 and dPc .
drc Pc drc (3) Discuss with two results.
-
(4) When the market rate falls to 5% per year, what are the prices for those bonds?
-
(5) Are there any big differences between them (from problem 1) and prob- lem 5))? Discuss it.
7) Lets find the respective new bond prices using the durations.
(1) What are the new bond prices when the interest falls to 5% per year? Using the below equation, calculate the new bond prices approximately.
P1 P0+P0 =P0+dP0r=P0+(DP0)r dr
2
(2) What are the new bond prices (with continuously compounding interest rate) when the interest falls to 5% per year? Using the below equation, calculate the new bond prices approximately.
dPc P1c P0c +P0c = P0c + 0 rc = P0c +(Dc P0c)rc drc
8) Compare bond prices from problem 6-4) with the results from problem 7-1) and 7-2).
3




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


